* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular Unit Day 2
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
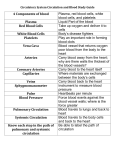
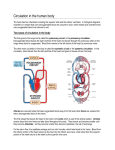
Cardiovascular Unit (Day 2) Bell Ringer: Read Pages 180-181 in your health book. Define any ten(10) bold words. Save these to be turned in with your test. Circulation Circulation is the movement of the blood through the heart and around the body. Steps to Circulation: #1-Vena Cava- These two veins are the largest in the body; they carry deoxygenated blood (blood without oxygen) to the right atrium of the heart. Steps to Circulation: #2- Right Atrium-The upper right chamber of the heart squeezes deoxygenated blood through the tricuspid valve filling the right ventricle. Steps to Circulation: #3- Tricuspid ValveA "flap" between the right atrium and the right ventricle that allows blood to flow in one direction only. Steps to Circulation: #4- Right VentricleThe lower right chamber of the heart contracts and sends the blood through the pulmonary artery. Steps to Circulation: #5- Pulmonary Valve-A "flap" between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery that allows blood to flow in one direction only. Steps to Circulation: #5A- The pulmonary arteries carry blood to the lungs where the blood loses carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen when you breathe. Steps to Circulation: #5B- The pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood back to the heart into the left atrium of the heart. Pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins are considered your pulmonary vessels. Steps to Circulation: #6- Left Atrium- The upper left chamber of the heart contracts and sends oxygenated blood through the mitral valve filling the left ventricle. Steps to Circulation: #7- Mitral Valve- A "flap" between the left atrium and the left ventricle that allows blood to flow in one direction only. Steps to Circulation: #8- Left VentricleThe lower left chamber of the heart pumps the oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve into the aorta. Steps to Circulation: #9- Aortic Valve- A "flap" between the left ventricle and aorta that allows blood to flow in one direction only. Steps to Circulation: #10- Aorta- The largest artery in the body branches off into numerous smaller arteries that carry oxygenated blood to the rest of the body Steps to Circulation: The body takes the oxygen out of the blood and uses it in your body's cells. The cells say thanks by using the oxygen, making carbon dioxide and other stuff it needs to get rid of, and dumping the carbon dioxide and wastes back into the blood to be carried away. It all happens in less than a minute (about 60 seconds to pump blood to every cell in your body) How Much Air Do We Need? About 21% of the air we breathe in is oxygen. We use about ¼ of that, therefore about 15% is breathed out for rescue breathing which is plenty of oxygen for the victim. Composition of the Earth's Atmosphere http://education.jlab.or g/glossary/abund_atmo s.html Circulation Video Clip The End!!