* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Volcanoes
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Rinjani wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Volcano (1997 film) wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
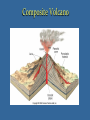
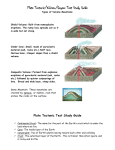
Types of Volcanoes Effects on Earth Learning Target I will explain how different types of volcanoes are made and what kind of impact volcanoes have on Earth. Shield Volcano • broad with gently sloping sides • built of layers of lava (runny) • quiet eruptions (like Hawaii) • largest mts. on Earth (Mauna Kea) Cinder Cone Volcano • Steep sides & loosely packed • Made of pyroclastic material (medium eruptions) • Erupt for short time • Occur in clusters; on sides of shield & composite volcanoes Paricutin On February 20, 1943, Paricutin, a cinder cone volcano in Mexico, formed from the crevasse in a cornfield and grew to be several hundred meters tall in just a few days. This volcano continued to erupt for 9 years and grew to be over 1,300 feet tall. Composite Volcanoes “Stratovolcanoes” • Most common volcano • Broad bases & sides that get steeper towards the top • Eruptions start explosive, followed by quieter eruptions of lava • mostly at convergent boundaries • the tallest volcanoes in the world (Mt. Fuji in Japan) Composite Volcano Mt. Saint Helens Krakatau •In August of 1883, a composite volcano, Krakatau in Indonesia erupted with such force that the island it was on disappeared, killing more than 36,000 people. •It launched a series a Tsunamis that devastated the surrounding coastlines. •It affected the world’s weather and climate for a couple of years. Craters & Calderas •Crater – a funnelshaped pit at the top of the central vent •Caldera – when the magma chamber empties & its roof collapses Sunset Crater near Flagstaff, Arizona Copyright © 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Katmei Caldera Formation of Crater Lake Lava Plateaus • Fissures – long cracks in the Earth’s crust - Quiet eruption; runny lava - Spreads evenly over thousands ft² • Lava plateau – resulting landform (Columbia River Plateau) Impact on Earth • Ash (fall-out) - Block out sun for days Weight can collapse buildings Smother plants & animals Blanket towns Dam up rivers & cause floods Climate change • Trees & buildings blown down or burnt • Build mountains • Melt glaciers • Avalanche & flood (mahars) Climate Change • Volcanic ash & sulfur-rich gases can reach the upper atmosphere • Ash can block out enough sunlight to cause the average global temperature to drop noticeably • Example: 1991 Mt. Pinatubo dropped global temp by 0.5°C • Can cause milder, wetter summers & harsher, longer winters