* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prokaryotes:
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Lyme disease microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
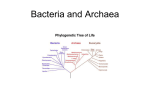
Prokaryotes: Archaea & Bacteria The Tree of Life All living things classified in three domains: Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Amazing Living Things Microbes important to all life: Decomposition Over half of Earth’s More biomass bacterial cells than human cells in your body! Prokaryotes Prokaryotes have: DNA or RNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, plasma membrane Most prokaryotes have a cell wall, a capsule (around the cell wall) and a flagellum Prokaryotes don’t have: Organelles such as nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria. Generalized Prokaryote Nucleoid DNA Plasmid DNA Cytosol Flagellum Capsule Plasma Membrane Cell Wall Bacteria/Archaea Habitats (name a place, and they live there!) They are specialists human skin, mouth, respiratory tract, large intestine, urogenital tract, etc. salty Dead Sea extreme archea Aerobes pH in deep sea vents: 90-106o C and anaerobes Some Prokaryotes Thrive in Extreme Conditions Cyanobacteria in Yellowstone Hot Springs Archaea Unique lipid membranes, cell walls, and RNA EXTREME Environments: Swamps, hot springs, vent communities, cow stomachs concentrated salt environments hot, acidic environments Bacteria Shape: Cocci - round Bacilli - rod Spirilla - spirals Three Common Bacterial Shapes (b) (a) (c) bacillus cocci spirillus The Prokaryote Flagellum Flagella Bacterium Bacteria Reproduction Reproduction is asexual, by simple splitting (binary fission) Daughter cells are genetic clones of the parent cell Binary Fission DNA Benefits of Bacteria Symbiosis (mutualism) Ruminants’ digestive tracts Nitrogen fixing in soil, nodules on certain legumes Bacteria on/in the human body: intestines and vitamin K and B12 Biodegradation - oil Food production - cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut Decomposers Our Relationship With Bacteria Harmful Bacteria Some cause disease = pathogenic In humans: Strep throat Toxins - tetanus, botulism Pneumonia "Flesh-eating" bacteria Plague Tuberculosis Cholera Lyme disease ANTIBIOTICS= anti bacterial!!! The Causes of Tooth Decay Transmission of Bacterial Pathogens Airborne Water Food Direct (skin contact, blood, and other body fluids) Insects and other hosts such as deer tick (Lyme). Germ Theory of Disease Theory that microorganisms are the cause of disease. 1859 – Louis Pasteur Credited with the idea that human diseases were caused by bacteria and viruses (germ theory) Very important discovery in the field of medicine Also created vaccinations to prevent disease Infectious Diseases Average age of death, in first world countries, jumped 30+ years in last century due to antibiotics enhanced hygiene and nutrition Antibiotic-resistant infections on the rise in hospitals in the U.S. This is due to bacterial evolution in response to widespread use of antibiotics!