* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2013_Cryan_Sexual_Selection copy
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Sexual coercion wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Sexual conflict wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
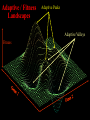
Selection: “Natural” Natural vs. “Unnatural” Unnatural Jason Cryan, Ph.D. Deputy Museum Director for Research & Collections Evolution is the pattern, Selection is the process Postulates of Natural Selection Individuals within species are variable Some variation is passed to offspring More offspring produced than can survive Offspring that survive and reproduce are those with most favorable variations 1809-1882 “The Origin of Species…” on the INTERNET http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/origin.html Selection: Acts on individual phenotypes to produce a distinct change in trait distributions within a generation Evolution: A population-level change in allele frequencies across generations, as a consequence of selection Fitness: the ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in its environment, relative to other individuals in its species The offspring of a ‘more fit’ individual will constitute a greater percentage of the next generation than the offspring of ‘less fit’ individual Adaptive / Fitness Landscapes Adaptive Peaks Adaptive Valleys Fitness The Plant Kingdom “The evolution of plants is an important chapter in the history of life. However, it’s a pretty dull chapter, so we’ll skip it.” a fern or something Important Selective Forces Eat! Don’t get Eaten! Don’t get Sick! Reproduce! SEXUAL BeautySELECTION is in the “Differences among individuals eye of the beholder in success at getting mates” Sexual Dimorphism Reproductive structures Secondary sexual characters Body size Coloration Exaggerated traits Calling behavior In most cases, males are more conspicuous Asymmetries in Sexual Reproduction I Females tend to invest more in offspring than males Gamete size: eggs larger than sperm; embryos generally not provisioned by males Parental care: females usually responsible for offspring care during maturation Asymmetries in Sexual Reproduction II Differential limits on reproductive success Female reproductive success limited by egg production (limited offspring number) Male reproductive success limited by number of mates (unlimited offspring number) Prediction 1. Female reproductive success should level off after a certain number of matings 2. Male reproductive success is proportional to the number of mates Behavioral Consequences of Asymmetric Limits on Fitness Intrasexual Selection (Competition): If access to females is the primary limiting factor in reproductive success, males will compete with other males for mating opportunities Intersexual Selection (Female Choice): If female reproductive success is not limited by access to males, then females will be selective about which males they mate with in order to maximize the quality of the male’s reproductive investment Males Usually minimal investment in offspring Gamete size: sperm smaller than eggs Parental care: in most non-human animal species, males have little or nothing to do with raising young Male-Male Competition Combat Advertisement Sperm Competition New Male Takeover Combat Body size related to competitive ability Mating males larger than non-mating males Some male structures enhance competitive ability Galapagos Marine Iguanas Advertisement: Leks and Displays Leks: male-defended territories solely for purpose of displays and mating...no resource being protected; 1 or very few males mate with most females Mating Center Sperm Competition When females participate in multiple matings, the male sperm competes to fertilize the eggs Strategies for sperm competition: 1. Increased ejaculate volume 2. Physical removal of sperm from previous matings 3. Copulatory plugs 4. Prolonged mating and female guarding New Male Takeover: Infanticide Males form coalitions to take over pride Offspring of previous coalition killed by new males Infanticide amount to about 10% of lion mortality Females abort fetuses when new males take over pride Humans: When an unrelated stepfather lives with a family including children under the age of 2, infanticide is 70× more likely to occur (Hrdy, S.B. 1999. Mother nature: a history of mothers, infants, and natural selection. New York: Pantheon Books) It’s not just the guys…. Females Usually a costly investment in offspring Gametes: egg production, embryonic provisioning Parental care: protection & provisioning Female Choice Females of many species mate preferentially with males that have larger, more intense, or more exaggerated characters such as color patterns, ornaments, vocalizations, or display behaviors Sexual characters & courtship displays originally thought of as species-specific signals designed to encourage females to mate Darwin hypothesized that displays were used to advertise male quality, and that females actually use this information to choose among possible mates Male Quality: genetic quality general health parasite load Nuptial Gifts Females get direct benefit through resource acquisition Runaway Selection A self-reinforcing process of preference for a nonadaptive (or even maladaptive) trait Elements of Evolution by Natural Selection 1. Individuals within species are variable 2. Some variation is passed to offspring 3. More offspring produced than can survive 4. Offspring that survive and reproduce are those with most favorable variations Elements of Evolution by Sexual Selection 1. Individuals within sexes are variable 2. Some variation is passed to offspring 3. The variation leads to differential mating success among individuals Further Reading