* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 4
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Optical fiber wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Fiber Bragg grating wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
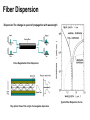
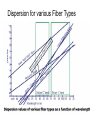
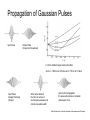
EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 4 Fiber Dispersion From the movie Warriors of the Net Types of Dispersion • Modal dispersion: different modes propagate at different group velocities • Material dispersion: the index of refraction of the medium changes with wavelength • Waveguide dispersion: index change across waveguide means that different wavelengths have different delays • Polarization mode dispersion: if waveguide is birefringent Definitions Group velocity Group delay Dispersion vg 1 1 c k D Wave Packet Construction Group and Phase Velocity Transform Limited Frequency Spread Rectangular Pulse Pulse modulated Sine wave Gaussian modulated Sine wave Optics-Hecht & Zajac Spectral properties of digitally modulated signals1 No spectral component at the clock frequency For Non-Return to Zero Encoded Data Pulse Propagation through Fibers Response of a multi-mode fiber to a single short pulse Broadening of a short pulse after transmission through different types of fibers Fundamentals of Photonics - Saleh and Teich Material Dispersion Refractive Index of Pure Silica and its derivatives Material Dispersion Parameter for pure silica and germanium doped silica Optical Fiber Communications-Keiser Fiber Optic Communications-Palais Zero Dispersion Slope Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner Fiber Dispersion Dispersion:The change in speed of propagation with wavelength Pulse Degradation from Dispersion Typical fiber Dispersion Curve Ray optics View of the origin of waveguide dispersion Polarization Mode Dispersion Polarization Maintaining Fiber Non-Polarization Maintaining Fiber Random power transfer occurs between different polarization modes as the pulse propagates, if the two modes have different propagation velocities then the pulse will broaden Representative Fiber Characteristics Dispersion for various Fiber Types Dispersion Shifted and Dispersion Flattened Fibers Chromatic Dispersion Parameters of a singlemode fiber Fundamentals of Photonics - Saleh and Teich Waveguide Dispersion mechanism As Mode field diameter More of the mode travels in the cladding. Cladding index is lower so pulse velocity resulting in dispersion Comparison of Dispersion Characteristics Propagation of Gaussian Pulses Input Pulse Output Pulse chirped and broadened 2<0 for standard single mode silica fiber and Ld ~ 1800 km at 2.5 Gb/s and ~115 km at 10 Gb/s Input Pulse Already Positively Chirped After some distance the chirp is removed and the pulse assumes its minimum possible width Upon further propagation the pulse will continue to broaden and acquire chirp. Optical Networks a Practical Perspective-Ramaswami and Sivarajan