* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carrier Trunk Lines
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Atomic clock wikipedia , lookup
Amateur radio repeater wikipedia , lookup
Waveguide (electromagnetism) wikipedia , lookup
Equalization (audio) wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Microwave transmission wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
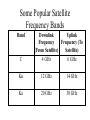
Carrier Trunk Lines Carrier Trunk Lines • Trunk lines are high-speed lines that connect the switches of carriers • There are several kinds of trunk lines – – – – Optical fiber Radio transmission Microwave transmission Satellite transmission • LEOs • VSATs Optical Fiber • Thin Core of Glass – – – – Surrounded by glass cladding Inject light in on-off pattern for 1s and 0s Total reflection at core-cladding boundary Little loss with distance Cladding Core Light Source Reflection • Modes Optical Fiber – Light entering at different angles will take different amounts of time to reach the other end – Different ways of traveling are called modes – Light modes from successive bits will begin to overlap given enough distance, making the bits unreadable Light Source Reflection Single Mode Fiber • Single Mode Fiber is very thin – Only one mode will propagate even over fairly long distances – Expensive to produce – Expensive to install (fragile, precise alignments needed) – Used by carriers to link distant switches Multimode Fiber • Core is thick – Modes will appear even over fairly short distances – Must limit distances to a few hundred meters – Inexpensive to purchase and install – Dominates LANs Graded Index Multimode Fiber • Index of fraction is not constant in core – Varies from center to edge – Reduces time delays between different modes – Can go farther than if core has only a single index of fraction (step index multimode fiber) – Dominates multimode fiber today Multimode Optical Fiber and Frequency • Signal Frequency Determines the Propagation Distance before Mode Problems Become Serious • Short Wavelength (high frequency) – Signals do not travel as far before mode problems occur – Uses the least expensive light sources – Good for LAN use within buildings • Long Wavelength (low frequency) – Signals travel farther but light sources cost more – Within large buildings and between buildings Wave Division Multiplexing • Use multiple light sources of different frequencies – Place a separate signal on each – Increases the capacity of the optical fiber Radio Transmission • Oscillating electron generates electromagnetic waves with the frequency of the oscillation • Many electrons must be excited in an antenna for a strong signal Radio Propagation • Propagation Characteristics Depend on Frequency – At lower frequencies, signals bend around objects, pass through walls, and are not attenuated by rain – At higher frequencies, there is more bandwidth per major band Major Bands • Frequency Spectrum is Divided into Major Bands • Ultra High Frequency (UHF) – Signals still bend around objects and pass through walls – Cellular telephony • Super High Frequency (SHF) – – – – Needs line-of-sight view of receiver Rain attenuation is strong, especially at the higher end High channel capacity Used in microwave, satellites Microwave Transmission • Terrestrial (Earth-Bound) System • Repeaters can relay signals around obstacles Satellite Transmission • Essentially, places repeaters in sky – Idea thought of by Sir Arthur C. Clarke • Satellite broadcasts to an area called its footprint • Uplink is to satellite; downlink is from satellite Uplink Footprint Downlink Some Popular Satellite Frequency Bands Band C Downlink Uplink Frequency Frequency (To (From Satellite) Satellite) 4 GHz 6 GHz Ku 12 GHz 14 GHz Ka 20 GHz 30 GHz