* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vulnerability Indicators + Assessment
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Ministry of Environment (South Korea) wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
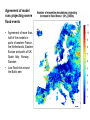
Vulnerability indicators and their relation to the measure selection Source FAO Natasha Marinova ClimWatAdapt Second stakeholders meetingmeeting 30 March 2011, Budapest DPSIR Framework Water Scarcity – Water stress Drivers Pressures Climate change T • • • • • Population GDP Technology dev. Markets (from SCENES) State Impacts Precipitation (and propagation of its effects on hydrological cycle) Evapotraspiration Morphology Topology Soil water holding capacity •Structural changes •Land use changes: Urbanization •Resource use efficiency •Management practices Jobs Incomes Quality and quantity of waste water Droughts Drivers Pressures Climate change T • • • • • Population GDP Technology dev. Markets (from SCENES) Precipitation (and propagation of its effects on hydrological cycle) Evapotraspiration Morphology Topology Soil water holding capacity •Structural changes •Land use changes: Urbanization •Resource use efficiency •Management practices State Changes in return period of drought events Impacts • Relative area affected by droughts • People affected by drought Baseline: Minimum flow during a drought event with recurrence period of 50 years D50base Future (2050): Minimum flow during a drought event with a recurrence period of 10 years D10future Severe drought event if D10future< D50base Not adjusted to the drought event water demand Quality and quantity of waste water Jobs Incomes Population affected by droughts for EcF and SuE scenarios Agreement of model runs projecting severe drought events • Large areas in the Mediterranean Western and Eastern Europe with agreement of up to 100% • Agreement of more than half of the models in parts of France, Ireland, UK • Heterogeneous result in Central and Western Europe Floods Drivers Pressures Climate change T • • • • • • Population GDP Technology dev. Markets (from SCENES) • Precipitation (and propagation of its effects on hydrological cycle) Evapotraspiration Morphology Topology Soil water holding capacity use changes – urbanization, deforestation, development in flood prone zone, control of rivers Level of protection (design return level) State Changes in magnitude of 1-in-100 y flood event Impacts • Area affected by floods • People affected by floods Land • • • • River bed sedimentation Loss of wetlands and riparian zones Soil sealing Not properly planned drainage Jobs Incomes Relative area affected by floods • Based on the ensemble median • More than 80% in part of the UK and the Netherlands • ~ 20% in southern Norway, parts of France, and the Alps People affected by floods Agreement of model runs projecting severe flood events • Agreement of more than half of the models in parts of western France, the Netherlands, Eastern Europe and parts of UK, Spain, Italy, Norway, Sweden • Low flood risk around the Baltic see Sea Level Rise People affected by SLR, 2080 Source PESETA, Coastal Report Thank you!