* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
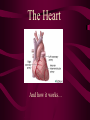
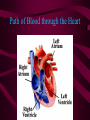
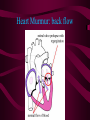
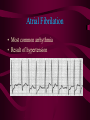
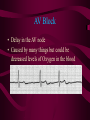
The Heart And how it works… Heart Beats Heat Beats Step 1: Enter Atrium Right Side - Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through 2 large veins - Superior vena cava: upper half of the body - Inferior vena cava: below the diaphragm Left Side - Oxygenated blood (from the lungs) enters the left atrium through the pulmonary vein - Comes from the lungs Heart Beats Step 2: Contract Atrium • Blood flows from the atrium into the ventricle • The atrioventricular (AV) valve allows for a one-directional flow • The AV valve closes once the ventricle is full - LUB Heart Beats Step 3: Contract Ventricle • Right ventricle contracts • Blood flows through the semilunar valve into the left pulmonary artery – DUB • Blood flows towards the lungs • Left ventricle contracts • Blood flows through the semilunar valve into the right pulmonary artery • Blood flows out towards the body Path of Blood through the Heart Heart Sounds • Two normal heart sounds – Lub: closure of the AV valves (beginning of ventricular contraction - systole) – Dub: closure of the semilunar valves (end of ventricular systole – diastole) • Other sounds – Heart murmur: turbulent blood flow Heart Murmur: back flow Overview: Blood Flow • • • • • • • • • • Blood in body Into heart via vena cava (vein) Right atrium Right Ventricle Left pulmonary artery (deoxygenated) Lungs (becomes oxygenated) Pulmonary vein Left atrium Left ventricle Arteries (oxygenated towards body tissue) Connecting the Heart to the Lungs & the Body Setting the Heart’s Tempo • Heart muscles contract without being stimulated by external nerves (myogenic muscles) • Heart muscle does not all contract at the same rhythm when separated • Heart rhythm is set by the sinoatrial (SA) node – specialized nerve cells • Nerve impulses travel to a second node AV node which sends the message toward the ventricles Normal Sinus Rhythm • P wave followed by a ventricular response Atrial Fibrilation • Most common arrhythmia • Result of hypertension AV Block • Delay in the AV node • Caused by many things but could be decreased levels of Oxygen in the blood Ventricular Fibrilation • The ventricles are not contracting as a unit • There is no clear cardiac output • Commonly known as a Heart Attack Flatline: • Asystole: no cardiac electrical activity (no contractions or blood flow) – cannot be treated with defibrillation