* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
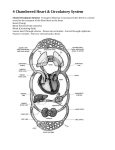
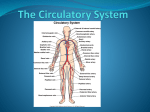
Internal Transport • Gastrovascular cavity makes circulatory system unnecessary • Open and closed circulatory systems • What are the limits an open circulatory system places on an organism? • What is the difference between an artery and a vein? • Arteries carry blood away from the heart • Veins bring blood back to the heart • Why do veins have valves and arteries do not? • Veins move blood against gravity without benefit of the heart contraction • Blood flow: – Heart arteries arterioles capillaries venules veins heart • Which chamber of the heart receives the blood? • Which chamber pumps the blood? Vertebrate Circulatory Evolution • Fish have 2 chambered heart, one beat circuit: – 1 atrium – 1 ventricle • Amphibians have 3 chambered heart: – 2 atria – 1 ventricle • Reptiles have 3 – 4 chambered heart: – Septum keeps 2 parts of ventricles separate • Mammals and birds have 4 chambered heart! The Heart • • • • Cardiac muscle Atria have thin walls Ventricles have thick and powerful walls Systole = ventricular contraction blood is pumped • Diastole = ventricular filling • Lub dub = heart sounds opening and closing of the valves – Lub = contraction of ventricles (AV closing) – Dub = blood recoiling against SL valves • Heart murmur = valve defect • CO = cardiac output ; – Volume of blood pumped/ minute • SV = stroke volume: – Amount of blood pumped by L ventricle/contraction • CO is effected by heart rate and SV • Myogenic heart can regulate its own rhythm • SA node is the pacemaker of the heart Arteries and Veins • How do differences between arteries and veins reflect their different functions? • Artery wall is very thick to absorb pulsation from heart • Veins are wider in diameter and are not as muscular • Veins have valves • Capillaries have only single layer of endothelium Blood Pressure • The force that blood exerts against vessel walls • BP is greater in arteries than veins • Pulse is measure of BP • Exact BP is measured as systolic/diastolic pressures • Constricted blood vessels have higher BP than dilated vessels • In veins heart has little effect on BP • How, then does blood move in veins? Blood Flow Velocity Blood Flow Through Capillary Beds Capillary Movement of Fluids Lymphatic System • Lymphatic system returns lost blood to circulatory system • Lymph nodes filter the lymph • Help fight infection Blood Smear Blood Clot Heart disease • • • • Atherosclerosis Strokes Blockage Bypass How can 1 heartbeat circulate blood through 2 capillary beds? What are the advantages and disadvantages of the amphibian circulatory system? • What is the change seen in reptiles that was not present in amphibians? Why do endotherms have the greatest need for a 4 chambered heart? Birds and mammals show convergent evolution of 4 chambered heart!