* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hales_ith15e_powerpoint_lectures_chapter15
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
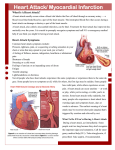
Chapter 15 Preventing Major Disease Elizabeth Lytle, MPH, BSN, RN Los Altos School District Topics Of Focus For This Chapter Cardiometabolic Health Heart Attack Diabetes Stroke Hypertension Cancer Cholesterol Lifestyle Cardiometabolic Health Approaching the connection between risk factors, symptoms and diseases Cardio Heart Blood vessels Biochemical processes involved in Metabolic body functioning Control Weight and Waist Circumference Weight Waist Size Overweight teens have high risk of diabetes and heart disease in future Obese men have dramatically higher risk of dying Subcutaneous fat and visceral fat are dangerous Avoid waists of: 40 inches for men 30 inches for women Potbelly with normal weight Physical Activity Decreases Risk All Men Women Least fit are at greater risk of death More rigorous exercise = greater protection and longevity 30 minutes/day of moderate activity lessens risk Fitness more important than overweight or obesity in cardiometabolic risk Smoking Is The Most Significant Risk Factor Causes over 250,000 deaths per year Causes peripheral arterial disease Active and passive smoking Accelerate artery clogging Increase risk of developing coronary heart disease Control Blood Sugar To Decrease Risk Check your blood sugar to see if you are at risk Blood Sugar Healthy Under 100 Prediabetes 100-125 Diabetes Over 125 High Blood Pressure Increases Work Of Heart Systolic Over Diastolic Systolic = pressure during heart contraction Diastolic = pressure during heart relaxation Effects Heart muscle gets strong and stiff Accelerated development of plaque Action Control with diet, exercise and possibly medication Control Cholesterol and Triglycerides Total Cholesterol less than 200 AND: Desired Numbers HDL over 40 mg/dL LDL less than 100 Low Triglycerides Effects Best indicator of plaque in arteries Action Cut back on high-fat foods Exercise more Cholesterol In Food Risk Factors You Cannot Control Family history Race and ethnicity Age Metabolic Syndrome Is An Epidemic High blood pressure General Effects High insulin levels Abnormal cholesterol levels Abdominal obesity Waist measurement (40 in, 35 in) Triglycerides 150 or more Diagnosis = HDL less than 40 mg/dL 3 or more Blood Pressure of 130/85 or higher Blood Sugar 110 mg/dL or higher Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors Overweight or obese Age 60 or older Physically inactive or exercise less than 3 times/week Parent or sibling with diabetes Having baby over 9 pounds or gestational diabetes Blood pressure 140/90 or higher More Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors African American, Alaskan Native, American Indian, Asian American, Hispanic/Latino or Pacific Islander HDL below 35 or Triglycerides above 250 Impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance test History of cardiovascular disease Conditions associated with insulin resistance Fasting blood sugar 101-125 = Prediabetes Diabetes Diabetes Shortens Life Expectancy Women 8.4 years Men 7.8 years Normal Response To Eating • Blood glucose increases • Triggers pancreas Insulin Released Blood Sugar Decreases • Glucose moved into cells • Energy needs met • Excess urinated out Normal Blood Sugar Uncontrolled Diabetes • Blood glucose increases • Triggers pancreas NO Insulin Released Blood Sugar INCREASES • Glucose remains in blood • Energy needs unmet • Ketones produced Ketoacidosis Effects Of Uncontrolled Diabetes Damaged blood vessels Blindness Amputation Kidney failure Heart attack and stroke Types Of Diabetes Type 1 Immune system attacks insulin producing cells in pancreas Develops often in young people, but can appear in adults Type 2 Pancreas does not make enough insulin or body is resistant to its insulin Diabetes during pregnancy Gestational At risk for diabetes later in life Decrease Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes Exercise 30 minutes 5 days/week If overweight, lose weight Diet rich in complex carbohydrates and fiber Diet low in sodium and fat Eat fruits and vegetables Take medication recommended by physician Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetes Increased thirst and urination Flu-like symptoms Weight loss or gain Blurred vision Slow-healing sores or frequent infections Nerve damage Red, swollen, tender gums Detecting Diabetes Anyone over age 45 should be screened for diabetes every 3 years Random blood sugar test Fasting blood glucose test Glucose challenge test Controlling Diabetes Decreases Risk A A1c less than 7 percent B Blood Pressure 115/75 C Cholesterol LDL less than 160 Hypertension Risks Effects Family history Obesity when young Race Death especially for those with diabetes, kidney disease and obesity Lifestyle changes Decrease sodium to 1.5 grams/day Treatment Increase potassium to 4.7 grams/day Exercise Medication Numerous Effects Of High Blood Pressure Understanding Blood Pressure Numbers Type of BP Systolic Diastolic Prehypertension 120-139 80-89 Mild 140-159 90-99 160 + 100 Moderate-Severe Low Less than 90 Hypertension is any one of the values above or a combination of values Lipoproteins: Cholesterol And Triglycerides Risk None Borderline High High Total Cholesterol Triglycerides Less than 200 Less than 150 200-239 150-199 240 + 200 + Lowering Lipoproteins Decreases Risks Include nuts, soy, oats, plant sterols Diet Weight management Physical activity Statins Medication Needed for about half of those with high lipoprotein levels Few Meet Criteria For Ideal Heart Health Never smoked or quit more than 1 year ago BMI less than 25 150 + moderate or 75 + vigorous minutes of exercise/week 4 + components of healthful diet Total cholesterol less than 200 Blood pressure below 120/80 Fasting blood sugar below 100 Heart Anatomy Heart Anatomy Overview Of Blood Flow Through Heart • Blood from body moves into right atrium Right Ventricle Contracts • Blood moves into right ventricle Right Atrium Contracts • Blood moves to lungs and then pulmonary vein Left Atrium Contracts Left Ventricle Contracts • Blood moves into left ventricle • Blood moves through aorta to brain and body How Blood Flows Through Body Understanding The Heart Myocardium Heart muscle 2-layer membrane surrounding heart Pericardium Lubricant between layers allows heart muscle to move freely Systole Contraction of heart Period between contractions when Diastole heart fills with blood Smallest blood vessels in body Capillaries Deliver oxygen via the blood and take up waste Cardiovascular Risk Factors Education Low education level at higher risk Chronic = plaque & high blood pressure Stress Episodic = creates unstable plaque Acute = trigger heart attack Depression and heart disease are linked Depression Depressed women more likely to have heart attack Anger Angry men at much higher risk Cardiovascular Risk Factors Continued C-Reactive protein signals inflammation CRP Increased CRP increases risk Homocysteine May influence atherosclerosis Sudden increases in blood pressure Illegal Drugs Left ventricular contraction Irregular heart rhythms Bacterial Infection Streptococcus and chlamydia Tips For Women To Avoid Heart Disease Abstain from smoking BMI less than 25 Exercise 150 + moderate or 75 + vigorous minutes each week week Eat 4 + components of healthful Non-HDL cholesterol less than 230 Blood pressure below 120/80 Fasting blood sugar below 100 Heart Disease Symptoms Different In Women Pay attention to these early signs of disease Pain in back, between shoulders Sick to stomach Feeling scared or nervous Pain in belly above belly button New or worse headaches More Symptoms In Women Tiredness, even after getting enough sleep Trouble breathing Trouble sleeping Ache in chest Chest feeling ‘heavy’ or ‘tight’ Burning feeling in chest Pain or tightness in chest that spreads Aspirin Is Recommended For Some Aspirin may reduce heart attack risk, but may also increase bleeding Aspirin decreases clotting risk, but increases bleeding risk Must consider risk of gastrointestinal bleeding when choosing to take aspirin Men 45 to 79 to reduce risk of heart attack Women 55-70 to reduce risk of stroke Heart Health Conditions Coronary Artery Disease Arteriosclerosis – degeneration and hardening of arterial walls Atherosclerosis – arteriosclerosis plus plaque deposits on walls of arteries Heart Conditions Angina Pectoris Due to brief lack of oxygen to heart Severe, suffocating chest pain Heart Attack / Myocardial Infarction When portion of heart does not receive oxygen and begins to die Cardiac Arrest Heart stops beating Symptoms Of A Heart Attack 30 minutes or more of chest pain that is not relieved with rest Chest pain radiating to shoulder, arm, neck, back or jaw Anxiety Sweating or cold, clammy skin Nausea and vomiting Shortness of breath Dizziness, fainting or loss of consciousness If experiencing heart attack symptoms, take 325 mg of aspirin and seek immediate medical attention Cardiac Arrest CPR Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation Combining rescue breaths with chest compressions creates circulation AED Automatic External Defibrillator Portable device available in most public places can restart a heart that has a lethal rhythm Action Control with diet, exercise and possibly medication Cerebrovascular Accident Explained ‘Stroke’ occurs when blood supply to Defined brain in blocked Types Ischemic – blockage of flow by cerebral thrombus or cerebral embolism Hemorrhagic – blood vessels rupture Transient Ischemic Attack TIA Little strokes with minimal damage Doubles risk of heart attack Cerebrovascular Accident Risk Women, especially during hormonal changes Men across the lifespan Heart disease and diabetes Risk Obesity and diet high in fat and sodium Factors Age – risk doubles every decade after 55 Race – high in blacks and Hispanics High red blood cell count High blood pressure Effects Of Stroke On Brain Cancer Uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells Defined Abnormal cells divide and create tumors Forms Countless and with different genetics Action Infiltration – Crowds out healthy cells Metastasis – spreads through blood or lymph to other parts of body How Cancer Metastasizes Cancer Risk Affects all social, economic and educational levels Obesity Black Americans have higher mortality Heredity – such as BRCA gene Infectious Agents – Viruses Common Cancers Carcinoma Arises in epithelium Sarcoma Starts in supporting or connective tissues of body Leukemia Begins in blood-forming tissues Lymphoma Forms in lymph cells Cancer Warning Signs Change in bowel or bladder habits Sore that doesn’t heal Unusual bleeding or discharge Thickening or lump in breast, testis or elsewhere Indigestion or difficulty swallowing Obvious change in wart or mole Nagging cough or hoarseness Skin Cancer Basal Cell Cells in top level of skin Squamous Cells in epidermis Cell Actinic Not cancer, but 40% become Keratoses squamous cell carcinoma Malignant Most lethal form of skin cancer Melanoma Malignant Melanoma Is Most Dangerous Fair skin, light eyes or fair hair Tendency to burn instead of tan Risk Childhood sunburn or intermittent, Factors intense sun exposure Personal or family history Large number of moles or atypical moles Warning Signs Of Melanoma A Asymmetry B Border Irregularity C Color D Diameter Every Woman Is At Risk For Breast Cancer Increased Age Age at first childbirth Breast biopsies First period before 12 Many occupations Hormone Therapy Obesity Sedentary lifestyle 2 or more drinks per day White or African American Family History Risk Increases With Age Detecting Breast Cancer Recommended annually for Mammography women over 40 Best detection tool Breast SelfExam MRI Monthly at home Every 3 years by trained practitioner Recommended if strong family history or Hodgkin’s Disease Cervical and Ovarian Cancer Risks for cervical cancer Sexual activity before 16 Multiple sexual partners Secondhand smoke Genital herpes HPV Risks for ovarian cancer Family history of ovarian cancer Infertility Personal history of breast cancer Obesity Low levels of transferase Testicular Cancer Rates Are Increasing Men at 18-35 Risk Undescended testicle Chronic marijuana use Perform monthly testicular exam Detection One testicle larger than other Dull ache in groin or abdomen Treatment Surgery to remove testicle Radiation, chemotherapy Colon And Colorectal Cancer Age over 50 History of rectal cancer or polyps Smoking Risk Factors Alcohol consumption Prolonged high consumption of red and processed meats High-fat or low-fiber diet Ulcerative colitis Detection Colonoscopy at 50 Prostate Cancer Increasing age Family history Risk Factors Exposure to cadmium High number of sexual partners Frequent STIs High-fat diet Detection Prostate-specific antigen test Treatment Hormones and low-fat diet Chemotherapy and radiation Epilepsy Defined Diagnosis Sudden attacks of violent muscle contractions and unconsciousness Electroencephalogram (EEG) Recurring attacks Treatment Anticonvulsant drugs Asthma Risk Factors African American Inner-city Secondhand smoke exposure Wheezing Symptoms Shortness of breath Tightness of chest Coughing Steps To Control Asthma 1. Get away from trigger 2. Assess severity of attack 3. Use quick reliever 4. Suppress inflammation 5. Know when to call for help Ulcers Defined Open sores in lining of stomach or duodenum Cause Excessive acidic digestive juices Symptom Burning pain in upper abdomen Antibiotics (if H. pylori) Avoiding aspirin Treatment Eating small, frequent meals Taking antacids Not smoking or drinking and avoiding caffeine