* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download www.hkcem.com
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
History of biological warfare wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
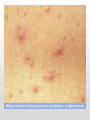
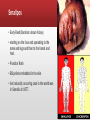
HKCEM College Tutorial Chickenpox Author Dr. Shek Kam Chuen Oct 2013 Case history ▪ F/3, come with her aunt ▪ Presented to AED for fever 38oC & vesicular rash for one days ▪ “?” cubicle ▪ nil contact, nil ILI symptom Fever with rash Very Sick People Must Take No Exercise ▪ DDX ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Varicella/viral rash Infectious mononucleosis Dengue fever Meningococcal disease Drug rash, Still’s disease Kawasaki’s syndrome: Polymorphous rash 5 Ds after fever Diagnosis ▪ 1. Smallpox ▪ 2. Herpes zoster ▪ 3. Bullous pemphigoid ▪ 4. Bullous impetigo ▪ 5. Chickenpox Chickenpox Rash ▪ Initially maculopapular, then vesicles,clear fluid ▪ Begins on face & trunk then centripetally ▪ Vesicle are round with erythematous base ▪ Crust ▪ All form of lesions are concurrently present Smallpox ▪ Early Rash(Duration: about 4 days) ▪ starting on the face and spreading to the arms and legs and then to the hands and feet. ▪ Pustular Rash ▪ BB pellets embedded in the skin ▪ last naturally occurring case in the world was in Somalia in 1977. Her aunt claimed that patient also pain on urination ▪ P/E>>Vesicular Vulval Rash>>?Genital herpes ▪ What is your action? ▪ 1. Refer to SHS service ▪ 2. Admit Paed as STD suspected (?abuse) ▪ 3. Give acyclovir cream for symptomatic relief ▪ 4. Re-assurance Most Diagnosis are clinical ▪ Laboratory Criteria (Any one of the following) ▪ Isolation of varicella zoster virus (VZV) from clinical specimens ▪ Demonstration of a ≥4x rise in antibody (Ab) titre ▪ Demonstration of viral antigen in vescular fluid or scrapings using fluorescent-Ab staining ▪ Positive PCR for VZV in clinical specimens HA Central Committee on Infectious Disease and Emergency Responses (CCIDER) Guideline on Varicella Zoster Virus Infections 22 May 2012 Chickenpox ▪ Modes of transmisson: Contact, Droplets, airborne ▪ Incubation periods: ▪ 10-21 days ▪ Can be prolonged to 28 days in immunocompromised patients and recipients of Varicella-Zoster IG Period of communicability: ▪ 2 days before onset of rash and continue until all lesions are crusted ▪ (usually within 1week from onset of rash). You noticed ▪ His aunt is pregnant, 35wks. ▪ What is your action? ▪ 1. Do nothing ▪ 2. advice chickenpox vaccination by GP as HA will not provide chickenpox vaccination ▪ 3. offer acyclovir PEP ▪ 4. enquire her chickenpox status Definition of susceptibility ▪ Individuals are considered susceptible if they DO NOT fulfill any one of the following: ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ History of chickenpox/herpes zoster History of varicella vaccination completed according to recommended schedule Positive VZV IgG serology Neonates (except preterm < 28 weeks or birth weight ≤1000g) born to immune mothers are protected by maternal antibody. Protection may be up to 6 months. Serological test is recommended in case of doubt Chickenpox Status ▪ Childhood infectious disease ▪ >95% adult are infected in childhood ▪ Ask patient’s mother ▪ In case of any doubt, pls do urgent varicella IgG test. ▪ Inform ICN to arrange an urgent test ▪ Enter the CMS that the quarantine period ▪ Advice patients not to attend antenatal clinic and must inform O&G MO when admitted for labour. ▪ Arrange FU in 96 hrs Management flowchart for susceptible pregnant women with chickenpox exposure. HKJEM 2009;01:46 Chickenpox in Pregnancy 1 ▪ Maternal risks ▪ In pre-antiviral era, mortality up to 25% ▪ Chickenpox pneumonia can be up to 10% ▪ Neonatal risks: ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ 2% of Congenital Varicellar Infection if < 20 weeks. Skin contracture, scarring, limb hypoplasia Eye, cataract 16-29% MR, microcephaly Chickenpox in Pregnancy 2 ▪ Between 20 to 36 wks ▪ No associated fetal effect ▪ Many child present with zoster in first few year. Chickenpox in Pregnancy 3 ▪ > 36 weeks ▪ Likely to infect the baby ▪ Neonatal chickenpox VZV in Pregnancy 18 Chickenpox in Pregnancy 4 ▪ Treatment acyclovir if within one days of rash and more than 20 weeks of gestation ▪ Informed consent for acyclovir ▪ VZVIG no effect if already rash develop Chickenpox status ▪ If IgG positive>> ▪ If IgG intermediate>>pending confirmation test by virus unit ▪ If IgG –ve>> ▪ What is your action? ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ 1. Quarantine 10-21days after last exposure 2. Chickenpox immunization 3. Acyclovir daily till delivery 4. VZVIg IMI VZIG ▪ Within 96hr after exposure ▪ May prevent or attenuate infection ▪ Limited data suggest that attenuation of disease might be achieved with VZIG up to 10 days after exposure. ▪ Not useful if chickenpox rash already develop ▪ Incubation period may prolong to 28 days VZIG ▪ IM VZIG is indicated and should be administered within 96 hours post-exposure for following high risk groups: ▪ Immunocompromised person ▪ Pregnant woman ▪ Neonates whose mothers have signs and symptoms of varicella around the time of delivery (i.e., 5 days before to 2 days after). ▪ Preterm infant <28 wk or birth weight ≤1000g exposed during neonatal period. ▪ Preterm infant (≥28 wk) exposed during neonatal period and whose mother do not have evidence of immunity to VZV. Other PEP to consider ▪ VZV vaccination ▪ As PEP within 5d of exposure for immunocompetent non-pregnant contacts >12 months of age ▪ Acyclovir ▪ As PEP within 10d post exposure. ▪ No clear recommendation Her aunt at follow up clinic ▪ VZV IgG was +ve, now 38 week ▪ However, she develop herpes zoster over the left chest wall. ▪ What is your action? ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Admit to isolation ward? VZIG to mother to prevent neonatal chickenpox VZIG to new born to prevent neonatal chickenpox Acyclovir ▪ Acyclovir is a FDA category B, no teratogenic effect A 32 wks pregnant triage nurse exposed to the chickenpox ▪ Contact tracing ▪ no history of chickenpox ▪ Urgent blood for IgG >> -ve ▪ Need for PEP? ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ 1. VZIG 2. Long term Acyclovir till birth 3. Immediate immunization 4. Is it a significant exposure? Significant exposure ▪ Definition of significant contact (any one): ▪ Continuous household contact, ▪ face to face contact > 5min, ▪ or conversation, ▪ Stay in the same room/cubicle for >15 min, Tang CL, et al. Hong Kong J Emerg Med. 2009;16:46-50 End THANK YOU
































![Antivirals are sometimes used. [46] [47]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001011126_1-55d72bad7d922af991bf9fcdd0a95bd9-150x150.png)
