* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Transport System - IB
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
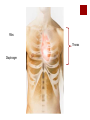
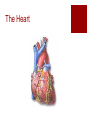
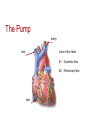
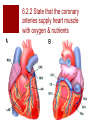
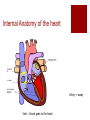
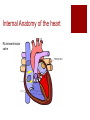
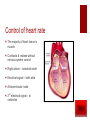
The Transport System The Heart and Circulatory System Ribs Thorax Diaphragm The Heart The Pump artery vein Jobs of the Heart #1 – Systemic flow #2 – Pulmonary flow vein 6.2.2 State that the coronary arteries supply heart muscle with oxygen & nutrients 6.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the heart. Internal Anatomy of the heart Artery = away Vein – blood goes to the heart Internal Anatomy of the heart Rt atrioventricular valve 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves. 6.2.3 left ventricle fills with blood Left ventricle contracts Closure of the atrioventricular valve to prevent backflow into the left atrium Dramatic increase in blood pressure inside the left ventricle which opens the left semilunar valve and allows blood to enter the aorta Due to the increase in pressure, blood leaves the heart through the aorta 6.2.5 Explain the relationship between the structure & function of arteries, capillaries and veins. Comparison of arteries, capillaries, and veins Artery Capillary Vein Thick walled Wall is 1 cell thick Thin walled No exchanges All exchanges No exchanges No internal valves No internal valves Have internal valves Internal pressure high Internal pressure low Internal pressure low Path of a Red Blood Cell Arteries Arterioles Capillary bed – one cell thick Venules Veins 6.2.4 Outline the control of the heartbeat in terms of myogenic muscle contraction, the role fo the pacemaker, nerves, the medulla of the brain & adrenaline. Control of heart rate The majority of heart tissue is muscle Contracts & relaxes without nervous system control Right atrium – sinoatrial node Electrical signal – both atria Atrioventricular node 2nd electrical signal – to ventricles What happens when you exercise? Increase demand for oxygen (cell respiration) Need to get rid of excess carbon dioxide Brainstem area (medulla) chemically sense the increase in CO2 Medulla signals cranial nerve (cardiac nerve) to increase heart rate SA node receives signal Changes timing Done exercising? Signal from medulla to different cranial nerve SA node receives signal Goes back to resting heart rate Other factors? Chemicals: Adrenaline Lub Dub 6.2.6 State that blood is composed of plasma, erythrocytes, leucocytes, (phagocytes and lymphocytes) and platelets. Components of blood Component Description Plasma Liquid portion of blood Erythrocytes Red blood cells (carry oxygen & carbon dioxide Leucocytes White blood cells (phagocytes and lymphocytes Platelets Cell fragments (assist in blood clotting) 6.2.7 State that the following are transported by the blood: nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, antibodies, urea, and heat. Transport by blood What is transported What it is or does Nutrients Glucose, amino acids, etc Oxygen Reactant needed for aerobis cell respiration Carbon dioxide Waste product of aerobic cell respiration Hormones Transported from gland to target cells Antibodies Protein molecules involved in immunity Urea Nitrogenous waste (filtered out of the blood by kidneys) Heat Skin arterioles (can change diameter in order to gain or lose heat