* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardio Practical What to know
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
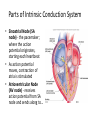
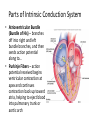
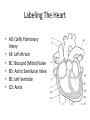
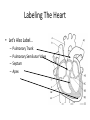
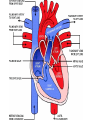
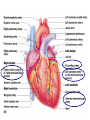
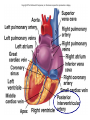
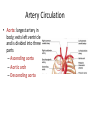
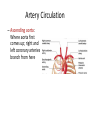
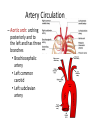
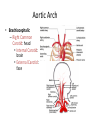
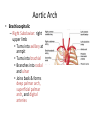
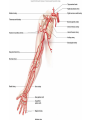
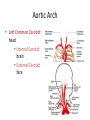
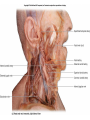
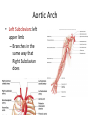
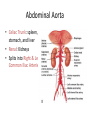
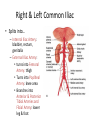
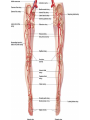
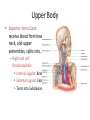
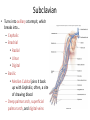
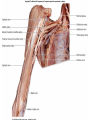
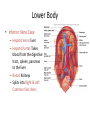
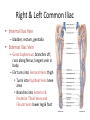
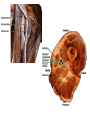
Arteries & Veins To Know For Practical Parts of Intrinsic Conduction System • Sinoatrial Node (SA node) - the pacemaker; where the action potential originates, starting each heartbeat • As action potential moves, contraction of atria is stimulated • Atrioventricular Node (AV node) - receives action potential from SA node and sends along to… Parts of Intrinsic Conduction System • Atrioventricular Bundle (Bundle of His) – branches off into right and left bundle branches, and then sends action potential along to… • Purkinje Fibers – action potential received begins ventricular contraction at apex and continues contraction back up toward atria, helping to eject blood into pulmonary trunk or aortic arch Labeling The Heart • AD: (Left) Pulmonary Artery • AE: Left Atrium • BC: Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve • BD: Aortic Semilunar Valve • BE: Left Ventricle • CD: Aorta Labeling The Heart • Let’s Also Label… – – – – Pulmonary Trunk Pulmonary Semilunar Valve Septum Apex Artery Circulation • Aorta: largest artery in body; exits left ventricle and is divided into three parts – Ascending aorta – Aortic arch – Descending aorta Artery Circulation – Ascending aorta: Where aorta first comes up; right and left coronary arteries branch from here Artery Circulation – Aortic arch: arching posteriorly and to the left and has three branches • Brachiocephalic artery • Left common carotid • Left subclavian artery Aortic Arch • Brachiocephalic – Right Common Carotid: head • Internal Carotid: brain • External Carotid: face Aortic Arch • Brachiocephalic – Right Subclavian: right upper limb • Turns into axillary at armpit • Turns into brachial • Branches into radial and ulnar • Joins back & forms deep palmar arch, superficial palmar arch, and digital arteries Aortic Arch • Left Common Carotid: head • Internal Carotid: brain • External Carotid: face Aortic Arch • Left Subclavian: left upper limb – Branches in the same way that Right Subclavian does Aorta • Descending Aorta – Thoracic Aorta: portion in thorax, above diaphragm. – Abdominal Aorta: below diaphragm; ends as two common iliac arteries Abdominal Aorta • Celiac Trunk: spleen, stomach, and liver • Renal: Kidneys • Splits into Right & Left Common Iliac Arteries Right & Left Common Iliac • Splits into… – Internal Iliac Artery: bladder, rectum, genitalia – External Iliac Artery: • turns into Femoral Artery: thigh • Turns into Popliteal Artery: knee area • Branches into Anterior & Posterior Tibial Arteries and Fibial Artery: lower leg & foot Vein Circulation • Three Major Sections emptying back into right atrium… – Coronary Sinus: Great, Anterior, Small, and Middle Cardiac Veins – Superior Vena Cava – Inferior Vena Cava Upper Body • Superior Vena Cava: receive blood from head, neck, and upper extremities; splits into… – Right and Left Brachiocephalic • Internal Jugular: Brain • External Jugular: Face • Turns into Subclavian… Subclavian • Turns into axillary at armpit, which breaks into… – Cephalic – Brachial • Radial • Ulnar • Digital – Basilic • Median Cubital joins it back up with Cephalic; often, a site of drawing blood – Deep palmar arch, superficial palmar arch, and digital veins Lower Body • Inferior Vena Cava – Hepatic Veins: liver – Hepatic Portal: Takes blood from the digestive tract, spleen, pancreas to the liver – Renal: Kidneys – Splits into Right & Left Common Iliac Veins Right & Left Common Iliac • Internal Iliac Vein – bladder, rectum, genitalia • External Iliac Vein – Great Saphenous: branches off, runs along femur, longest vein in body – EIV turns into Femoral Vein: thigh • Turns into Popliteal Vein: knee area • Branches into Anterior & Posterior Tibial Veins and Fibular Vein: lower leg & foot