* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart PPT
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
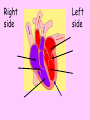
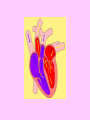
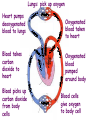
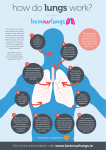
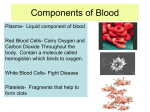
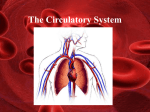
Your heart is a muscle about the size of your fist. It is constantly beating, on average about 1 beat every second. Open and close your fist, once every second. Do you get tired quickly? Lesson Outcomes • What are the four parts of the heart called? • Why does the heart need valves in it? • Where does each side of the heart pump blood? • Why is the left side of the heart thicker than the right side? • Why does the heart need it’s own blood supply if it is full of blood all day? • What would happen if that blood supply was blocked by fat and blood clots? Right side Left side Video Circulation Lesson Outcomes • What are the four parts of the heart called? • Why does the heart need valves in it? • Where does each side of the heart pump blood? • Why is the left side of the heart thicker than the right side? • Why does the heart need it’s own blood supply if it is full of blood all day? • What would happen if that blood supply was blocked by fat and blood clots? You are a red blood cell. Your job is to carry oxygen and carbon dioxide around the body. It’s like being a taxi driver. Tell your story: When do you pick up oxygen? When does the blood pick up carbon dioxide? What can you see on your journey? Lungs: pick up oxygen Heart pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs Blood takes carbon dioxide to heart Blood picks up carbon dioxide from body cells Oxygenated blood taken to heart Oxygenated blood pumped around body Blood cells give oxygen to body cell