* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tuberculosis Presentation
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
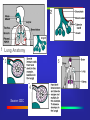
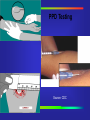
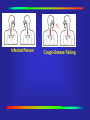
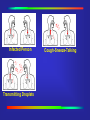
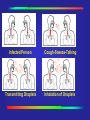
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Decline •During 2000, a total of 16,377 cases of tuberculosis (TB) (5.8 cases per 100,000 of population) were reported to CDC from the 50 states and the District of Columbia, representing a 7% decrease from 1999 and a 39% decrease from 1990. In 1992 there was a resurgence of TB in the United States. Reported Cases Ethnicity Source: CDC Rate per Population Source: CDC Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) •A slow growing bacteria that primarily affects the respiratory tract of humans. •Other areas that can be affected: TB Growth •What happens after the bacteria have entered the body? They begin to grow in the alveoli (small air sacs) of the lungs and then spread throughout the lung and body. 1 Lung Anatomy 5 3 4 Source: CDC Incubation •What is the usual incubation period? 2-10 weeks for TB infection Up to 2 years for TB disease (highest risk) •TB infected, Latent TB: Positive Skin Test-not contagious •TB disease/active: Showing symptoms and is highly contagious Treatment •Multidrug resistant They are trying many new different drug combinations to combat the drug-resistant strains. •DOT Directly Observed Therapy Directly Observed Therapy •DOT Directly Observed Therapy Source: CDC Testing •Two major screenings available to the general population: Tine Test (3 prong) PPD (Purified Protein Derivative) PPD Testing Source: CDC Transmission •Inhalation of infectious particles: Infectious particles are carried in the air after an active TB individual speaks, coughs, sneezes, or certain medical procedures are performed. •These particles are called droplet nuclei. •1-5 microns/ 1/5000 of an inch in size .... Infected Person ... ......... ..... .... ...... Infected Person ..... Cough-Sneeze-Talking ... ......... ..... .... ...... ..... Infected Person ... ...... ... ......... ..... .... ... ...... ..... ....... ...... ...... Transmitting Droplets Cough-Sneeze-Talking ... ......... ..... .... ...... ..... Infected Person ... ...... ... ......... ..... .... Cough-Sneeze-Talking .. ... ....... . .. .. ........ . . ... .. . . ... ....... .............. ......... ..... ........ .... ... ...... ..... ....... ...... ...... Transmitting Droplets ...... ...... Inhalation of Droplets Respirator •A respirator is a personal protective device that removes air contaminants such as dust, mists, and aerosols from the ambient air. •The ones used to protect against TB, filter out material down to 0.3 microns at 95% efficiency (N95). NIOSH approved Respirator Respirator N 95 NIOSH Approved Must be fit tested AFB Isolation •Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) isolation room: Warning signs Must be maintained under negative pressure. Exhaust air from the isolation room away from air intakes for the building, usually on the roof. Filters •High Efficiency Particulate Air filter (HEPA): Used to filter air for recirculation in an AFB isolation room at 0.3 microns at 99.97% efficiency. Settings at Risk •High Risk Settings: Health care settings Correctional institutions Homeless shelters Long-term care facilities for the elderly Drug treatment centers Where are your risks?