* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
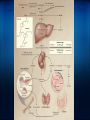
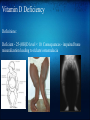
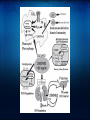
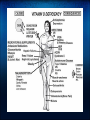
Vitamin D: Is It A Miracle Cure? Robert Coleman, M.D, F.A.C.E. Cotton-O'Neil Diabetes & Endocrinology Topeka, KS Physiology of Vitamin D Sources Sunlight 1.7-dehydrocholesterol via UVB (290-315 nm) and heat converted to Vitamin D3. UVB can also inactivate D Diet 1.Oily Fish 2.Dairy Supplements 1.Available as D3 and D2 Liver Metabolism 25 Hydroxylated in Liver by CYP2R1 Activation/Deactivation Activated in kidney by 1 alpha hydroxylase in response to 1.Elevated PTH 2.Low Calcium 3.Low Phosphate Then deactivated via 24 hydroxylase, oxidized, side chain cleaved, and excreted as calcitroic acid Basic Functions of 1,25-dihydroxy-Vitamin D Osteoblast - Activation of preosteoclast to osteoclast leading to bone resorption. Gut - Absorption of calcium via activation of VDR-RXR within lamina. Activates CaBP to bind and transport calcium across the gut surface. Kidney - decreases calcium excretion in the urine Other regulatory functions: Increased 24-hydroxylase to deactivate the D Negative feedback on parathyroid hormone production Vitamin D Deficiency Definitions: Deficient - 25-(OH)D level < 10. Consequences - impaired bone mineralization leading to rickets/ostoemalacia Vitamin D Insufficiency Insufficient - 25-(OH)D level <30. Consequences - calcium malabsorption, secondary hyperparathyroidism among multiple others... Bone Osteoporosis/Osteomalacia/Rickets Osteoporosis via calcium malabsorption and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Recent meta-analyses find low 25-D associated with increased fracture risk. Muscle Function and Falls Muscle pain and weakness. Biopsy proven atrophy of fast twitch (type II) fibers. These fibers are first recruited to avoid falling. Randomized prospective trials show vitamin D reduces fall risk by 20%. Cancer Vitamin D has antiproliferative and prodifferentiating effects on many types of cells. Small prospective trials of vitamin D in postmenopausal women found calcium+D recuced overall cancer risk by 60%. People living in higher latitudes have increased risk of Hodgkin's lymphoma, colon, pancreatic, prostate, ovarian, breast cancer compared to lower latitudes. 25-D levels below 20ng/dl associated with 30-50% increased risk of colon, prostate, and breast cancer. Immune System Vitamin D deficiency associated with increased respiratory infections. Vitamin D enhances monocyte mycobacterial killing by facilitating production of cathelicidin, an antimicrobial protein. Helper type 1 & 2 cells are vitamin D targets, causing a shift toward an anti-inflammatory profile. Vitamin D deficiency accociated with increased risk of autoimmune and infectious diseases. Diabetes/Cardiovascular Disease Vitamin D increases insulin production/secretion Observational studies associate low vitamin D with type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus Observational studies show association between low D and cardiovascular disease. Potential mechanism includes D effect on endothelium, vascular smooth muscle, and cardiomyocytes - all have D receptors. Prospective studies lacking for both of these conditions Psychiatric Vitamin D deficiency associated with increased incidence of schizophrenia and depression. May even be associated with in utero and early life levels - early brain development. Who should be tested? Although above complications are concerning, the amount of prospective data clearly showing benefit of population-based screening is still lacking. Therefore, risk based approach is recommended: Those at high risk for vitamin D deficiency for whom a prompt response to optimization of vitamin D status could be expected such as those with ... Osteoporosis, fall history, high risk of falls, malabsorption syndromes (celiac disease, radiation entertitis, bariatric surgery, etc), liver disease, use of medications known to alter vitamin D status, those with malignancy. How much to replace Multiple variables: Varied recommendations - USDA 400-600 int. units daily, National Osteoprosis Foundation 800-1000 daily, and other experts 2000+ daily. Age - Older require higher intake than younger (lower capability of skin production). Race - Needs of African Americans > Hispanic > Caucasian Individual differences beyond these Various approaches to replacement Sun exposure - risks of skin cancer, however judicious sun exposure may offer greater benefit than risk. Some experts suggest 15 minutes of arms/legs/face unprotected exposure daily, but variables including pigmentation, latitude, and time of day. Supplementation: 600,000 int. units of D2 over 2 months achieved 25-D levels over 30 ng/ml in 64% of patients 50,000 int. units of D2 weekly over 3 years achieved 25-D levels over 30ng/ml in 23/24 patients Various approaches to replacement (2) Rule of thumb: 1000 int. units of D3 daily expected to increase 25-D levels by 10ng/ml Vitamin D2 30% as effective in maintaining 25-D than D3. May need to triple doses if using D2. Suggestions for replacement in various situations Children: Breast Feeding w/o D supplementation up to 1 year: Preventative: 400 IU daily, sensible sun, 1-2000 IU D3 daily safe. Supplementation 400-1000 IU daily Deficiency: 200K IU every 3 months, 600K IU repeated in 12 wks, 12000 IU with calcium daily. Inadequate sun/supplementation/dark skin - 1yr to 18: Preventative: same as above Deficiency: 50K IU of D2 weekly x 8 weeks Replacement suggestions - Adults Inadequate sun/supplementation or age > 50: Prevention: 800-1000 IU D3 daily, 50K IU every 2-4 weeks, sensible sun. Up to 10K IU D3/day safe up for 5 months. Maintenance 50K IU D2 every 2-4 weeks Deficiency: 50K IU D2 weekly x 8 weeks, repeat until 25-D >30 ng/ml Pregnant/lactating: Prevention: 1000-2000 IU D2 daily, 50K IU D2 every 2 weeks, up to 4000 IU of D3 daily safe for 5 months. Maintenance same. Deficiency: same Replacement suggestions - Adults Malabsorption syndromes Prevention: adequate UVB, 50K IU D2 every 1-7 days, up to 10K IU D3/day safe for 5 months. Maint: 50K IU D2 weekly. Deficiency: UVB or 50K IU D2 every 1-2 days. Drugs that activate steroid and xenobiotic receptor and transplant drugs Prevention: 50K IU D2 every 2-7 days. Maint: 50K IU D2 every 1-4 weeks Deficiency: same References Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets. Michael F. Holick. J Clin Invest. 2006; 116(8):2062. Medical Progress:Vitamin D Deficiency. Michael F Holick. NEJM 2007; 357:266-281. Low Vitamin D Status: Definition, Prevalence, Consequences, and Correction. Neil Binkley. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 39 (2010) 287-301. Vitamin D: Metabolism. Sylvia Christakos. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 39 (2010) 243-253.