* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light and the electron
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
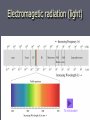
Light and the electron Quest continues to discover the structure of atom and how electrons are arranged within atoms. Wave Nature of Light ► Electromagnetic radiation – form of energy exhibiting wave-like behavior ► Ex. Visible light Wavelength (λ) ► Distance between adjacent peaks in a wave. Measured in meters. Speed of light (c) ► Light travels at 186,000 mi/s ► 3.00 x 108 m/s ► c = 3.00 x 108 m/s Frequency (Ʋ) ► Number of peaks which pass a point per second. ► Ʋ = 1/s (Hz) Wavelength vs. Frequency Putting it together ►c = λƲ ► 3.00 x 108 m/s = λƲ ► Pg. 121 practice problems 1-4 Electromagetic radiation (light) To microwave Particle Nature of Light ► Wave nature of light didn’t explain many important aspects – Why heated objects emit only certain frequencies of light at given temp.? ► Quantum concept – heated objects emitting different frequencies of light. Energy emitted corresponds to certain Ʋ & λ ► Quantum- minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom Max Planck ► Energy of quantum is related to the frequency of the emitted radiation ► Equantum = hƲ ► E = energy ►Ʋ = ? ► h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10–34 J · s ► Greater the frequency, greater the energy – directly proportional ► Pg. 124 practice problems 5,6 Atomic Emission Spectra – light produced in glowing neon signs ► Pass energy through tube filled with gas ► Causes electrons to absorb energy & become excited ► As unstable, excited electrons lose energy and spiral towards the nucleus they give off energy that corresponds with certain frequencies of light ► When emitted light is passed through a prism→ atomic emission spectra ► Each atom’s atomic emission spectrum is unique and can be used to determine if that element is part of an unknown compound. Pg. 126 Bohr e- Bohr e- Bohr e- Bohr e- Bohr e- Hydrogen spectrum