* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The significance of Medical Parasitology
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
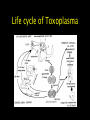
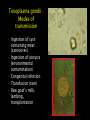
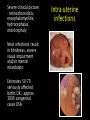
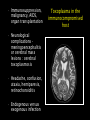
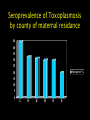
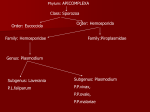
Protozoan parasite of human importance Disease : Toxoplasmosis Agent : Toxoplasma gondii Diverse routes of transmission Tissue-inhabiting Apicomplexan. Zoonosis. At risk groups. Life cycle of Toxoplasma Toxoplasma life cycle stages Toxoplasma gondii : Modes of transmission • Ingestion of cyst- • • • • containing meat (carnivores) Ingestion of oocysts (environmental contamination) Congenital infection Transfusion (rare) Raw goat’s milk, lambing, transplantation Percentage of Toxoplasma infection associated with type of meat consumed Country Beef (%) Pork (%) Lamb (%) Salami (%) Belgium 6 2 10 10 Denmark 27 2 8 4 Italy 12.5 3 0.5 12.5 Norway 19 3 21 3 Switz. 8 13 10 5 Adapted from Sukthana, 2006 Seropositivity rates Continents and countries Seropositivity (%) Europe Spain Austria France Norway UK Poland 28.6% 43% up to 75% 10.9% 57-93% 46.4-58.5% USA 16-40% Central and South America Costa Rica Argentina 76% 72% S.E. Asia Indonesia Thailand 58% 2.3-21.9% Symptomatology : Toxoplasma • Most infections benign • Rarely severe – hepatitis, encephalomyelitis, myocarditis • Few cases of retinochoroiditis which can progress to blindness • At risk groups (see over) • Severe clinical picture : retinochoroiditis, encephalomyelitis, hydrocephalus, microcephaly • Most infections result in blindness, severe visual impairment and/or mental retardation • Estimates 50-70 seriously affected births UK ; approx 3000 congenital cases USA Intra-uterine infections • Immunosuppression, malignancy, AIDS, organ transplantation • Neurological complications meningoencephalitis or cerebral mass lesions : cerebral toxoplasmosis • Headache, confusion, ataxia, hemiparesis, retinochoroiditis • Endogenous versus exogenous infection Toxoplasma in the immunocompromised host Cerebral toxoplasmosis : Centre for Disease Control (CDC) criteria for diagnosis • Recent onset of focal neurological abnormality consistent with intercranial disease or reduced consciousness • Evidence from brain imaging of a lesion (CT or MRI) • Positive serum antibody to T. gondii or response to treatment Diagnostic tests for Toxoplasma • Sabin-Feldman dye test (DT) • Enzyme immunoassay for T. gondii • • • • specific IgM (EIA) Immunsorbent agglutination assay (ISAGA) Enzyme immunoassay for IgG avidity Isolation and culture of parasite Direct detection by microscopy and PCR Differential Diagnosis • Immunocompetent adults (DT, IgM EIA) • Pregnant women (maternal serum DT, IgM EIA, IgG avidity; Amniotic fluid culture or PCR) • Neonates (DT, EIA, ISAGA for IgM, IgA) • Organ transplantation (DT, IgM EIA) • Immunodeficiency (serum and CSF : DT, EIA, ISAGA for IgM and IgA; PCR, culture, microscopy) • Avoid consumption of raw or undercooked meat • Litterpans should be changed daily • Wash hands after handling raw meat, litter pans & soil • Pregnant women should avoid contact with cats • Issue of prenatal screening Prevention and control Program for mass screening and prophylactic treatment of pregnant women for T. gondii Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Group IgG +ve IgM -ve No test No treat No test No treat Infection before pregnancy no risk IgG +ve IgM +ve Repeat IgG after 3 wks Treat if high or rising IgG -ve IgM -ve Treat if IgG +ve Possible infection soon after conception slight risk Treat if IgG +ve No previous infection, if seroconver. high risk Treatment : toxoplasmosis • Only accepted treatment pyrimethamine with trisulfapyrimines for 1 month • Intravenous clindamycin used to treat encephalitis in AIDS patients • In France spiramycin has been used to treat toxoplasmosis in pregnancy • Spiramycin is available in the US on a case-by-case basis Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis by county of maternal residance 45 40 35 30 25 Seroprev % 20 15 10 5 0 L W K M D D Toxoplasma gondii and Schizophrenia E. Fuller Torrey & Robert H. Yolken (2003) Emerging Infectious Diseases 9 (11) 1375-1380