* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 PPT/Notes A
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Planck's law wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
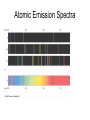
CHAPTER 5:Electrons in Atoms Light and Quantized Energy The Wave Nature of Light •Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation. •Light is a particle that travels as a wave. •See p 137 for parts of a wave. The Wave Nature Of light • Electromagnetic radiation Parts of a Wave • Wavelength is the length of a wave from one location to the same location in the next wave…crest to crest for example. • Amplitude is the vertical distance from origin to crest or origin to trough. • The trough is the ‘bottom-point’ of a wave and the crest is the ‘peak’ of a wave. • Frequency is how many waves per unit of time pass a point. • Period is how long it takes for a wavelength to pass a point. • F=1/period Wavelength and Frequency • c=f•λ • where c=3.00x108 m/s λ=wavelength and f =frequency. The Electromagnetic Spectrum • Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength,Energy, and Frequency • Wavelength and frequency are inversely related…like on a see-saw. • Ef λ The Particle Nature of Light • A quantum is the amount of energy required to move an electron from one energy level to the next. • E=hf • …where E=energy and h=Planck’s constant h=6.626x10-34Js • This calculates the energy of a photon or quantum. Atomic Emission Spectra Absorption and Emission Spectra • Absorption spectra …Emission Spectra 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Bohr’s model of the atom…