* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IGRT in CMUH
Brachytherapy wikipedia , lookup
Radiation burn wikipedia , lookup
Center for Radiological Research wikipedia , lookup
Industrial radiography wikipedia , lookup
Radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Proton therapy wikipedia , lookup
Medical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear medicine wikipedia , lookup
Neutron capture therapy of cancer wikipedia , lookup
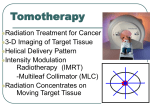
Somvilai Mayurasakorn, MD. Division of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University Machine characteristics • • • • • 6 MV accelerator 3.5 MV: MVCT No flattening filter Field Size in width: 40 cm Treatment length: 160 cm 6 MV LINAC 64 leaf MLC Pitch = Distance Traveled Per Rotation Slice Width MVCT detector array Machine characteristics • • • • • TOMO Binary multileaf collimator Optical sensors and pneumatic driven Binary 64 leaf MLC MLC leaf width: 6.25 mm (ISO) Field Size in length: 1, 2.5 and 5 cm by a set of moveable jaws 100 times faster MLC Speed MLC leaves that move at 250 cm/s to open or shut in 20 milliseconds Machine characteristics • Treatment is delivered through the full 360° • This is approximated in the planning process by 51 different beam directions • With a spacing of just over 7° • The rate of movement of the couch, relative to the thickness of the fan beam, is referred to as the pitch Allows treatment of very long volumes without field junctions Slice width Helical Tomotherapy Process • • • • • Imaging / Contouring Planning / Optimizing In-room megavoltage CT imaging Image Registration (IGRT) Treatment delivery Adaptive RT: Dose Guidance (Recalculation / Reconstruction ) Dose Modification Helical Tomotherapy • The complex integrated technologies • With multiprofessional team Physicist/dosimetrist Radiation oncologist Radiation therapist Radiographer Helical Tomotherapy • • • • Clinical use : Rationale for patient selection Treat patients who were considered likely to benefit from IGRT : to inform repositioning IMRT : complex target volume shapes, adjacent critical normal tissue structures Combined IGRT/IMRT approach University of Cambridge /Burnet et al. Clinical Oncology 2010;22:294–312 Helical Tomotherapy University of Cambridge /Burnet et al. Clinical Oncology 2010;22:294–312 Helical Tomotherapy Treatment planning • Inverse planned IMRT concepts • Dose volume constraints : typically same as conventional IMRT planning – For all target and normal tissue structures Helical Tomotherapy Treatment planning Tomotherapy Planning Parameters 1. Field Size in length : Jaw size – 5, 2.5 or 1 cm 2. Modulation factor – ratio of maximum leaf opening time to mean leaf opening time 3. Pitch Somvilai Mayurasakorn, MD. Division of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University Helical Tomotherapy Tomotherapy Planning Parameters • Smaller field widths, smaller pitches and higher modulation factors More conformal plans But increased treatment time !! Helical Tomotherapy Image acquisition and matching • MVCT fan-beam images • In-plane resolution of 0.78 mm at the bore center ; mean beam energy = 0.75 MeV • Set up slices thickness of 2, 4 or 6 mm – ‘fine’, ‘normal’ and ‘coarse’ settings • The scan length is kept as short as possible – always within the region of the PTV Helical Tomotherapy Image matching