* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
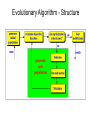
Review NNs • Processing Principles in Neuron / Unit – integrated input = sum of weighted outputs – activation transfer (threshold, sigmoid, linear function; new activation state; output) • NN Architectures (graph structure ...) – feedforward – recurrent – completely connected – connection graph (with weights) can be written as matrix Review NNs • Learning – supervised (backprop) – unsupervised (competitive learning, selforganizing networks) • Examples – NETtalk: Backprop learning of pronunciation; input is text (windows); output is articulatory features; weights adjusted with delta-rule – SOM: self-organizing network; adjusts weight vector (weights on input lines) of units towards best fitting input; units represent classes of similar inputs; character recognition 74.419 Artificial Intelligence 2004 - Evolutionary Algorithms • Principles of Evolutionary Algorithms • Structure of Evolutionary Algorithms • Michel Toulouse's Slides • Short note on Motion Control • Demos (PBS Archives, ‘Life’s really Big Questions, Dec 2000) featuring Karl Sims and Jordan Pollack GA Evolutionary Algorithms - Principles Evolution Processes I • Selection determines, which individuals are chosen for mating (recombination) and how many offspring each selected individual produces. • In order to determine the new population (generation), each individual of the current generation is objected to an evaluation based on a fitness function. • This fitness is used for the actual selection step, in which the individuals producing offspring are chosen (mating pool). Evolution Process II • Recombination produces new individuals in combining the information contained in the parents, e.g. cross-over. • Mutations are determined by small perturbations of parameters describing the individuals, which yield new offspring individuals. • Re-iterate Evolution Process until system satisfies optimization demands. Evolutionary Algorithm - Structure Motor Control • Define system based on physical description of architecture, including limbs and joints (parameterized) • Specify and modify parameters for control trained Neural Network Controller (sensor-actuator networks) Evolution of System (optimization criteria is movement in environment; race with other creatures) Karl Sims, MIT Leg Lab, Jordan Pollack References Key Researchers John H. Holland, University of Michigan, 1975 H.-P. Schwefel, University of Dortmund, Germany, 1973 Udo Rechenberg, University of Berlin, Germany, 1975, 1981 Karl Sims, GenArts Inc. Cambridge, MA http://www.genarts.com/karl/ Figures in this presentation taken from ‘The Genetic and Evolutionary Algorithm Toolbox for use with Matlab (GEATbx)’ www.geatbx.com/docu/algindex.html