* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart - 山东大学医学院人体解剖学教研室
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
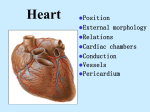
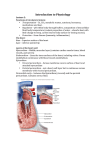
The Heart 山东大学医学院 解剖教研室 李振华 Position Lies within the pericardium in middle mediastinum Behind the body of sternum and coastal cartilages 2 to 6 In front of thoracic vertebrae 5 to 8 A third of it lies to the right of median plan and 2/3 to the left External characteristics-a hollow muscular organ, pyramidal in shape , somewhat larger than a closed fist; consists of four chanbers (right and left atria, right and left ventricles) Cardiac apex is formed by left ventricle and is directed downwards and forwards to the left. It lies at the level of the fifth left intercostal space, 1~2cm medial to the left midclavicular line (9cm from the midline) Cardiac base is formed by the left atrium and to a small extent by the right atrium. It faces backward, upward and to the right Two surface Sternocostal surface is formed mainly by the right atrium and right ventricle, and a lesser portion of its left is formed by the left auricle and ventricle. It is directed forwards and upwards Diaphragmatic surface is formed the ventricles- chiefly the left ventricle, directed backwards and downwards, and rest upon the central tendon of the diaphragm Three borders Right border-vertical, is formed entirely by right atrium Left border-round, is mainly formed by the left ventricle and partly by the left auricle Inferior border- horizontal, is formed by the right ventricle and cardiac apex Four grooves Coronary sulcus 冠状沟(circular sulcus) which marks the division between atria and ventricles, contains the trunks of the coronary vessels and completely encircles the heart Interatrial sulcus 房间沟-separates the two atria and is hidden by pulmonary trunk and aorta in front Interventricular grooves 室间沟- anterior and posterior, mark the division between ventricles (which separates the RV from the LV), the two grooves extend from the base of the ventricular potion to a notch called: the cardiac apical incisure 心尖切迹 Atrioventricular crux 房室交点-a junction of the posterior interventricular groove and coronary sulcus Chambers of the heart Right atrium 右心房 (RA) Three inlets Orifice of superior vena cava 上腔静脉口 -returns blood to the heart from the upper half of the body Orifice of inferior vena cava 下腔静脉口 -returns blood to the heart from the lower half of the body Orifice of coronar sinus 冠状窦口 -returns blood to the heart from the cardiac muscle One outle -right atrioventricular orifice 右房室口 Crista terminalis界嵴 -vertical ridge thatjfrom superior vena cave to inferior vena cave Sulcus terminalis 界沟 -groove on exterior of heart that corresponds to crista terminalis Two parts-separated externally by sulcus terminalis and internally by the crista terminalis Atrium proper 固有心房 In front of the ridge Pectinate muscles in wall Right auricle 右心耳-a small conical muscular pouch, projects to the left from the root of superior vena cava, pectinate muscles in wall Sinus venarum cavarum 腔静脉窦 Lies posterior to the ridge Smooth walls Fossa ovalis 卵圆窝-an oval depression, a remnant of the fetal foramen ovale, on the lower part of interatrial septum, the most common location of atrial septal defects (ASD) Limbus fossae ovalis 卵圆窝缘 – prominent margin of fossa ovalis Torus aortious 主动脉隆凸 Right ventricle (RV) 右心室 Receives deoxygenated blood from right atrium through right atrioventricular orifice One inlet-right artrioventricular orifice 右房室口 One outlet-orifice of pulmonary trunk 肺动脉口 Two parts-divided by the supraventricular crest 室上嵴, a muscular ridge between right atrioventricular orifice and orifice of pulmonary trunk Inflow tract-rough walls Trabeculae carneae肉柱 -irregularly arranged bundles of myocardium Septomarginal trabecula 隔缘肉柱-extends from interventricular septum to base of anterior papillary muscle, contains right bundle branch Papillary muscles乳头肌- conical-shaped , anterior, posterior and septal Out flow tract Conus arteriosus 动脉圆锥 cone-shaped, smooth area leading upward to orifice of pulmonary trunk Pumps blood through pulmonary orifice to pulmonary trunk Left atrium (LA) 左心房 Left auricle左心耳-projecting to the right, pectinate muscles in wall Four inlets-four orifices of pulmonary veins 肺静脉口open through the posterior wall One outlet-left atrioventricular orifice左房室口, blood leaves through left atrioventricular orifice to left ventricle Left ventricle (LV) 左心室 Has wall three times thicker than that of right ventricle One inlet-left atrioventricular orifice 左房室口 One outlet-aortic orifice 主动脉口 Two parts-divided by anterior cusps of mitral valve Inflow tract-rough walls Outflow tract – aortic vestibule 主动脉前庭, smooth area leading to aortic orifice Valves Tricuspid valve 三尖瓣 Guards right atrioventricular orifice Three triangular cusps: anterior, posterior and septal, the base of cusps are attached to fibrous ring surrounding the atrioventricular orifice Chordae tendineae 腱索-fine, white, connective tissue cords, attach margin of cusps to papillary muscles 乳头肌 Mitral valve 二尖瓣 Guards left atrioventricular orifice Two triangular cusps-anterior and posterior with commissural cusps between them (posteromedial and anterolateral commissures) Similar structures to those of right Similar functions for right and left atriventricular valves Open during diastole to allow blood to enter ventricles from atria Closed during systole to prevent regurgitation of blood into atria Valve of pulmonary trunk 肺动脉瓣 Guards the orifice of pulmonary trunk Has three semilunar cusps – each with free border that has central nodules of semilunar valve 半月瓣小结 Aorti vavle 主动脉瓣 Guards the aortic orifice Three semilunar cusps (right, left and post) Three aortic sinuses – bulges in aortic wall at level of valve that correspond to cusps Right-contains opening of right coronary artery Left-contains opening of left coronary artery Posterior-no opening Similar functions for pulmonary and aortic valves Opening during systole, with cusps pressed toward wall of vessel as blood is forced upward Closed during diastole Ventricular pressure drops in diastole Floating together of valve cusps, with free borders meeting, thus closing the valve Structure of the heart Walls of heart Endocardium心内膜-inner coat of the heart wall, and continuous with the valve flaps Myocardium 心肌 Arranged spirally Attached to fibrous rings surrouding the four orifices of heart Epicardium 心外膜-serous membrane (visceral pericardium) Interatrial septum 房间隔 Located between right and left atria Contains fossa ovalis and limbus Interventricular septum 室间隔 Located between right and left ventricles Has upper membranous part Has thick lower muscular part Fibrous skeleton 纤维骨骼 Fibrous rings that surround the atrioventricular, pulmonary, and aortic orifices Left and right fibrous trigons Conduction system of heart心传导系 Consists of specialized myocardial cells Sinuatrial node 窦房结 (SA node) Called the pacemaker cell (P cell) Located at the junction of right atrium and superior vena cava, upper part of the sulcus terminalis, under the epicardium Atrioventricular node 房室结 (AV node) Located in the lower part of interatrial septum just above the orifice of coronary sinus, under the endocardium Lower part related to membranous part of interventricular septum Atrioventricular bundle 房室束 (AV bundle) Passes forward through right fibrous trigon to reach inferior border of membranous part Divides into right and left bundle branches at upper border of muscular part of interventricular septum Right and left bundle branches 左、右束支 Right bundle branch-passes down on right side of interventricular septum to reach the septomarginal trabecular and into the base of anterior papillary muscle. Here it becomes continuous with the fibers of Purkinje fibres Left bundle branch-passes down on left side of interventricular septum beneath the endocardium. It usually divides into two branches, which eventually become continuous with the Purkinje fibers Purkinje fibers 普肯野氏纤维 -continuous with myocardium Arterial supply Left coronary artery 左冠状动脉 Arises from left aortic sinus Runs between pulmonary trunk and left auricle into coronary sulcus Branches Anterior interventricular branch 前室间支 -travels downward in anterior interventricular groove around inferior margin of heart to posterior interventricular groove Circumflex branch 旋支-travels to left in coronary sulcus to posterior aspect Distribution-supplies left atrium and ventricle, lesser portion of anterior wall of right ventricle, and anterior 2/3 of interventricular septum Right coronary artery 右冠状动脉 Arises from the right aortic sinus Runs forward between right auricle and pulmonary trunk into coronary sulcus Branches Right marginal branch 右缘支 -travels along inferior bord Posteror interventricular branch 后室间支-travels downward in posterior interventricular groove, it anastomosises near the apex with the anteriorinterventricular branch of the left coronary artery Distribution: supplies right atrium and ventricle, posterior 1/3 of interventricular septum, posterior wall of left ventricle, the sinuatrial node and atrioventricular node Venous drainage Coronary sinus 冠状窦 Located in posterior part of coronary sinus Carries most of venous blood from myocardium to right atrium Tributaries Great cardiac vein 心大静脉 Middle cardiac vein 心中静脉 Small cardiac vein 心小静脉 Anterior cardiac veins 心前静脉-3~4 small vessels, drain into right atrium Smallest cardiac veins 心最小静脉-drain into all chambers, mainly atria Pericardium 心包 Fibrous pericardium 纤维心包 Attached to central tendon of diaphragm inferiorly Blends with outer coat of great vessels superiorly Serous pericardium 浆膜心包 Visceral pericardium (epicardium) Parietal pericardium Pericardial cavity 心包腔 Potential space between visceral and parietal pericardium Contains film of pericardium fluid Pericardium sinus Transverse sinus of pericardium 心包横窦-posterior to ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk, anterior to superior vena cava and left atrium. Oblique sinus of pericardium 心包斜窦-cul-de-sac , posterior to heart, bounded by pulmonary veins on either side Surface markings of heart Right border-corresponds to a line running from the upper border of right third costal cartilage ±1.2cm from the margin of sternum, downwards to sixth sternocostal joint Apex-in the fifth left intercostal space 7~9cm from the midline Left border-represented by a line running from apex upwards and medially to a point on lower border of left second costal cartilage ±1.2cm from sternal margin Lower border-represented by a line joint the lower end of right border to apex Dissection of the heart