* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The RESPIRATORY System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
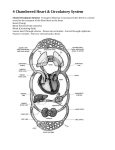
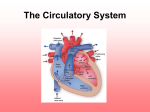
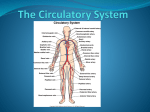
The CIRCULATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Medical Terminology • • • • • • Hemo- blood rrhea- flow or discharge Arterio- artery Thrombo– clot Brady– slow -rrhagia – excessive flow or discharge • Cardio- heart • RBC – red blood cell • WBC – white blood cell • • • • • • Angio- vessel -emia - blood condition Tachy- fast BP – blood pressure P- pulse CBC – complete blood count • CPR- cardiopulmonary resuscitation • EKG/ECG electrocardiogram vocabulary arrhythmia: An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm, such as beating too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregularly circulation: Movement in a circle or circuit, especially the movement of blood through bodily vessels as a result of the heart's pumping action. murmur: An abnormal sound, usually emanating from the heart, that sometimes indicates a diseased condition. palpitation: Irregular, rapid beating or pulsation of the heart. varicose veins: :An enlarged tortuous blood vessel that occurs chiefly in the superficial veins and their tributaries in the lower extremities. Also known as varicosity. Functions of the Circulatory System • Transports nutrients and waste. – Arteries pick up nutrients and deliver the nutrients to each body cell. – Veins carry away waste products and excess fluid of each body cell. Functions of the Circulatory System • Transports heat. – Regulates heat by distributing heat generated by muscles. • Transports oxygen to body cells and carbon dioxide away from body cells. – Arteries carry oxygen to cells. – Veins take carbon dioxide away from cells. Functions of the Circulatory System • Transports hormones through the blood stream. • Transports antibodies. – help the body fight infection. Structures of the Circulatory System Heart 1. Hollow organ 2. Pumps blood throughout the body 3. Three layers: a. pericardium b. myocardium c. endocardium 4. Four chambers Top = Atria/um Bottom = Ventricles 5. Four valves (valves prevent backflow!) 6. Arteries = AWAY from heart 7. Veins = BACK to heart The 4 Chambers of the Heart Right Atrium Left Atrium Receives unoxygenated blood from veins; pumps to right ventricle. Receives oxygenated blood from lungs; pumps to left ventricle. Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Receives blood from right atrium and Pumps blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) Pumps blood through the aorta to the body (Systemic Circulation) Valves of the Heart • Atrioventricular Valve (AV Valve) between the Atrium and the ventricle, also known as the tricuspid and mitral valves. • Semi-Lunar Valve between ventricle and artery leaving the heart, also known as the pulmonary and aortic valves. Blood flow through the Heart • Superior & Inferior Vena Cava • Right Atrium • Tricuspid Valve • Right Ventricle • Pulmonary Semilunar Valve • Pulmonary Arteries • • • • Lungs Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve • Left Ventricle • Aortic Semilunar Valve • Aorta Blood Vessels • Closed system for flow of blood • Types of Blood Vessels: – A. Arteries (smooth muscle), b. Arterioles, c. Capillaries (smallest), d. Venules, and e. Veins (valves) Vein Artery Valve Arterioles Venules Capillarybed Blood 1. Provides vital transportation for the body 2. Four components – Red blood cells (erythrocytes) Bind to hemoglobin – White blood cells (leukocytes) Immune system – Platelets (thrombocytes) Clotting elements – Plasma (liquid) Blood • Provides vital transportation for the body • Four components – Red blood cells (erythrocytes) – White blood cells (leukocytes) – Platelets (thrombocytes) – Plasma Types of Blood Cells Diseases and Disorders Circulatory System Anemia • Blood disorder where capacity of the blood to transport oxygen is decreased • Usually red blood cell count is diminished • Causes: – Internal bleeding, mineral deficiencies, decreased RBC production, increase in RBC destruction by spleen • Symptoms: – Fatigue, chest pain, skin pallor, increased heart rate, difficulty breathing Heart Attack (myocardial infarction) • Coronary artery or a branch of the coronary artery is blocked • Symptoms: – Chest pain – Crushing pressure behind the breastbone and chest pain radiating to the neck, jaw, abdomen, shoulder or left arm – Nausea – Vomiting – Difficulty breathing – Anxiety or fear What is a Heart Attack? High Blood Pressure (hypertension) • Can contribute to coronary artery disease, strokes, kidney failure, and sudden rupture of the aorta • Sustained systolic blood pressure of over 140 or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of over 90 is considered hypertension • Usually there are no symptoms other than a mild headache Atherosclerosis • Build-up of fatty deposits on the inner walls of arteries • Restricts the flow of blood • Fats and other particles combine to form plaque • Calcium can be deposited by plaque and cause the area to harden Careers • • • • • Emergency Medical Technician Surgical Technician Cardiologist Phlebotomist Electrocardiogram (ECG) Technician Emergency Medical Technician The EMT-Intermediate (EMT-2 and EMT-3) has more advanced training that allows the administration of intravenous fluids, the use of manual defibrillators to give lifesaving shocks to a stopped heart, and the application of advanced airway techniques and equipment to assist patients experiencing respiratory emergencies. • Training ranges from 6-12 months • Salary ranges from less than • 30,000/yr Surgical Technician • Before surgery - help prepare the operating room by setting up surgical instruments and equipment, sterile drapes, and sterile solutions. During surgery technologists pass instruments and other sterile supplies to surgeons and surgeon assistants • Training ranges from 6-12 months • Salary ranges from • $40,000/ year Cardiologist • Cardiology is the study of cardiovascular illness, the care of all things related to the heart. It is a specialization amongst physicians. Cardiology also includes arteries and it used to diagnose and treat conditions like blockages. Cardiologists should not be confused with cardiac surgeons. • Training is usually 10-12 years • Salary is more than $100,000/year Phlebotomist • A phlebotomist is someone who is trained to collect blood sample in a clinical environment. They usually work under the supervision of the Medical Laboratory Scientist. After the phlebotomist collects the blood, they process and analyze the specimen with sophisticated laboratory equipment. • Training is about 6 months • Salary is usually less than $30,000/yr Electrocardiogram (ECG) Technician Perform a noninvasive procedure using ultrasound instrumentation to record vascular information such as vascular blood flow, blood pressure, changes in limb volume, oxygen saturation, cerebral circulation, peripheral circulation, and abdominal circulation. Many of these tests are performed during or immediately after surgery. • Training is about 2 years • Salary ranges from $40,000/Yr