* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparison of Failure Rates for External and Implantable
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
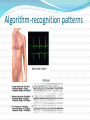
By Sam Annor (EE5811-Biomedical Instrumentation-Fall 2007). •Background •Defibrillation process •Defibrillator types •AED usage-pictorial •AED usage-video •Algorithm- how VF is detected •What does it mean algorithm mean? •Results and analysis -failure •ICD usage •ICD failure analysis •Safety/risk analysis •Conclusion •Acknowledgement to Collaborators •References It is estimated that Cardiovascular diseases account for the majority of death in the US with a total toll of about 11 million people per annum 1 Estes III, Mark. “Automatic External Defibrillators in the Public Domain – Am I Ready to Use One?” Circulation 112 (2005): e349–e351. •Ventricular Fibrillation(VF) • When a ventricular arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) becomes very fast and irregular, it's called ventricular fibrillation • Ventricular • Tachycardia(VT) is a tachycardia, or fast heart rhythm that originates in one of the ventricles of the heart. • The process used to curtail Ventricular Fibrillation(VF) and Ventricular Tachycardia(VT) •Unless treatment is given in 5 to 10 minutes, ventricular fibrillation causes death. •Devices Used in the process- Defibrillators •Two Types•Automatic External Defibrillators(AEDs) -in vitro • •Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators(ICDs) – in vivo have electronic analyzer circuitry that monitors the cardiac rhythm and alerts when a defibrillation shock is needed. AED in use Video of AED use The algorithm for recognizing VF and committing to shock delivery is as follows: (1) The AED will begin to charge if it detects at least two "positive intervals" within a 9.6 sec period. A positive interval is defined as six or more deflections that are at least 0. 150 mV (1.5 mm trough-topeak) in amplitude with a maximum slope of 3.2 mV/sec (termed VF counts) occurring in a 2.4 sec period (rate at least 150/min). (2) The AED will discharge if it detects a third positive interval within 7.2 sec of the start of capacitor charging. Thus it takes a minimum of 4.8sec (2 x 2.4) to begin charging; it requires a minimum of 7.2 sec (3 x 2.4) to commit to a shock after being presented with VF. Algorithm-recognition patterns Smaller cardiac mass in Children will cause their VF to differ from Adult. Children have faster supra VT than adult Results AED failed to properly diagnose VT hence with an average sensitivity of 56% However for VF the sensitivity was 96% on the average Used when ventricular fibrillation and tachycardia are frequent and continuous defibrillation are needed. •A 36-year-old man with an ATLAS+ DR V- 243 (St. Jude Medical, Inc., St. Paul, MN, USA) dual chamber implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) received a shock while cycling, but was otherwise asymptomatic •Medtronic leads are designed for use with an ICD as part of a cardiac system. Leads are intended for delivering therapies and/or sensing in the atrium and/or ventricle of the heart •Doesn’t everyone know how to be safe? • Several attempts are done to ensure safety like FDA regulation, various compliance- annual trainings, increased litigation, etc. •The fact remains safety education is hard to sell, hard to pay attention to and hard to remember. •Why? • -reluctance to learn • -resistance to change •Federally, FDA is charge with the mandate of ensuring the medical devices are SAFE. However the FDA relies on the manufacturers to provide with data on malfunction of the device. • If your are the manufacturer- Will you always report the needed data? •Tom O’Dea Ph. D., P. E. C.C.E –Healthcare Engineering •Prof. Jim Holte 1. Estes III, Mark. “Automatic External Defibrillators in the Public Domain – Am I Ready to Use One?” Circulation 112 (2005): e349–e351. 2. “Defibrillation.” Wikipedia. 1 Dec. 2007 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Defibrillator>. 3. KR Stults, DD Brown and RE Kerber. “Efficacy of an automated external defibrillator in the management of out-ofhospital cardiac arrest: validation of the diagnostic algorithm and initial clinical experience in a rural environment” Circulation 73 (1986): 701-709. 4. Frank Cecchin, Dawn B. Jorgenson, Charles I. Berul, James C. Perry, A. Andrew Zimmerman, Brian W. Duncan, Flavian M. Lupinetti, David Snyder, Thomas D. Lyster, Geoffrey L. Rosenthal, Brett Cross and Dianne L. Atkins “Is Arrhythmia Detection by Automatic External Defibrillator Accurate for Children? : Sensitivity and Specificity of an Automatic External Defibrillator Algorithm in 696 Pediatric Arrhythmias” Circulation 103 (2001): 2483-2488. Based on my presentation why was VT showing lower Sensitivity readings compared to VF in children under 13 years old?