* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sed & Meta Rx
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Ore genesis wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Sediment transport wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary budget wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
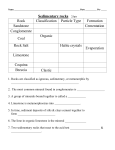
Today: Origin and Interpretation of Sedimentary Rocks Wed: Origin and Interpretation of Metamorphic Rocks Sedimentary Rocks — Why Care? • They are the repository of Earth’s history, especially the history of how the surface environment (including life) changed over time. To extract this history, we need to be able to “read” this rock record. • They hold all of the oil, gas,coal, and water — locating these materials requires an understanding of the physical characteristics of different sedimentary rocks and how those characteristics change in 3-D. Coconino Sandstone Coconino Sandstone up close thin slice of Coconino sandstone seen through microscope un-cemented quartz sand grains from a sand dune So how are sedimentary rocks made? Physical & Chemical Weathering → Sediment & Dissolved Ions hincks146-147 Sedimentary Structures in the Coconino This is the modern environment where large cross-beds form Wind Direction Fig. 5.21abc W. W. Norton So cross beds are tilted in the direction of flow (downstream) Fig. 5.21d Stephen Marshak Uniformitarianism — depositional environments of today are physically the same as ancient environments, so clues from the modern can be used to infer ancient environments from sedimentary rocks, or “the present is the key to the past” ripples Stephen Marshak Ancient ripples Stephen Marshak Mud cracks Stephen Marhsak Ancient mudcracks Stephen Marhsak Modern Alluvial Fan, Death Valley Fig. 5.24c © Martin Miller Ancient Alluvial Fan Deposits OOIDS (made of calcite — CaCO₃) imply shallow (<3m), tropical marine depositional environment Monte Bove in Italy 800 meters of oolitic limestones Ooids with cement, seen in a thin section, through a microscope 2 mm So, the question is — how can we explain such a thick pile of shallow-water sediments? We need to think about isostasy and sea level change in our search for an explanation of how we can get such thick piles of sediment, all of which appear to be deposited in fairly shallow water. Isostasy Isostasy Equilibrium level for wooden block time 1 time 1 time 4 time 4 So, the question remains — how to get such a thick pile of shallow-water sediments? Add a Weight Increase Density Thin Crust Raise Sea Level As sea level goes down, previously deposited sediment will be eroded In our case, crustal thinning makes sense because the sediments in question were deposited during and after continental rifting. Summary on Making and Interpreting Sedimentary Rocks • Make sediment • Transport & deposit sediment • Create space to allow sediment to accumulate • Compact and cement sediment Depositional environments are interpreted based on studies of modern environments where sediment is deposited. Metamorphic rocks