* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download You Light Up My Life
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
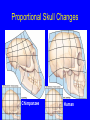
Principles of Evolution Chapter 24 Classification of Humans • • • • • • • Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primates Hominidae Homo sapiens Challenges to Early Beliefs • Biogeography - discovery of species in isolated locales • Comparative morphology - similarities between animals, parts with no functions • Fossils - deep layers with simple fossils, overlying layers with increasing complexity Charles Darwin • Proposed the theory of evolution by way of natural selection • Influenced by – Observations made while naturalist on H.M.S. Beagle – Conversations with other naturalists – Writings of Thomas Malthus Variation in Populations • Individuals do not evolve; populations do • Members of a population have similar traits • Details of traits vary among individuals • Some variation results from genetic differences (different alleles) Mutation • A heritable change in DNA • Most are harmful • Some are neutral • A few are beneficial Natural Selection • Individuals vary • Some variations are heritable • Some versions of traits increase fitness • Natural selection is the difference in survival and reproduction in individuals who have different versions of a trait Evolving Populations • A population is evolving when some forms of a trait are becoming more or less common relative to the other forms • Over time, shifts in the makeup of gene pools have been responsible for the amazing diversity of life forms on Earth Other Changes to Gene Pool • Genetic drift – Founder effect – Virtually no Native Americans with type B blood • Gene flow – Physical movement of alleles – Helps keep neighboring populations genetically similar Species • A genetic unit consisting of one or more populations of organisms • Members can interbreed and produce fertile offspring under natural conditions • Reproductively isolated from other species Speciation time A time B time C time time D Fossils • Usually hard parts • Form in sedimentary rock • Stratification • Fossil record is biased Biogeography Distribution of plants and animals Plate tectonics Comparative Morphology • Homology • Analogy – Similarity in body parts in different organisms – Similarity in body parts in different organisms – Attributable to descent from a common ancestor – Attributable to similar environmental pressures Homologous Structures Vertebrate forelimbs Comparative Embryology • Early vertebrate embryos strongly resemble one another • Same plan of development Fish Reptile Bird Mammal Proportional Skull Changes Chimpanzee Human Evidence from Comparative Biochemistry • Molecular clocks – Neutral mutations • Protein comparisons – Cytochrome C • Nucleic-acid comparisons – Base-pairing of DNA or RNA from one species to another Extinctions - End of the Line • Background extinction – Local changing conditions • Mass extinction – Catastrophic global event – 65 million years ago – Probably asteroid impact Adaptive Radiation • New species of a lineage moves into a wide range of habitats • Has occurred in the human lineage • Homo habilis remained in Africa • H. erectus went to Europe, Asia • H. sapiens evolved by 100,000 years ago Trends in Human Evolution • Upright walking • Refined hand movements • Enhanced daytime vision • Changes in dentition • Changes in brain and behavior Comparison of Skeletal Organization Trend toward Longer Life Spans and Dependency From Primates to Hominids • 60 million years ago – Tropical forests – Small rodents, tree shrews • 54 - 38 million years ago – Primates in trees • 36 million years ago – Tree-dwelling anthropoids • 10 - 5 million years ago – First hominoids Early Earth • Primitive atmosphere – H2 – N2 – CO – CO2 – Probably no O2 Complex Compounds Form Organic compounds may have: • Formed when lightning interacted with gases in early atmosphere • Assembled on clays in tidal flats • Formed near hydrothermal vents Emergence of First Living Cells • Self-Replicating Systems – RNA – DNA • Plasma Membranes – Proto-cells