* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.Anatomy & Physiology of Kidney - RIMS College
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
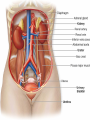
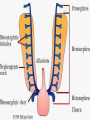
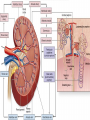
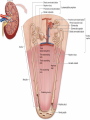
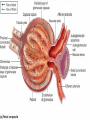
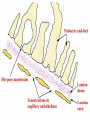
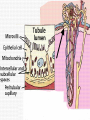
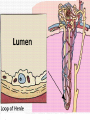
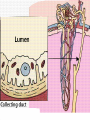
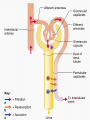
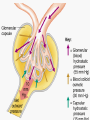
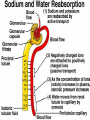
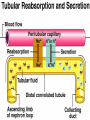
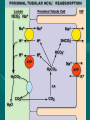
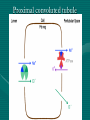
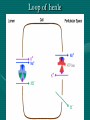
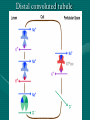
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF KIDNEY RENAL ANATOMY RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Proximal convoluted tubule Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of henle Distal convoluted tubule = = Na+ K+ H+ EVALUATION OF RENAL FUNCTION Measurement of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) • GFR is essential to renal function • Most frequently performed test of renal function. • Measurement is based on concept of clearance: - “The determination of the volume of plasma from which a substance is removed by glomerular filtration during it’s passage through the kidney” Determination of Clearance • Clearance = (U xV)/P Where U is the urinary concentration of substance x V is the rate of urine formation (mL/min) P is the plasma concentration of substance x • Units = volume/unit time (mL/min) Inulin GFR • Gold Standard • Complex procedure – Bolus dose followed by constant infusion – Timed urines, with bloods taken midpoint of collection periods, for inulin assay. – GFR is taken as the mean for each period. Isotopic GFR • 99mTc-DTPA 51Cr-EDTA • Single bolus injection with blood taken for isotopic counting at intervals Creatinine Clearance • Timed urine collection for creatinine measurement (usually 24h) • Blood sample taken within the period of collection. Problems: • Practical problems of accurate urine collection and volume measurement Plasma Creatinine Concentration Difficulties: • Production determined by muscle massrelated to age, sex and weight. • Concentration inversely related to GFR. – Small changes in creatinine within and around the reference limits = large changes in GFR Cystatin-C • • • • Small size - freely filtered at glomerulus Constant production rate by all nucleated cells No known extra-renal excretion routes Not influenced by muscle mass, diet or subjects sex Blood urea level • Untill 75 % renal function is lost • Metabolism of proteins & synthesised in liver • May be rised when – High protein intake – Excessive protein catabolism – steroids ,tetracyclines – Absorption of blood from GIT • Low level –reduced dietary intake Renal blood flow • PAH clearance • Normal values 500-600 ml /min Urinary Concentration • Urine specific gravity • Water deprivation test Urinary Acidification Done in suspected cases of RTA • Urine pH • Sod. Bicarbonate loading test • Ammonium chloride loading test THANK YOU