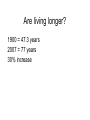* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 01-Introducing Health Psychology
Health psychology wikipedia , lookup
Occupational health psychology wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Diseases of poverty wikipedia , lookup
Sociology of health and illness wikipedia , lookup
Introducing Health Psychology What people die from is changing • 1900 - Acute Infectious diseases – Pneumonia – Tuberculosis (TB) – Diarrhea and enteritis • 2005 - Chronic diseases – Cardiovascular diseases • Heart disease • Stroke – Cancer Young people (1 - 44) most likely to die from: • Accidents (unintentional injuries) • Violent deaths – Murder (Homicide) – Suicide Ethnicity and disease • Diseases and life span vary by ethnicity. E.g. Japanese live longer that European Americans European Americans live longer that African Americans Income and Disease Poverty & low education = health problems & lower life expectancy Unrelated to ethnicity Education and disease Inverse relation between education and disease More education = less disease Are living longer? 1900 = 47.3 years 2007 = 77 years 30% increase Why has the life expectancy increased? Main factor = lower infant mortality Will health care cost you more? Costs have increased faster than inflation Why are medical costs increasing? Aging population Sophisticated medical technology Complex surgical procedures What is health? Biomedical model (Western medicine) Disease is exclusively a biological process Pathogen (disease-causing organism) = disease No pathogen = health Most useful for infectious diseases What is health? Newer (more inclusive model) Biopsychosocial model Includes: Biological, Psychological, and Sociological (social) influences. Viewpoint of health psychologists Eg. Psychosomatic illness Advantages of the Biopsychosocial model Better for current model of lifestyle diseases Adds Psychological and social aspects Views health as a positive condition Not just the absence of illness Advantages of the Biopsychosocial model Sees many diseases resulting from a combination of: Genetics Physiology Social support Personal control Stress Compliance Personality Poverty Ethnicity Cultural beliefs What is the focus of health psychology? Health enhancement Disease prevention Rehabilitation Interdisciplinary team member