* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI)
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Candidiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
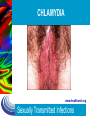
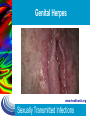
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Overview Definition of STIs: “What are they?” Transmission: “How are they spread?” Types of infection: – Bacterial (Chlamydia, LGV, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) – Viral (HSV, Hepatitis B, HIV, HPV) – Parasitic (Pubic lice, scabies, trichomoniasis) Prevention: “How can I protect myself?” Testing: “Where can I go for help?” www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Sexually Transmitted Infections Today our country faces an epidemic of STIs. – An epidemic is an outbreak of an infectious disease that affects a large population – About 12 million new cases of STIs are reported each year – Two-thirds about all STI cases occur in adolescents and young adults Sexually Transmitted Inflections are infectious diseases spread from person to person that are most commonly passed through sexual contact: 1. Oral 2. Vaginal 3. Anal www.healthunit.org 4. Skin-to-skin Sexually Transmitted Infections STIs and Adolescents Why are teens as a group at particularly high risk for infection from STIs? One reason is that teens who are sexually active are likely to exhibit one or more of the following behaviours: 1. 2. 3. Having more than one sexual partner rather than committing to a single, long-term relationship Engaging in unprotected sex Selecting partners at higher risk, such as those with a history of multiple sex partners or intravenous drug use. An additional risk for teen females is that they lack an immunity to some of the pathogens that cause STIs www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections STIs and Adolescents Cont’d Why are teens with an STI less likely to seek medical attention when compared to an adult? 1. Some teens are simply unaware of what action to take 2. Fear of disapproval by parents or other adults at home 3. Refuse to believe that they could have an STI 4. Through denial and rationalization, they ignore the signs and symptoms of infection www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections TRANSMISSION The primary means of transmission of STIs is sexual contact. – NOTE: A person who practices abstinence from sexual activity reduces his or her risk of contracting an STI In order for transmission to occur, it is necessary to have: – A body fluid with the germ in it – A way of spreading the germ from one person to another www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections BODY FLUIDS: Which one’s are considered infectious? Semen Vaginal fluid Blood Fluid in sores or blisters Saliva Tears Sweat Urine Ear wax www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections METHODS OF TRANSMISSION: Low Risk or No Risk Abstaining Hugging Kissing Holding hands Dancing Sitting on toilets Sharing lip balm Mutual monogamy Massage Sharing forks, knives, etc. www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections METHODS OF TRANSMISSION: High Risk Sexual Intercourse vaginal anal oral Blood-to-blood contact Sharing needles or other drug-use equipment Tattoo or body piercing Infected mother to her baby www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Bacterial vs. Viral STI’s Bacterial STI’s include Chlamydia, LGV, gonorrhea & syphilis Can be treated and cured with antibiotics Untreated infection can cause PID, infertility, & epididymitis Viral STI’s include HPV, HIV, Herpes, & Hepatitis B There is NO cure Medication available to treat symptoms only Can pass onto others for the rest of your life www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Chlamydia The most common bacterial STI – Greatest number of infections found in people 15 to 24 years old STI caused by bacteria that affect the genital mucous membrane, primarily in the lining of the urethra of the male and in the cervix and vagina of the female Symptoms in male: – Symptoms in female: – Unusual discharge from penis and a burning sensation during urination Unsual discharge from vagina, painful urination, pain in pelvic region 50% have NO symptoms - men and women Can be treated with antibiotics If left untreated, can cause: 1. Nongonococcal Urethritis: infection caused by several kinds of bacteria-like organisms that infect the urethra in males and the cervix in females 2. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: painful infection in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and/or uterus. www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections CHLAMYDIA www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections GONORRHEA The 2nd most common bacterial STI Most common in people aged 15 to 29 Can affect the cervix, urethra, rectum, throat, and occasionally the eyes Can be treated with antibiotics www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections GONORRHEA: Signs & Symptoms Female – Increased vaginal discharge – Painful urination – Lower abdominal pain – Bleeding after sex and between periods – Pain during sex Male – Thick, yellowishgreen discharge from penis – Painful urination – Testicular pain or swelling – Rectal pain, discharge or itching www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections GONORRHEA www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Trichomoniasis A vaginal infection that can lead to urethra and bladder infections Can be cured with a medicine that can be prescribed only by a physician Can cause Vaginitis (common inflammation of the female genitals) www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Genital Warts (Herpes Simplex Virus - HSV) It is a viral infection characterized by pink or reddish warts with cauliflower-like tops that appear on the genitals Caused by a virus called the human papilloma virus (HPV) Once infected, a person has the virus for the rest of her or his life A physician may remove the warts, but they may reappear NOTE: This STI is known to be one of the causes of cervical cancer in women. www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Genital Herpes (Herpes Simplex Virus - HSV) Two types: HSV-1, causing cold sores, and HSV-2, causing genital herpes It is a viral infection characterized by blister-like sores in the genital area Spread through direct vaginal, oral or anal sexual contact with an infected partner Also transmitted by receiving oral sex from a partner with a history of cold sores Symptoms can be treated with antiviral medications, but NO CURE www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Genital Herpes – Signs & Symptoms Prior to an outbreak, the person may feel a tingling or burning sensation where the virus first entered the skin Painful sores (external or internal) Inflammation and redness Fever Muscular pain Tender lymph nodes www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Genital Herpes www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections SYPHILIS An STI that attacks many parts of the body and is caused by a small bacterium called a spirochete A bacterial infection that progresses in stages – Primary: (3 days – 3 months) starts as a small, painless sore called a chancre; goes away on it’s own – Secondary: (2 – 24 weeks) rash on the body, palms of hands & soles of feet, hair loss, feeling sick – Latent: (2+ years after infection) signs and symptoms disappear, but infection begins to attack the heart and blood vessels of the CNS. Note: relapse into the second stage can occur. – Neurosyphilis: (10-30 years) the heart, skin, brain, and spinal cord are affected. Due to CNS impairment, a person man experience paralysis and convulsions www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Hepatitis B (HBV) Virus that attacks the liver Most infected people (90%) naturally produce antibodies to fight the disease, but some develop chronic HBV and will carry the virus for the rest of their life Chronic infection can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and cancer There is NO CURE, but vaccination can prevent infection www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Hepatitis B Woman suffering from liver cancer caused by HBV Photo courtesy of Patricia Walker, MD www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections HIV/AIDS HIV is a virus that destroys the immune system over time, robbing the body of its ability to fight other infections and illnesses Once the immune system is weakened, other infections occur and AIDS develops (the fatal stage of HIV infection) The virus is present in blood, semen, vaginal secretions & breast milk www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections HIV / AIDS – Signs & Symptoms 2 to 4 weeks after exposure, some people experience mild flu-like symptoms that last a few weeks, then disappear Many people have NO symptoms until years after exposure The only way to know is to get TESTED! www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Candidiasis Pronounced kan-duh-DY-uh-suhs A yeast infection of the vagina Usually occurs without sexual contact, but is often passed to a partner during sexual contact Symptoms include: yellowish discharge, strong odour, and itching Can be cured through medicated creams and tablets sold over the counter www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Pubic Lice & Scabies Infections caused by parasitic infestations Pubic lice: tiny crab-like insects that nest in pubic hair & bite their host to feed on blood Scabies: mites that burrow below the surface of the skin to lay their eggs Can live for 1 – 3 days on bedding, towels and clothing Treated with medicated creams & lotions www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Pubic Lice www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Scabies mite www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections STI Prevention Abstain from sexual intercourse (only method that is 100% effective) Don’t share needles or other drug-use equipment Have only 1 mutually faithful, uninfected sexual partner Get tested for STI’s before having sex Use a latex condom & spermicide Avoid alcohol & other drugs www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections When should I get tested? Once you become sexually active, you need a check-up & STI testing once a year You also need an STI test if: – – – – – – You didn’t use a condom or the condom broke Your partner has an STI Your partner is having sex with someone else You have ever injected drugs You or your partner have any STI symptoms You have been raped www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Responsibilities of Infected Individuals Treatment for sexually transmitted diseases is an important personal as well as social responsibility 1. The individual must take action to have the disease treated 2. It is also important for a person infected with an STI to notify all people with whom he or she has had sexual contact. 3. Educate partners about the symptoms and risks of the particular STI and encourage them to have a medical checkup www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Where to go for help: Parents Health Teacher Health Unit Clinic Family Doctor or Nurse Practitioner Walk-in-clinic Hospital Emergency Department www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections Remember… …your medical information will always remain CONFIDENTIAL! www.healthunit.org Sexually Transmitted Infections