* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download light
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
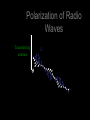
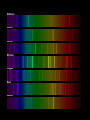
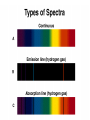
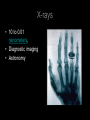
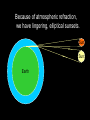
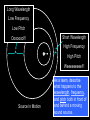
Light The Electromagnetic Connection • A changing magnetic field produces an electric field, and a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. • Electric and Magnetic fields can produce forces on charges • An accelerating charge produces electromagnetic waves (radiation) • Both electric and magnetic fields can transport energy – Electric field energy used in electrical circuits, e.g., released in lightning – Magnetic field carries energy through transformer, for example Electromagnetic Radiation • Interrelated electric and magnetic fields traveling through space • All electromagnetic radiation travels at c = 3108 m/s in vacuum – the cosmic speed limit! – real number is 299792458.0 m/s exactly Examples of Electromagnetic Radiation • AM and FM radio waves (including TV signals) • Cell phone communication links • Microwaves • Infrared radiation • Light • X-rays • Gamma rays • What distinguishes these from one • Uses of Electromagnetic Waves Communication systems – One-way and two-way • • • • • Radar Cooking (with microwaves) Medical Imaging (X rays) “Night Vision” (infrared) Astronomy (radio, wave, IR, visible, UV, gamma) All that we experience through our eyes is conveyed by electromagnetic radiation… The Electromagnetic Spectrum • Relationship between frequency, speed and wavelength f ·l = c f is frequency, l is wavelength, c is speed of light • Different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation are better suited to different purposes • The frequency of a radio wave determines its propagation characteristics through various media Polarization of Radio Waves Transmitting antenna E Reception of Radio Waves E Receiving antenna works best when ‘tuned’ to the wavelength of the signal, and has proper polarization Electrons in antenna are “jiggled” by passage of electromagnetic wave Questions Why are car radio antennas vertical? Why are cell phone antennas so short? How do polarizing sunglasses work? Radio waves • Radio waves – between 100-1m long • Communication, radio and tv • AM- amplitude modulation • FM Frequency modulation Microwaves • Wavelength between 1m and 1mm long • Used for communication, radar and cooking food Infrared • Wavelength between just below visible light • Between 750nm and 1mm • Perceived as heat • Night vision, heating • Nanometer is 1/1000000000 of a meter Visible light • Color Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Violet Wavelength(nm) 780 - 622 622 - 597 597 - 577 577 - 492 492 - 455 455 - 390 Frequency 384 - 482 482 - 503 503 - 520 520 - 610 610 - 659 659 - 769 Spectroscopy • spectrometer is an optical instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum • Elements give off different emission spectra when they glow • These can be used to identify the presence of elements Hydrogen Helium Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Neon Sodium Properties of visible light • Absorption- light is absorbed by matter • Why does your flashlight become dim at a distance • Scattering is the release of light by the matter • Prism- Refracts light twice, different wavelenghts are refracted more than others The Visible Spectrum A range of light waves extending in wavelength from about 400 to 700 nanometers. Things that create a Spectrum • • • • Prism Raindrops CD’s Spectroscopes – Contains a Diffraction Grating Emission Spectra • Hot gas produces a bright line emission spectrum. (Bright Lines) Absorption • When an electron is raised to a higher energy level, the atom is said to be excited. Emission • When the electron returns to a lower energy level, energy is released in the form of light. Transmission • Matter that allows visible light to easily pass through are transparent • Matter that scatters light is translucent • Matter that does not transmit light is called opaque Ultraviolet • Wavelenghts above visible light 400nm1nm • Photons have enough energy to kill living cells • Present in sunlight X-rays • 10 to 0.01 nanometers, • Diagnostic imaging • Astronomy Gamma rays • Shorter then .01nm • Radioactive decay • Great penetrating power Parts of the Human Eye (Supplement Handout) • • • • • • • Cornea – bends light Iris – controls the amount of light Pupil - opening Lens – focuses light onto retina Retina – back of eye Fovea – center of your vision Optic Nerve – “signal wire” (causes blind spot) Blind Spot Demo O X • Rods - brightness receptors • Cones - color receptors – Three Types: Red, Green, Blue • Cones are more numerous in the center of your vision. • Rods are more numerous around the periphery of your vision. • Demo – Moving markers near periphery Color Deficiency Color Vision • Colorblindness - about 10% of population • Red-green is predominant • Yellow-blue - a few What is color? • Different wavelengths of light are perceived as different colors. • White light contains equal amounts of these colors. (ROY G. BIV) Fill in the Blanks • Black objects _______ all of the pure absorb colors. • White objects _______ all of the pure reflect colors. • Transparent objects _______ all of the transmit pure colors. Mixing Colored Light Color Addition • Additive Primary Colors: • Red • Green • Blue • One can produce any color by varying amplitude and mixture or red, green and blue light. • Complementary Colors - any two colors that add together to produce white • e.g. magenta + green = white After Images and “Conal Fatigue” • The human eye will see complimentary colors after staring at a color picture. Transparent and Opaque • Transparent – you can identify objects through it • Translucent – you see diffuse light coming through it • Opaque – you cannot see any light coming through it – Opaque objects cast shadows. The Electromagnetic Spectrum • • • • • • • Radio Waves Microwaves Infrared Visible Light Ultraviolet X-rays Gamma Rays mnemonic • • • • • • • Raging Martians Invade Roy G. Biv Using X-rays and Gamma Rays Atmospheric Refraction • Our atmosphere can bend light and create distorted images called mirages. • http://astro.sfasu.edu/movies/Highway Mirage 1.mpg • What causes stars to twinkle? – Atmospheric Turbulence Because of atmospheric refraction, we have lingering, elliptical sunsets. Sun Sun Earth Holography • Holography- technique that produces a 3D image without a lens Why is the sky blue? • Nitrogen and Oxygen in our atmosphere scatter high frequencies of light. Why are sunsets red? • Red light is scattered the least by our atmosphere. • The greatest path of sunlight through the atmosphere is at sunset or sunrise. Why are clouds white? • The color of light scattered by clusters of water molecules vary with the size of the clusters. • The size of clusters of water molecules (droplets) vary in clouds. What happens when the source in in motion? Movie #1 Java Long Wavelength Low Frequency Low Pitch Ooooooo!!! Short Wavelength High Frequency High Pitch Weeeeeeeee!!! Source in Motion As a team, describe what happens to the wavelength, frequency, and pitch both in front of and behind a moving sound source. Doppler Effect • Examples: – moving cars and trains • Sound • Movie #2 – moving buzzer in a nerf ball (in class)