* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Agents of Erosion - Bethpage Union Free School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
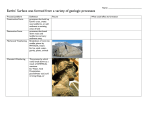
Agents of Erosion AIM: What forces cause erosion? Vocabulary Erosion Mass movement Landslide Creep Slump Mudslide Avalanche Liquefaction Retaining Walls Slope 1. Erosion Movement of sediments from one location to another. Landforms are created by a combination of weathering and erosion. Often the forces that cause erosion also cause the weathering of the sediment at the same time. 2. Gravity a. ***Driving force of all erosion **** b. Causes Mass Movement or Mass Wasting (Ex - Landslides, mudslides, slump and creep) c. Affected by slope, ground cover, water, climate Can be triggered by earthquakes d. Sediments are angular and rough a. Landslides or rockslides – fast moving Retaining walls and metal nets help prevent landslides b. Mudslides Downward flow of water, rock and soil After heavy rain when ground is overly saturated, where vegetation has been stripped, and on steep slopes Volcanoes can trigger a melt Liquefaction – when the land becomes fluid and moves c. Slump – a sudden sag or dip d. Creep – very slow movement downhill Slanted fences, walls, trees or gravestones are a sign of creep. e. Avalancheinvolves snow and ice http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=B2F A4835-7736-4E1E-BAAF841B64AF37F9&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US 2. Wind a. Erodes fine, small, loose, dry material b. Contributes to abrasion (physical weathering) c. Affected by velocity, sediment size, ground cover, water d. Sediments are angular with frosted or pitted appearance e. Occurs in deserts, arid areas, seashores Wind erosion forms sand dunes. Wind makes odd shapes and angular rocks Wind also makes swirly patterns The Great Dust Bowl – the Dirty 30s Wind can erode away topsoil Vegetation reduces erosion of dunes Draw a sand dune with the sand blowing from the right. How does gravity play a role in wind erosion? Gravity causes wind to drop it’s sediments in a new location. What kind of weathering does wind cause while it’s eroding sediments? Wind carries sand and fine particles which can abrade rock (abrasion by wind). Weatherhing and erosion games http://www.glencoe.com/sec/science/Scie nce600/co/530.php?iRef=530&iChapter= 16 http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_a ssets/science/virtual_labs/E06/E06.html http://www.kineticcity.com/mindgames/w arper 1) The photograph shows a sand dune that formed in a coastal area. This sand dune was most likely formed by A) water flowing from the left B) water flowing from the right C) wind blowing from the left D) wind blowing from the right The picture below shows a geological feature in the Kalahari Desert of southwestern Africa. Which process most likely produced the present appearance of this feature? A) wind erosion B) volcanic eruption C) earthquake vibrations D) plate tectonics 3. Glacial Landmasses a. Glacier – a large mass of moving ice, found in areas of - High elevation ( mountaintops) - High latitude ( polar regions) b. Two types: Valley glacier – long and narrow, forms high in the mountains Continental glacier – ice caps, covers much land, ex – Greenland, Antarctica, Alaska 3. Glaciers c. Gravity pulls weight of glacier down mountain d. Glaciers can move cm/day e. Affected by slope, weight, and velocity f. Erodes many sizes - boulders to sand g. Sediments are unsorted (mixed sizes) h. Sediments have sharp angles, irregular shapes,rough, grooves (striations) i. Carve U-shaped valleys Ice ages – when glaciers covered large parts of the Earth’s surface Glaciers – carve a U-shaped valley As the glacier moves it drags sediment downhill. Other glacial landforms Glacial erosion Plucking – rocks freeze to the glacier and moves it Abrasion – rocks in glacier scratch bedrock causing striations Striations – grooves carved in rock can tell you the way a glacier moved Glacial Deposition When sediments are eroded, they must come to rest somewhere. They are deposited in a location that creates a landform. Glaciers deposit sediments, as well as water, wind and gravity. Glacial Deposition Till – the sediment piles that are created by glaciers are unsorted deposits, meaning they have many shapes and sizes of sediments. Glacial Deposition Moraine – till deposited at the edge of a glacier makes a mound How moraines are formed http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/eg eo/flash/18_1.swf Glacial Deposition Drumlin-elongated whale-shaped hill formed by glacial ice. They point the direction of glacial retreat. Glacial Deposition Glacial Erratic – a boulder dragged by a glacier to a new location, from a different origin Glacial Deposition A kettle lake is a hole left by a chunk of ice and filled by melting glacial water and runoff. Glacial Deposition Glacial Outwashsediments washed away from the glaciers front end. These sediment are deposited, sorted by size in layers. Glacial Deposition Eskers – a long winding ridge formed when a river of melting ice forms inside the glacier Glacial Outwash Glacier Game http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_a ssets/science/virtual_labs/ES07/ES07.ht ml 4. Wave Action a. Wave action brings in (deposits) and carries away (erodes) sand along coastlines. b. Wind creates waves. b. Affected by tides. c. Sediments are rounded from abrasion. Waves shaping the coast 5. Stream erosion (Running Water) a. ****Primary agent of erosion **** b. Size of sediment carried depends on velocity of water c. Sediments are rounded from abrasion d. Carve V-shaped valleys Stream carved V-shaped valley Streams weather and erode waterfalls – softer rock erodes, while harder rock remains Waterfall formation waterfall formation Broken boulders at the bottom of the falls Question… Which agents of erosion also weather rocks at the same time? Question… How is gravity involved in stream erosion? Now it’s your turn… 1. Look at the following pictures 2. Identify the type of erosion 3. Match the cut-out sediment type transported in each example.