* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EKG Recognition for EMT’s
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
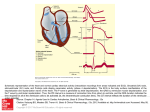
EKG Recognition for EMT’s (Part 2) Scott S. Shadoin EMT-P Boca Raton Fire Rescue Boca Raton, Fl Emergency Medical Consultants Port St. Lucie, Fl Professional Disclosures • None Objectives • Discuss the anatomy of the heart • Understand the components of an ECG • Understand the following ECG’s • Ventricular Rhythms • AV Heart Blocks • Pacemaker Rhythms Cardiac Anatomy • Myocardium • Muscle of the heart • Should contract when stimulated • Atria • Upper chambers of the heart • Ventricles • Lower chambers of the heart Cardiac Anatomy • Septum • Separates left and right sides of atria and ventricles • Cardiac Skeleton • Separates the atria from the ventricles • Impermeable to electricity • Electrical conduction system • Pathways through the heart for electricity Electrical Conduction System • Electricity created in Sinoatrial Node travels through electrical system • Myocardium contracts in response to stimulation • Depolarization • Change in cells electrical potential • Muscle contracts in response • Repolarization • Cell resets to original electrical potential • Muscle is relaxed Electrical Conduction System Electrical Conduction System Electrical Conduction System • Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) • Pacemaker of the heart • Sends electricity into atrium • Bachmann’s Bundle (intra-atrial pathway) • Delivers electricity to left atrium • Atrioventricular node (AV Node) • “Doorway” to ventricles • Pauses electrical flow Electrical Conduction System Electrical Conduction System • Bundle of His • Splits in L/R bundle branches • Connects AV node to Purkinje fibers • Bundle branches • Travel through ventricular septum • Left bundle splits into anterior/posterior fascicle • Purkinje fibers • Disseminate electricity through the ventricles Electrical Conduction System EKG Paper Left to right = TIME -Small box = .04 sec -Large box = .20 sec -3 second ticks/marks Up/down = DIRECTION -Up = Positive -Down = Negative Height = VOLTAGE -10 small boxes = 1mV ECG Components • P wave • First part of the ECG complex • Atrial depolarization • QRS • Usually largest voltage • Ventricular depolarization • T Wave • Ventricular repolarization ECG Pieces • P waves • Round (ish) • Upright • <.12 sec (3 small boxes wide) • <.25 mv (2 ½ small boxes high) ECG Pieces • Q wave • If it occurs, first negative deflection after the P wave • Septal depolarization • < .04 sec (1 box wide) • < 1/3 total height of QRS ECG Pieces • R wave • First positive deflection after the P wave • Usually largest voltage on ECG • Beginning phase of ventricular depolarization • Entire QRS .04 - .12 sec (1 to 3 small boxes) ECG Pieces • S wave • Return to baseline after R wave • May be small or not present • Late or ending of ventricular depolarization ECG Pieces • T wave • Positive (usually) deflection after the QRS • Ventricular repolarization Electrode placement Lead I From Right arm to Left arm Lead 2 From Right arm to Left leg Lead 3 From Left arm to Left leg *Lead 2 is the typical monitoring lead ECG Rules 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the rate? Is it regular? How do the P waves look? PR Interval? QRS width? Interpretation? Clinical Significance? Rate? • Ventricular Rate • R to R • 6 second rule • Number of R waves in 6 seconds x10 • Triplicate method • # of large boxes (5 small boxes) between R waves, divide into 300 • 1 box = 300, 2 box = 150, 3 box =100, etc Regular? • Measure distances from R to R • Can be slightly irregular with breathing, etc P waves and PR Interval? • Should be upright • Consistent in shape • QRS Relationship • From start of P wave to QRS <.20 sec (5 small boxes) • P in front of every QRS (consistent PR interval) • QRS after every P wave QRS width? • Narrow • < .10 probably supraventricular (2 ½ small boxes) • Wide • >.12 Probably ventricular (3 small boxes) Ventricular Rhythms Ventricular Tachycardia • Rate? • >100 • Regular? • Yes • P waves? • None • PR Interval? • None • QRS? • Wide >.12 sec • Same shape Ventricular Tachycardia Torsades de Pointes • Rate? • >100/min • Rhythm? • No • P waves? • None • PR Interval? • None • QRS width? • Wide > .12 sec • Polymorphic • Electrical rotation Torsdaes de Pointes Ventricular Fibrillation • Rate? • Atrial: None • Ventricular: Irregular and chaotic • Regular? • No • P waves? • None • PR Interval? • None • QRS width? • Wide >.12 sec Ventricular Fibrillation Coarse Fib Fine Fib Idioventricular • Rate? • < 40/min • Regular? • Yes • P waves? • None • PR Interval? • None • QRS width? • Wide > .12 sec Idioventricular Accelerated Idioventricular • Rate? • 40 – 100/min • Regular? • Yes • P waves? • None • PR Interval? • None • Q waves? • Wide > .12 sec Accelerated Idioventricular Agonal • Rate? • Atrial: None • Ventricular <20/min • Regular? • Can be regular or irregular • P waves? • None • PR Interval? • None • QRS width? • Wide > .12 sec Agonal AV Heart Blocks 1° AV block • Rate? • Atrial: 60 – 100/min • Ventricular: Same as atrial rate • Regular? • Yes • P waves? • Round, upright, uniform • PR Interval? • PR Interval >.20 sec • QRS width? • Narrow (M.B.W.W.A.C.) 1° AV block 2° AV block Type 1 (Wenckebach) • Rate? • Atrial: 40 – 60/min • Ventricular: < Atrial rate • Regular? • No (P’s are, QRS’s are not) • P waves? • Upright, round, consistent • P in front of every QRS • QRS does not always follow every P • PR Interval? • PR Interval gets progressively longer • QRS width? • Narrow (M.B.W.W.A.C.) 2°Av block Type I (Wenckebach) 2°AV Block Type II • Rate? • Atrial: 60 – 100/min • Ventricular: < Atrial Rate • Regular? • Can be either (P’s are regular, QRS’s are not) • P waves? • Round, upright, consistent • P in front of every QRS • QRS does not follow every P • PR Interval? • PR Interval is always the same • QRS width? • Narrow (M.B.W.W.A.C.) 2° AV Block Type II 3°AV Block (CHB) • Rate? • Atrial: 60 – 100/min • Ventricular: 20 – 60/min • Regular? • Yes, but no • P to P is regular, R to R is regular (but not together) • P waves? • Round, upright, consistent • P – QRS relationship nonexistent • PR Interval? • PR Interval is always varied • QRS width? • Usually wide 3°AV Block (CHB) Pacemakers Atrial Pacemaker • Rate? • Atrial: 60 – 100/min (ventricular follows atrial) • Regular? • Yes • May be irregular if demand pacemaker • P waves? • Round, upright, consistent • Small short pacemaker spike in front of P • PR Interval? • < .20 seconds • QRS width? • Narrow (M.B.W.W.A.C.) Atrial Pacemaker Ventricular Pacemaker • Rate? • Ventricular: 60 – 100/min • Regular? • Yes • May be irregular if demand pacemaker • P waves? • None • PR Interval? • None • QRS width? • Wide • Pacemaker spike in front of QRS Ventricular Pacemaker AV Sequential Pacemaker • Rate? • Atrial: 60 – 100/min • Ventricular: Same • Regular? • Yes • P waves? • Round, upright, consistent (preceded by spike) • PR Interval? • PR Interval < .20 sec • QRS width? • Wide (preceded by a spike) AV Sequential Pacemaker Let’s Practice! Ventricular Fibrillation 2°AV block (Wenckebach) Torsades de Pointes AV Sequential Pacemaker 3° AV block (CHB) Ventricular Pacemaker Ventricular Tachycardia 2° AV block Type II Atrial Pacemaker 1° AV block 3° AV block (CHB) In case you forget…. In case you forget…Part 2 In case you forget…Part 3 Scott S. Shadoin [email protected] Applause!!! Psst! You want a few more??? Premature Atrial Conctraction (P.A.C.) • An early firing of atria, causes ventricles to contract • Identified by: • An early complex (irregular rhythm) • P wave looks different than rhythm • If it is really early P wave may be hidden in previous T wave Premature Atrial Contraction (P.A.C.) Premature Junctional Contraction (P.J.C.) • An early firing of the AV Junction, causes ventricles to contract • Identified by: • An early complex (irregular rhythm) • P wave irregularity • Missing, inverted, retrograde Premature Junctional Contraction (P.J.C.) Premature Ventricular Contraction (P.V.C.) • An early firing of a cell within the ventricle, causing it to contract • Identified by: • An early complex (irregular rhythm) • Wide, bizarre QRS that does not resemble others in the rhythm • 1 – Complex • 2 – Couplet • 3 – Is a “RUN” or “SALVO” (considered V tach) Premature Ventricular Contraction (P.V.C.) P.V.C.’s – Part Deux! • Bigeminy – Every OTHER beat is PVC • Trigeminy – Every THIRD beat is PVC • Quadrageminy – Every FOURTH beat is PVC P.V.C.’s – Part Deux! Ok, that’s really it…. [email protected]