* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Part 2 Powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
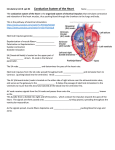
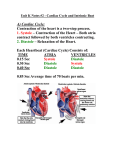
Heart pt 2: Function Cardiac Cycle • The heart goes through the cardiac cycle to contract and pump blood through the body efficiently • The cycle is deemed to start when the sinoatrial node (SA node) initiates an action potential • The SA node is the pacemaker of the heart and is influenced by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems SA node to AV node • The SA node stimulates the atria to contract, filling the ventricles • The SA node also stimulates the AV node which then stimulates the ventricles – This delay allows the ventricles to fully fill up before initiating ventricular contraction • If the SA node fails the AV node can take over but the ventricles don’t fill all the way Completion of Contraction • Once the AV node has delayed the signal for a moment it transmits it to the AV bundles, which go through the septum of the heart • At the base of the ventricles the AV bundles become the bundle branches that innervate the ventricles • Ventricles contract, closing AV valves and forcing blood out the aorta and pulmonary trunk Ventricular Pressure • When the ventricles contract, they squeeze blood at a high pressure into the major arteries • The pressure in the major arteries is approximately equivalent to the pressure in the heart – 120/80 means peak pressure of 120 when the left ventricle squeezes, 80 when it relaxes – These are also called systole and diastole Systole and Diastole • Systole is the maximum blood pressure caused by a chamber’s squeezing • Atrial systole is followed by ventricular systole • When the ventricles are refilling it is known as diastole (minimum blood pressure) • 120/80 is average healthy blood pressure • Varies somewhat by age, size, etc. Measuring Blood Pressure • The theory behind measuring blood pressure works on two principles: 1. The pressure in the major arteries is approximately equivalent to the left ventricle 2. When the external squeezing pressure on an artery is greater than its blood pressure, the blood flow stops • • When the arm cuff cuts off blood pressure entirely, this is systolic pressure When the arm cuff allows all blood to flow again, this is diastolic pressure – In between these two points, blood only squirts through at diastole but not systole which makes a distinctive sound Measuring Blood Pressure Systemic Blood Pressure Blood Volume and Pressure • The more blood is in the blood vessels, the harder the heart has to work to pump it – High blood pressure can result from excess of water (usually from eating too much salt) – Low blood pressure can result from not enough salt, blood loss, or dehydration • Excess high blood pressure (hypertension) can eventually overwork the heart Electrocardiogram • The electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is the famous “beep beep” in the hospital • Measures the electrical activity of the heart – First small wave (P wave) corresponds to SA node depolarizing – Large wave (QRS complex) corresponds to AV node and ventricles depolarizing – Second small wave (T wave) is repolarization of ventricles • If the SA node fails, the p wave disappears and the AV node becomes the pacemaker (junctional rhythm) – Time for an artificial pacemaker! EKG Breakdown EKG Readings Cardiac Output • The total volume of blood that is pumped by each ventricle per minute is the cardiac output (CO) – Fun fact: the CO of the left and right ventricles should be the same! Think about it! • Affected by stroke volume (amount of blood pumped per beat) and heart rate – These are affected by the overall health, activity, and autonomic nervous systems See you Friday! • Friday: blood vessels • Next week: Exam! – Monday: Review day – Wednesday: Exam #3 – Friday: Good Friday holiday