* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms Vs. Molecules
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
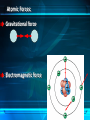
Atoms and Molecules The power of tiny things Structure of an Atom Three Kinds of Particles: Protons (+) Inside nucleus Neutrons Inside nucleus Electrons (-) Moving rapidly around the nucleus The Role of Electrons Moving so quickly that it is impossible to pinpoint an electrons location at any given time. Think of the blades of a fan. Electrons move around the nucleus much like the fan blades, but in 3 dimensions. Just the facts: Just how small is an atom? A penny contains about 20,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 atoms. When an atom gains or loses electrons, it is called an ion. Ions can form when two atoms chemically bond to form a new substance. Na+ (sodium) + Cl- (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) More facts: Isotopes Isotopes (atoms with different numbers of protons and neutrons) can become unstable and are called radioactive. They can be used to identify certain chemical reactions, or for nuclear development. Atomic Forces: Gravitational force Electromagnetic force Atomic Forces: Strong force (in the nucleus) Hold the nucleus together Weak force (in neutrons) A neutron can change into a proton or electron little particles, BIG SPACES. Most of an atoms mass comes from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. An atom’s volume is mostly due to the electron cloud around it. Did you know? A human hair is about one MILLION atoms thick!!!! Molecules Molecules are two or more atoms joined together in a set ratio. The atoms are joined by the outer ring of electrons, called the valence electrons. Putting it all in perspective http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/investigations/es0501/es0501page06.cfm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MUeFzvHz8Bw