* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Nanotoxicology wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Carbon nanotubes in photovoltaics wikipedia , lookup
Drexler–Smalley debate on molecular nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Nanomedicine wikipedia , lookup
Impact of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Carbon nanotubes in medicine wikipedia , lookup
Regulation of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Scanning tunneling spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Scanning joule expansion microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic force microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photoconductive atomic force microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
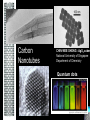
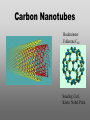
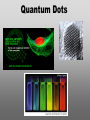
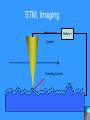
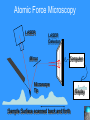
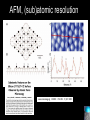
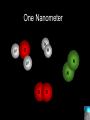
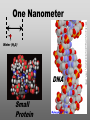
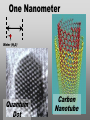
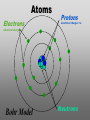
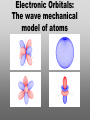
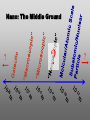
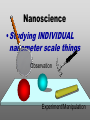
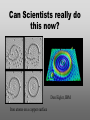
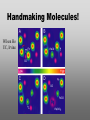
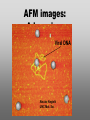
Nanoscience Nanotechnology What is it? What exactly is Nanoscience? What exactly is Nanotechnology? Are they Different? Vials of Quantum Dots NOTE: What follows is my view of these subjects What is Nanotechnology? The Space Elevator? Ultra high strength materials allow tower to be built into space !(?) What is Nanotechnology? Tiny machines in your body curing cancer? What is Nanotechnology? DNA Computers in a beaker that vastly outperform our fastest supercomputers? Well …. Sort of…. Not Really…. • Some of these amazing views of the future have a grain of reality in them • We’ll take a look at advances in –Materials science –Nanobiotech –Molecular computing Nanotechnology TECHNOLOGIES Nanomaterials Nanolithography Scanning Probe Microscopy Self-Assembly APPLICATIONS Super fast/small computers Super strong materials Super Slippery Materials Tissue Engineering Drug Delivery Sensors Materials Science: Nanomaterials Human Made Materials Biologically made materials Calcium Carbonate Silica Calcium phosphate Hydroxyapatite Calcite 10 mm Superhydrophobic Surfaces: The Lotus Effect Carbon Nanotubes CHIN WEE SHONG : AgS2 cubes National University of Singapore Department of Chemistry Quantum dots Carbon Nanotubes Buckminster Fullerene C60 Smalley, Curl, Kroto. Nobel Prize The Forms of Carbon Diamond Buckyball Graphite Graphein: (Greek) to write Nanotube Carbon Nanotubes: Cylinders of Sheet Lattices Nanotubes have chirality Multiwall CNT=Nested tubes What’s the big deal about carbon nanotubes??? • Amazing Mechanical Properties • Amazing Electrical Properties: – Can be conductors or semiconductors – Could be the building block of nanocomputing Applications: Composite Materials nanotubes poking out of fractured edge of polymer composite Applications: Electronics 21 APRIL 2000 VOL 288 SCIENCE www.sciencemag.org Crossed Nanotube Junctions M. S. Fuhrer,1 J. Nyg.rd,1 L. Shih,1 M. Forero,1 Young-Gui Yoon,1 M. S. C. Mazzoni,1 Hyoung Joon Choi,2 Jisoon Ihm,2 Steven G. Louie,1 A. Zettl,1 Paul L. McEuen1 * Applications: Field Emission 1 Samsung prototype carbon nanotube display Applications: Field Emission 2 Otto Zhou. UNC Physics Cold Cathode X-ray machine The potential advantages of the future CNT X-ray devices are fast response time, programmable xray intensity, programmable spatial distribution (Figure 3), ultra-fine focal spot, rapid pulsation capacity, long lifetime, low energy consumption, miniaturization, and low cost. Quantum Dots Microfluidics Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Myosin V/ Actin Motor Myosin V Molecular Motors Use ATP to do Mechanical Work Advanced Techniques • Scanning ProbeMicroscopy • Lithography Why Nano now? What has enabled Nanoscience? An incomplete list . . . . • Advances in Computing Power • New Generation of Scientific Instruments Scanning Probe Microscopes Scanning Tunneling Mic. (STM) Very Sharp Tip scans over sample surface Atomic Force Mic. (AFM) Magnetic Force Mic. (MFM) Near Field Scanning Optical Mic. (NSOM) ATOMIC RESOLUTION STM, Imaging - Battery + Current Tunneling Current Sample Sample STM images, Examples http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem3/medialib/media_portfolio/07.html Atomic Force Microscopy LASER LASER Detector Mirror Computer Microscope Tip Sample Surface scanned back and forth Display AFM, (sub)atomic resolution Nanoguitar Craighead Group, Cornell What is Nano?? • Nano refers to the scale of nanometers. • This is the scale of molecules, proteins, and other nanoobjects that are the topics of this course. How big is nano? • Nano means one billionth (x 10-9) • Written another way: x 0.000000001 • One nanometer equals 0.000000001 meters (or 0.000000003 feet) One Nanometer H H O H N H N O O One Nanometer Water (H20) DNA Small Protein One Nanometer Water (H20) Quantum Dot Carbon Nanotube What is matter made of? Atoms Molecules What are atoms ? How big are they? How well can we “see” them? • Atoms are roughly 2-5 Angstroms in dimension 2-5 * 10 -10 m ~1Ǻ Take a millimeter and divide it into 1000 parts: micron 10-6 m Take one micron and divide it into 1000 parts: nanometer 10-9 m Take one nanometer and divide in 10 parts: angstrom 10-10 m Atoms Electrons Protons electrical charge= +e electrical charge= -e Bohr Model Neutrons Electronic Orbitals: The wave mechanical model of atoms S-Orbital P-Orbital D-Orbital F-Orbital S-Orbital P-Orbital D-Orbital F-Orbital Galactic Scale Nano: The Middle Ground “Macroscopic” Scale “Microscopic” Scale Nanoscale Subatomic scale: Nuclear Physics Partical Physics atoms Molecular / Atomic Scale Nano: The Middle Ground ? ? ? What is Nanoscience? How is nanoscience different than •Chemistry •Biology •Physics Eigler et al. NATURE 363, 1993 What distinguishes nanoscience from other sciences? The study of nanometer scale things? DNA Carbon Nanotubes Water Isn’t this just Biology and Chemistry?? YES … and NO. Chemistry done in beakers (many billions of molecules) Nanoscience • Studying INDIVIDUAL nanometer scale things Observation Experiment/Manipulation Can Scientists really do this now? Don Eigler, IBM Iron atoms on a copper surface Atomic Manipulation Scanning Probe Tip Atom Handmaking Molecules! Wilson Ho UC, Irvine. Nanoscience vs. Nanotechnology Nanoscience: exploring and studying the properties of the nanoscale Applying the unique properties of the nanoscale to technology Why Nano now? What has enabled Nanoscience? An incomplete list . . . . • Advances in Computing Power • New Generation of Scientific Instruments Scanning Probe Microscopes Scanning Tunneling Mic. (STM) Very Sharp Tip scans over sample surface Atomic Force Mic. (AFM) Magnetic Force Mic. (MFM) Near Field Scanning Optical Mic. (NSOM) ATOMIC RESOLUTION Scanning Probe Mic: Sharp tip Sharp tip moves over surface and measures some property Scanning Probe Tip Sample Sample STM, Nobel Prize 1986 Binnig and Rohrer STM images, Examples http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem3/medialib/media_portfolio/07.html AFM images: Adenovirus Viral DNA Atsuko Negishi UNC Mat. Sci. Titin unfolding Titin http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research /smd_imd/titin/ Pulling Titin 2 Images and Manipulation of DNA ! Departmento Física de la Materia Condensada UAM Asylum Research http://www.nihms.nih.gov Nanocalc A 1. 2. 3. 4. How many atoms in your piece of Aluminum? How big is an Aluminum Atom? How many atoms on the surface of the piece? What is the ratio of surface atoms to volume atoms? 5. If your piece was 10nm*10nm*10nm what would the ratio be? 6. If your piece was a sphere of 2nm radius what would the ratio be? Nanocalc B Lets say you have a cube of solid material 1 m on a side. A. What is the total surface area? B. If you split it into cubes 0.5 m on a side, what is the total surface area of all the pieces? C. If you split into cubes 1 mm (10-3m) on a side, what is the total surface area? D. If you split inot cubes 1 micron on a side (10-6m) what is the total surface area? E. If you split into cubes 1 nanometer (10-9m) what is the total surface area? (for each answer, try to come up with an intuitive way of describing the area : tennis courts, football fields etc.) 27Al makes up 100% of naturally occurring Al Atomic mass : 26.9815 amu 13 protons 14 neutrons