* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ventricular Septal Defect
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
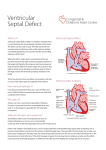
Cardiovascular Common Cardiovascular Disorders in Children • Congenital Heart Defects • Congestive Heart Failure • Acquired Heart Disease Review of Normal Circulation How to Understand Congenital Defects • Think of blood as: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Red highly O2 saturated Blue unsaturated Purple medium O2 saturated (mixed) Lavender- reduced volume of medium O2 saturated (mixed) ▫ Pink reduced volume of O2 saturated ▫ Light Blue Reduced volume of unsaturated Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation Fetal Shunts • foramen ovale shunts mixed blood from right atrium to left atrium (hole in the atrial septum) • ductus arteriosus accessory (extra) artery, shunts mixed blood away from lungs to descending aorta • ductus venosus accessory (extra) vein, carries oxygenated blood from umbilical vein into lower venous system How does the fetus receive sufficient oxygen from the maternal blood supply? • Fetal hemoglobin carries 20-30% more oxygen than maternal hemoglobin • Fetal hemoglobin concentration is 50% greater than mother’s • Fetal heart rate 120-160bpm (increases cardiac output) Newborn What happens to the shunts after birth? Transition from intrauterine to extra- uterine life • Cord is clamped • Neonate initiates respirations • O2 levels rise • Greater pressure in the left atrium • Decreased pressure in the right atrium • Immediate closure of foramen ovale Transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life • After O2 circulates systemically, over 24 hours, the pressure in the left ventricle will become greater than the pulmonary artery and closes the ductus arterosis • The absent flow of blood through the umbilicus gradually closes the ductus venosus over 12 hr to 2 weeks Cardiac Defects Either • Ductal closure failure (no structural abnormality) • Structural abnormality Cardiac Catheterization • Primary method to measure extent of cardiac disease in children • Shows type and severity of the CHD • Insert tiny catheter through an artery in arm, leg or neck into the heart • Take blood samples and measure pressure, measure o2 saturation, and as an intervention Cardiac Catheterization-Post Op • Monitor closely (cardiac monitor, continuous pulse ox) VS q 15 • Assess dressing at insertion site for infection, hematoma • Dressing must remain dry for 1st 48-72 hrs • Palpate a pulse distal to the dressing to assure blood flow • Keep extremity straight for 48 hrs after procedure • If Congenital Defect is suspected or confirmed, • Intervention is Important to Prevent CHF Congestive Heart Failure Congestive Heart Failure • Heart doesn’t pump blood well enough • Can not provide adequate cardiac output due to impaired myocardial contractility • Causes in children: ▫ Defects ▫ Acquired heart disease ▫ Infections Congestive Heart Failure • Most common cause in children is congenital heart defects • Increased volume load or increased pressure in heart • Excess volume and pressure builds up in lungs leading to labored breathing • Builds up in rest of body leading to edema Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms • • • • • • 1st sign is tachycardia tire easily rapid, labored breathing decreased urine output increased sweating, pallor peripheral edema CHF Diagnosis and Treatment • CXR- shows enlargement • Echocardiogram- dilated heart vessels, hypertrophy, increase in heart size • Treatment is aimed at reducing volume overload, improve contractility • May require surgery Congestive Heart Failure Medical Management • Digoxin • Lasix • Potassium Digoxin • Strengthen the heart muscle, enables it to pump more efficiently • Digoxin toxicity: vomiting, bradycardia • Need HR, EKG, drug levels • Check apical pulse first, don’t give if HR < 100 bmp in infants and < 70 bpm in children • Parents need teaching to assess apical pulse Lasix • Helps the kidneys remove excess fluid from the body • Potassium wasting • Must administer potassium supplements Congenital Heart Defects Congenital Heart Disease • 35 different types • Common to have multiple defects • Range from mild to life threatening and fatal • Genetic and environmental causes Blood Flows From High to Low Pressure Lower Pressure Higher pressure Types of Congenital Heart Defects Acyanotic Defects • Purple blood (mixed and too much blood sent to lungs but not enough to cause cyanosis) • Septal defects ▫ Ventra Septal Defect (VSD) ▫ Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) • Patent Ductus Arteriosis(PDA) Cyanotic Defects ▫ Light blue blood (too little sent to lungs) ▫ Pulmonic Stenosis ▫ Pink blood (too little O2 sent to body) ▫ Coarctation of the aorta • Light blue & purple blood (poor perfusion to lungs and body) ▫ Tetrology of Fallot Acyanotic Defects Septal Defects- increased pulmonary blood flow • Left to right shunting (acyanotic defect) ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Sends already sat blood back to lungs Increased cardiac workload Excessive pulmonary blood flow Right ventricular strain, dilation, hypertrophy Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) • Most common CHD • Hole in ventral septum • High Pressure in LV forces blood back to RV • Results in increased pulmonary blood flow • Higher than normal artery pressure Symptoms • Size of the defect varies • Loud harsh systolic heart murmur • Right ventricular hypertrophy • O2 level of RV higher than normal on catheterization Treatment • Small defects ▫ Medical Management (Digoxin, Lasix, K+) ▫ Prophylactic antibiotics to prevent infective endocarditis ▫ Close spontaneously • Large defect ▫ May develop CHF, poor feeding, failure to thrive ▫ Suture or patch hole closed (open heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass) ▫ Pulmonary artery banding to reduce blood flow to lungs if not stable for surgery Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) • Hole in atrial septum • Pressure in LA is greater than RA (blood flows left to right) • Oxygen rich blood leaks back to RA to RV and is then pumped back to lungs • Results in right ventricular hypertrophy Symptoms • Harsh systolic murmur • Second heart sound is split: “fixed splitting” ** diagnostic of ASD • Pulmonary valve closes later than aortic valve- risk for pulmonary edema • Fatigue and dyspnea on exertion • Poor feeding, failure to thrive • Large defect may cause CHF Treatment ▫ Medical Management (Digoxin, Lasix, K+) ▫ Prophylactic antibiotics to prevent infective endocarditis ▫ Not expected to close on own ▫ Suture or patch hole closed (open heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass) ▫ Pulmonary artery banding to reduce blood flow to lungs if not stable for surgery Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) • Failure of ductus arteriosus to close completely at • Blood from the aorta flows into the pulmonary arteries to be reoxygenated in the lungs, returns to LA and LV • More common in preemies H to L Symptoms • Preterm infants born with CHF and respiratory distress • Fullterm infants may be asymptomatic with a continuous “machinery” type murmur • Tire easily, growth retardation (shorter, weigh less, less muscle mass) • Prone to frequent respiratory tract infections Treatment • Administration of Indomethacin (prostaglandin inhibitor) to stimulates ductus to constrict • Surgical management ductus is divided and ligated • Usually performed in first year of life to decrease risk of bacterial endocarditis Summary of Acyanotic Defects • VSD & ASD ▫ Rt hypertrophy ▫ Pulm edema ▫ Pulm htn • PDA ▫ Pulm edema ▫ Pulm htn Cyanotic Defects Cynaotic Defects- decreased pulmonary blood flow Right to left shunting- sends unsaturated blood into O2 saturated blood and circulates to body • Pulmonic Stenosis • Coarctation of the Aorta • Tetralogy of Fallot Pulmonary Stenosis • Valve Stenosis • Obstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract • Decreased pulmonary blood flow Symptoms • Systolic ejection murmur with a palpable thrill • Right ventricular hypertrophy • Mild to moderate cyanosis from reduced pulmonary blood flow • High ventricular pressure may cause blood to back up into right atrium and force foramen ovale to open to allow blood to flow from right to left atrium • Can lead to right ventricular failure, CHF Treatment ▫ Medical Management (Digoxin, Lasix, K+) ▫ Oxygen ▫ Prophylactic antibiotics to prevent infective endocarditis ▫ Surgical Management Pulmonary balloon valvuloplasty via cardiac cath If unsuccessful valvotomy Coarctation of Aorta • Constriction of the aorta at or near the insertion site of the ductus arteriosus Higher pressure • Reduces cardiac output (impedes blood flow from heart to body=pink blood) • Aortic pressure is high proximal to the constriction and low distal to the constriction-Risk for CVA Pink Blood Symptoms • Systolic murmur • BP is about 20 mm/Hg higher in arms than in lower extremities • Upper extremity hypertension • Diminished pulses in lower extremities • Poor lower body perfusion • Lower extremity cyanosis Treatment ▫ Medical Management (Digoxin, Lasix, K+) ▫ Oxygen ▫ Administration of PGE1 (prostaglandin) infusions ▫ Maintain ductal patency and improves perfusion to lower extremities- although will cause increased pulmonary flow ▫ Surgical repair within first 2 years Tetralogy of Fallot Blood is light blue • • • • • Consists of 4 Defects VSD RV hypertrophy Blood is purple Pulmonic Stenosis Overriding aorta Symptoms • cyanotic at birth when PDA closes • increased respiratory rate, may lose consciousness • “tet spells” or hypercyanotic episodes often preceded by crying, feeding or stooling • tire easily especially with exertion, difficulty feeding and gaining weight • become increasingly cyanotic over the first few months • symptoms of chronic hypoxemia Treatment Treatment of tet spells • Knee-chest position then apply O2 • Do not leave alonecyanosis can cause LOC, death Symptoms Medical management • Symptomatic newborn: PGE1 infusion to maintain ductal patency • Digoxin, Lasix, K+ • Older infants: close monitoring for worsening of hypoxia • Surgical management: done at 3-12 months of age, in stages • primary open-heart repair: close VSD, open pulmonary valve, remove obstructing muscle Caring for the Child with a Congenital Heart Defect • Taking infant home before corrective surgery • Provide parents with information about care • Review steps for follow-up care, emergency management (s/s respiratory distress, CPR) • Key: promote normalcy within the limits of the child’s condition Caring for the Child with a Congenital Heart Defect • Preoperative:undergoing corrective surgery • Explain procedures to parents and child, assure understanding • Encourage child and parents to express fears • Prepare child for surgery and post-op, show models of equipment (chest tube) Caring for the Child with a Congenital Heart Defect Postoperative: • Monitor cardiac output • Support respiratory function • Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance • Promote comfort (IV morphine, sedatives) • Promote healing and recovery Acquired Heart Diseae HTN Endocarditis Rheumatic Fever Kawasaki Disease Hypertension • Primary HTN ▫ Caused by increased body mass ▫ Genetics • Secondary HTN ▫ Cause is from an underlying condition such as kidney disease or heart defects Hypertension • No set systolic and diastolic number for diagnosis • Need to compare to child’s age, gender and height • If 3 different readings are above the 95th percentile for that child then diagnosis is confirmed Hypertension • Managed by eliminating the primary cause if possible ▫ Exercise, life style modification • • • • ACE inhibitors ARBs Beta-Blockers Ca Channel Blockers Infective Endocarditis • Inflammation of the lining of the valves and arteries • Caused by bacterial and fungal infections in the blood stream that infects an already existing injured endocardium • Children at risk: cardiac defects, severe valve disorders Infective Endocarditis • Symptoms: ▫ Fever, fatigue, headache, N/V, new or changed murmur, CHF, dyspnea • Treatment: ▫ Antibiotics IV for 2-8 weeks, surgery to replace valves, treatment of CHF Rheumatic Fever • Acute RF is leading cause of acquired heart disease (but has decreased in US b/c abx) • Inflammatory autoimmune condition • Seen in children age 5-15 • Usually follows untreated strep A infection (pharyngitis) • Causes scarring of the mitral valves Symptoms • • • • • Tachycardia Polyarthritis Chorea Erythema marginatum (nonpuritic) Subcutaneous nodules • Carditis Treatment • Treat current strep infection • Treat other symptoms • Streptococcal prophylaxis for 5 years ▫ Penicillin IM every month or ▫ Penicillin by mouth twice daily Kawasaki Disease • Acquired heart disease in children under age 5 • Occurs due to antibody vascular injury post infection • Boys>girls • Asian decent • Multisystem vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels) • 3 stages of illness • Affects the coronary arteries Kawasaki Disease first stage day 1-14 • Prolonged fever • Bilateral, nonpurulent conjunctivitis • Changes in mouth (erythema, fissures, crusting of lips, strawberry tongue) • Induration of hands and feet • Erythema of palms and soles • Erythemous rash • Enlarged cervical lymph nodes Kawasaki Disease second stage day 15-25 • Fever and most of the previous symptoms resolve • Extreme irritability develops • Anorexia • Lip cracking and fissuring • Desquamation of fingers and toes • Arthritis • Vascular changes in myocardium and coronary arteries if untreated Kawasaki Disease Third phase- day 26-40 • Lasts until all symptoms disappear Management • Prevent or reduce coronary artery damage • Gamma-globulin IV started in phase 1 • High dose aspirin therapy at same time (80100mg/kg/day once daily) started in phase 2 • Continued through weeks 6-8 of disease Practice Questions! • The indicated area on the diagram showed higher than anticipated oxygen level on cardiac catheterization. The nurse concludes that is diagnostic for which CHD? (Select All that Apply) • 1. PDA • 2. VSA • 3. Coartation of Aorta • 4 ASD • 5. Tetrology of Fallot A parent of a toddler with Kawaski’s disease tells the nurse “I just don’t know what to do with my child. He’s never acted like this before.” The nurses best reply is: 1. 2. 3. 4. Don’t worry. This type of behavior is typical for a toddler Irritability is part of Kawasaki’s disease. Please don’t be embarrassed Perhaps your child would benefit from stricter limits You seem to be in need of a referral to our Child Guidance Center When assessing a child for signs and symptoms of rheumatic fever, which symptoms should the nurse anticipate? 1. 2. 3. 4. Tachycardia and joint pain Bradycardia and swollen joints Loss of coordination and pruritic rash Poor weigh gain and fever • The nurse assessing a newborn and auscultates a split S2. The nurse should further assess for: 1. Cyanosis 2. Crackles 3. Hypoxemia 4. Blood pressure differences in extremities Which nursing intervention is most effective in preventing rheumatic fever in children? 1. 2. 3. 4. Refer children with sore throats for a throat culture Include an ECG in the child’s yearly physical examination Assess the child for a change in the quality of the pulse Assess the child’s blood pressure A newborn with patent ductus arteriousus is scheduled to receive indomethacin. The nurse administers this medication to: 1. 2. 3. 4. Open the ductus arteriosus Close the ductus arteriosus Enlarge the ductus arteriosus Maintain the size of the ductus arteriosus Which congenital heart defect necessitates that the nurse take upper and lower extremity blood pressure readings? 1. Coarctation of the aorta 2. Tetralogy of Fallot 3. Ventricular septal defect 4. Patent ductus arteriosus An infant with ventricular septal defect develops congestive heart failure and is placed on digoxin therapy twice a day. The infant vomits the morning dose of digoxin. The most appropriate nursing intervention is to: 1. 2. 3. 4. Notify the pediatrician as soon as possible Take the infant’s pulse for 1 minute and repeat the dose of digoxin Skip the dose and give twice the amount at the next dose Repeat the dose and chart that the infant vomited the first dose The parents of a newborn with small ventricular septal defect ask why their baby is being sent home instead of undergoing immediate open heart surgery. The nurse’s best response is: 1. 2. 3. 4. Your baby’s condition is too serious for immediate open heart surgery Ventricular septal defects are not repaired until the infant is older Your baby has a small defect, and it is likely to close spontaneously Your baby must be fully immunized before surgery An infant with tetralogy of Fallot becomes hypoxic following a prolonged bout of crying. The nurse’s first action should be to: 1. Administer oxygen 2. Administer morphine 3. Place the infant in the knee-chest position 4. Comfort the infant