* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vital Signs
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
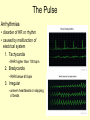
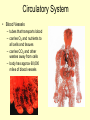
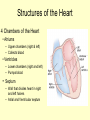
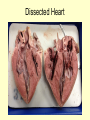
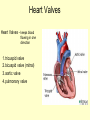
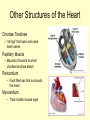
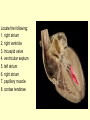
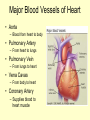
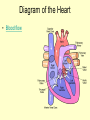
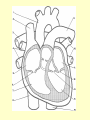
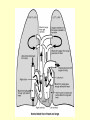
Vital Signs Vital Signs • Homeostasis – state of equilibrium • Vital Signs – body functions essential to life – assessment of • • • • pulse respiration blood pressure temperature The Pulse • Pulse: – Measures HR – Blood vessels expand & contract when heart beats – Reflects condition of CV system – Normal RHR = 60 to 100 bpm – Heart Facts Pulse Sites Location of pulse sites: • carotid artery (neck) • brachial artery (anterior elbow) • radial artery ( wrist) • femoral artery (inguinal) • popliteal (posterior knee) • dorsalis pedis (top of foot) • posterior tibial (medial ankle) The Pulse Arrhythmias • disorder of HR or rhythm • caused by malfunction of electrical system 1. Tachycardia - RHR higher than 100 bpm 2. Bradycardia - RHR below 60 bpm 3. Irregular - uneven heartbeats or skipping of beats The Pulse • Rapid but weak pulse – Shock – Dehydration – Heat exhaustion • Rapid and strong – Heat stroke – Hypertension (high blood pressure) Circulatory System • Blood Vessels – tubes that transports blood – carries O2 and nutrients to all cells and tissues – carries CO2 and other wastes away from cells – body has approx 60,000 miles of blood vessels Circulatory System Types of blood vessels – Arteries & Arterioles • carry O2 blood away from heart to all body cells and tissues – Veins & Venules • carry deoxygenated blood to the heart from body cells – Capillaries • connects arterioles and venules – Blood Vessels Human Heart Facts • Facts – – – – Size of your fist Adult female – 8 oz Adult male – 10 oz Beats approximately 100,000 times a day – Pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood a day Structures of the Heart 4 Chambers of the Heart • Atriums – Upper chambers (right & left) – Collects blood • Ventricles – Lower chambers (right and left) – Pumps blood • Septum – Wall that divides heart in right and left halves – Atrial and Ventricular septum Dissected Heart Heart Valves Heart Valves - keeps blood flowing in one direction 1.tricuspid valve 2.bicuspid valve (mitral) 3.aortic valve 4.pulmonary valve Other Structures of the Heart Chordae Tendinae – “strings” that open and close heart valves Papillary Muscle – Mounds of muscle to which chordae tendinae attach Pericardium – Fluid filled sac that surrounds the heart Myocardium – Thick middle muscle layer Locate the following: 1. right atrium 2. right ventricle 3. tricuspid valve 4. ventricular septum 5. left atrium 6. right atrium 7. papillary muscle 8. cordae tendinae Major Blood Vessels of Heart • Aorta – Blood from heart to body • Pulmonary Artery – From heart to lungs • Pulmonary Vein – From lungs to heart • Vena Cavas – From body to heart • Coronary Artery – Supplies blood to heart muscle Diagram of the Heart • Blood flow Blood Pressure Blood Pressure – pressure exerted by circulating blood against the walls of arteries • Systolic (top #) – ventricles contracting • Diastolic (bottom #) – ventricles relaxing – atriums contracting Blood Pressure Normal – 120/80 Abnormal systolic: • below 100 or above140 Abnormal diastolic: • below 65 or above 90 • Measuring Blood Pressure Blood Pressure • Hypertension – high blood pressure – indicator of cardiac problems and strokes • Hypotension – low blood pressure – could indicate shock, dehydration or internal bleeding Respiration • Respiration (breathing) – brings O2 into body while taking CO2 out of body • Single respiration – one inspiration (in) and one expiration (out) Respiration 15 years and older • 15 to 20 breaths per minute Well-trained athlete • 6 to 8 breaths per minute Abnormal Respiration in Athletes Asthma • bronchial tubes constrict • wheezing sound Bronchitis • inflammation of bronchial tubes • difficulty breathing Fx or bruised ribs • painful to breath • fx could puncture a lung Temperature Temperature • internal body temp • normal – 98.6º F • abnormal – illness – heat exhaustion – heat stroke Emergency Care • Key to dealing with emergencies: – Establish and implement Emergency Action Plan (EAP) – Careful observation of athlete – Accurate measurement of vital signs • CPR • 911 Assessments Assessment • evaluation of a patient’s physical condition • look, listen, touch (palpate) Visual observations include: • deformities • discoloration • inability to function • incoherent Types of Assessments Primary Survey • examination to determine life threatening injuries - Performed 1st - If conscious, move to secondary survey Secondary Survey • head to toe physical exam –pinpoint injury or condition –still could be emergency situation Primary Survey Primary Survey • A = airway • Breathing? • Not, open airway • Protect cervical spine • B = breathing • C = circulation • Assess pulse • No pulse? CPR and 911 Secondary Survey • History – consciousness, MOI, symptoms • Observation – Looking for swelling, discoloration, deformities • Palpation – Touch and feel injured area • Special Tests – ROM, strength testing, specific tests SOAP Notes Subjective • History and subjective info • What the athlete tells you • MOI, pain, symptoms Objective • What you observe • Measurements and tests Assessment • Likely diagnosis Plan • Treatment plan • RICE, NSAIDS, rehab, ect….