* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Got Blood?
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
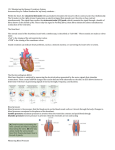
Heart Beat & Blood Flow PUMP IT Heart Video Pulmonary Artery Lungs Pulmonary Vein Right Ventricle Left Atrium Right AV Valve Left AV valve Right Atrium Left Ventricle Vena Cavae Aorta Body Use Page 320 of your text book to label your heart diagram located in your workbook… The Heart… muscular organ, size of your fist surrounded by a fluid-filled membrane: pericardium which reduces friction 1. Circulation PULMONARY CIRCULATION deoxygenated blood pumped from the right side of the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries blood picks up oxygen (oxygenated) and travels back to the left side of the heart via the pulmonary veins. the pulmonary arteries are the only group of arteries that carry deoxygenated blood the pulmonary veins are the only group of veins that carry oxygenated blood SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION left side of heart pumps blood to the entire body via the aorta (largest artery) from the aorta blood is diverted to: a) coronary arteries - serve heart tissue b) upper body arteries c) lower body arteries d) Hepatic/Portal system (digestive) two large veins: the superior and inferior vena cava return blood to the right side of the heart Heart Beat • The stimulus that triggers a heart beat is an electrical signal from a bundle of nerve tissue in the right wall of the atrium. •This bundle is called the Sinoatrial node (SA node) or the pacemaker (because it sets the pace for our heart beat). Heart Beat • The electrical signal from the SA node causes muscle cells to contract and relax rhythmically. • The signal leaves the SA node and spreads out over the left and right atria and makes them contract simultaneously. Heart Beat • As the atria contract, the signal reaches the atrioventricular (AV) node. • The AV node sends the impulse first through the bundle of His in the septum and then to the Purkinje fibers along the outside of the left and right ventricles. Heart Beat • The signal traveling along the Purkinje fibers causes a simultaneous contraction of the left and right ventricles. • The contractions and relaxations continue rhythmically 70-90 times a minute. Heart Animation Heart Beat Sounds • Our heart beat is a long and loud “lub” followed by a “dub” sound. • The “lub” sound is made by the sudden closing of the AV valves and the opening of the semi lunar valves. This happens right after atria contract. • The “dub” sound is made by the closing of the semilunar valves and the opening of the AV valves. This happens right after the ventricles contract. • See and hear an actual heart beat here! If a valve does not close completely, then a murmur is detected This murmur is the sound of blood rushing backwards through a valve, and creates a gurgling sound Reading a heart beat - Electrocardiogram • The voltage change in the heart can be measured by by electrocardiogram (ECG). • The heart emits different voltages as muscles contract and relax, which are observed on a graph. • You will need to know how to read one! Reading a heart beat - Electrocardiogram External Regulation of Heart Rate The S.A node is regulated externally by the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves which conduct electrical impulses from the medulla oblongata of the brain Stress Relaxed Activates sympathetic nerves Activates parasympathetic nerves Signals to S.A Node to increase H.R Signals to S.A Node to decrease H.R BENEFIT OF CARDIOVASCULAR EXERCISE Why do doctors say we need cardiovascular exercise at least 3 times a week? The answer lays in our hearts! Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume Cardiac output = amount of blood pumped by heart (ml/min) Cardiac output is an indicator of the level of oxygen being delivered to our body and the amount of work the body’s muscles can perform. Two factors affect cardiac output: heart rate and stroke volume. Cardiac Output = heart rate x stroke volume Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume Heart rate = number of heartbeats per minute. Stroke volume = amount of blood forced out of the heart with each heartbeat. Stroke volume is affected by how much blood returns to our heart and how strong the ventricles contract to push the blood out. Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume The average cardiac output is 4900mL a minute (remember we have about 5000mL of blood in our body). Because cardiac output is heart rate x stroke volume, the larger an individual’s stroke volume is, the smaller the heart rate has to be. (Don’t take my word for it…..try a calculation yourself and see!) Ex: Calculating Cardiac Output Tom’s heart has a stroke volume of 50 mL and a heartrate of 100 beats per minute. Calculate his cardiac output. Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume Regular cardiovascular exercise enlarges the ventricular chambers, increases the elasticity of the ventricles, and strengthens the ventricle walls. With stronger ventricles, the heart has more power to push out more blood on each contraction (increase stroke volume). Because of this, a low heart rate is an indicator of high cardiovascular fitness, because as stroke volume increase, heart rate should decrease! Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume Knowing what you do about cardiac output, who is the most physically fit person: Individual Heart rate (beats/min) Stroke Vol. (ml/beat) Cardiac OP (ml/min) A 70 70 4900 B 98 50 4900 C 35 140 4900 Blood Pressure Sphygmomanometer – measures blood pressure – gauge that measures the pressure that blood exerts during ventricular contraction (systolic blood pressure) ~ 120 mm Hg – also measures pressure during ventricular relaxing (diastolic blood pressure) ~ 80 mm Hg Why would internal hemorrhaging (bleeding) cause diastolic blood pressure to drop? Blood pressure changes as the heart beats: When left ventricle pumps out the blood Pressure rises to a MAXIMUM SYSTOLIC blood pressure When left ventricle is filling with blood Pressure falls to a MINIMUM DIASTOLIC blood pressure Blood pressure is described by two numbers: – Example of a healthy individual: 120 means: 80 – systolic blood pressure is 120 mm Hg – diastolic blood pressure is 80 mm Hg healthier values are usually lower, although it is possible to have blood pressure that is too low Measuring Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Two factors affecting blood pressure 1. Cardiac output – cardiac output, blood pressure 2. Arteriolar Resistance – diameter causes a blood pressure – diameter causes a blood pressure How to measure your blood pressure: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gmic 13mvsgo Hypertension Caused by increased resistance to blood flow which results in increased blood pressure High blood pressure can lead to weakened blood vessels Major cause is diet, but may also be hereditary Response to Exercise NS stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline (epinephrine) – This stimulates the release of RBC’s – Increased RBCs = increased O2 transport – Adrenaline also increases heart rate and breathing which increases O2 transfer rate through body Regulation of Blood Pressure Nervous system responses cause either increased outflow of blood from arteries (sympathetic NS) or decrease heart rate and stroke volume (parasympathetic NS) Why is high blood pressure a problem? The heart must work harder to pump blood which can cause it to enlarge and weaken There is a increased force on the blood vessels, which can cause them to weaken and increase the risk of stroke or heart attacks Increase chance of blood clot formation Thermoregulation Let’s Try This - We know that stroke volume increases with cardiovascular fitness. The higher the stroke volume, the quicker it takes your heart rate to return to rest after exercise. We are going to do a little test with the blood pressure lab (open your book to page 278 to see what we are going to do). Copy these charts Condition Blood Pressure (mmHg) Heart Rate (beats/minute) Cardiac Output (mL/min) Stroke Volume (mL/beat) Control (regular) Caffeine Physical Activity Nicotine Resting Heart Rate (beats/minute) 4500 (female) 5500 (male) To Do: Textbook Questions p. 335 #2, 5, 7, 10