* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Conduction
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
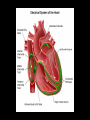
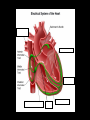
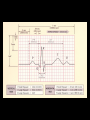
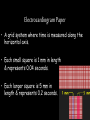
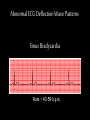
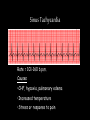
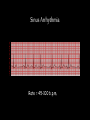
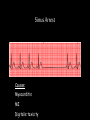
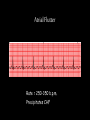
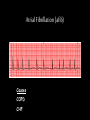
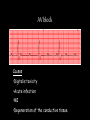
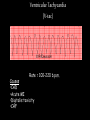
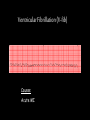
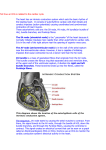
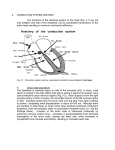
Cardiac Conduction Physiology of Cardiac Conduction • The excitatory & electrical conduction system of the heart is responsible for the contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle. • The sinoatrial node (SA node) is the pacemaker where the electrical impulse is generated. Cardiac conduction pathway 1. SA node fires to the AV node through gap jxn’s 2. AV node delays 0.1 s for atrial diastole 3. AV node fires to the AV bundle (HIS) 4. AV bundle depolarizes through right & left bundle branches 5. Bundle branches carry impulses through Purkinje fibers to the ventricular myocardium for ventricular systole Total time of conduction = 0.22 s Nodal Firing Rates • • • • Sa node = 75 b.p.m. AV node = 50 b.p.m. AV bundle = 30 b.p.m. Purkinje fibers = 30 b.p.m. What would happen if the SA node could not conduct an impulse to the AV node? Heart block (no gap jxn’s found between atria & ventricles) How to Read an Electrocardiogram Paper • A grid system where time is measured along the horizontal axis. • Each small square is 1 mm in length & represents 0.04 seconds. • Each larger square is 5 mm in length & represents 0.2 seconds. ECG Voltage • Is measured along the vertical axis. • 10 mm is equal to 1mV. Heart rate can be calculated from the EKG strip • When the rhythm is regular, the heart rate is 300 divided by the number of large squares between the QRS complexes. • For example, if there are 4 large squares between regular QRS complexes, the heart rate is 75 (300/4=75). Heart rate can be calculated from the EKG strip • Can be used with an irregular rhythm to estimate the rate. Count the number of R waves in a 6 second strip and multiply by 10. • For example, if there are 7 R waves in a 6 second strip, the heart rate is 70 (7x10=70). Quick Quiz • True or false • On a typical EKG grid, 5 small squares, or 1 large square, represent 0.20 seconds of time True PQRST wave Deflection waves P wave • Lasts 0.08 s • Results due to depolarization from SA node throughout atria • Atrial systole • Normal duration is not longer than 0.11 seconds (less than 3 small squares) • Amplitude (height) is no more than 3 mm Deflection waves QRS complex • Lasts 0.08 s (Normally not longer than 0.10 s in duration) • Results due to depolarization of ventricles • Ventricular systole & atrial diastole • R waves are deflected positively and the Q and S waves are negative T wave • Results due to repolarization of ventricles • Lasts 0.16 s • Ventricular diastole Normal ECG Deflection Wave Pattern Abnormal ECG Deflection Wave Patterns Sinus Bradycardia Rate = 40-59 b.p.m. Sinus Tachycardia Rate = 101-160 b.p.m. Causes •CHF, hypoxia, pulmonary edema •Increased temperature •Stress or response to pain Sinus Arrhythmia Rate = 45-100 b.p.m. Sinus Arrest Causes Myocarditis MI Digitalis toxicity Atrial Flutter Rate = 250-350 b.p.m. Precipitates CHF Atrial Fibrillation (afib) Causes COPD CHF AV block Causes •Digitalis toxicity •Acute infection •MI •Degeneration of the conductive tissue. Ventricular Tachycardia (V-tac) Rate = 100-220 b.p.m. Causes •CAD •Acute MI •Digitalis toxicity •CHF Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib) Causes Acute MI Asystole