* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Risk In ESRD Patient - Saudi Society of Nephrology
Survey
Document related concepts
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
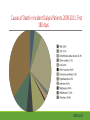
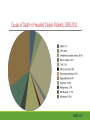
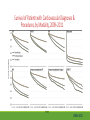
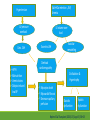
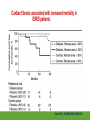
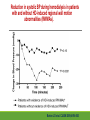
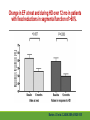
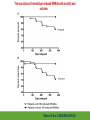
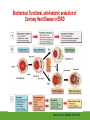
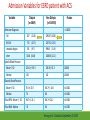
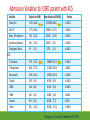
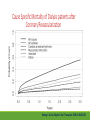
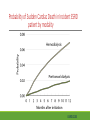
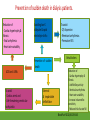
Cardiac Risk In ESRD Patient DR.BADR ALHOMAYEED.MD NEPHROLOGY AND KIDNEY TRANSPLANT CONSULTANT FEB/8/2014 Objectives: Relation ship between ESRD and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Risk factors for the development of cardiovascular disease in ESRD patient. Different cardiovascular manifestations in ESRD patient. Efforts to reduce cardiovascular risk in ESRD patient. Conclusion. Cardiac Diseases in maintenance Hemodialysis patients: Result of the HEMO Study Percentage of Patients 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Any cardiac disease Ischemic Heart disease Congestive heart failure Arrythmia Other heart disease Kidney International (2004) 65,2380-2389 Causes of Death in Incident Dialysis Patients, 2009-2011, First 180 days USRDS 2013 Causes of Death in Prevalent Dialysis Patients, 2009-2011 USRDS 2013 Survival of Patients with Cardiovascular Diagnoses & Procedures, by Modality, 2009–2011 USRDS 2013 Risk Factors For Cardiovascular disease in ESRD patients. Henrich W L CJASN 2009;4:S106-S109 Congestive Heart Failure in Dialysis Patients Congestive heart failure is a common presenting symptoms of cardiovascular disease in dialysis population. CHF contributes significantly to mortality and morbidity and also worsens the quality of life in ESRD patients. Overt left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is very common. Myocardial disease can also reduce cardiac reserve, making the patient more vulnerable to episodes of hypotension during dialysis. Rates of a CHF diagnosis in ESRD patients USRDS 2013 Heart failure in prevalent dialysis patients, by modality, 2011 USRDS 2013 Long-term Survival of Incident Hemodialysis Patients who are Hospitalized for Congestive Heart Failure, Pulmonary Edema, or Fluid Overload. Banerjee D et al. CJASN 2007;2:1186-1190 Salt+H2o retention , AVF, Anemia Hypertension LV pressure overload Conc. LVH HPTH Malnutrition Uremic toxins Dialysis induced low BP LV volume over load Eccentric LVH Vascular remodeling Overload cardiomyopathy LV dilatation & Hypertrophy Myocytes death Myocardial fibrosis Decrease capillary perfusion Diastolic dysfunction Systolic dysfunction Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15 [Suppl 5]: 58–68 Cardiac fibrosis associated with increased mortality in ESRD patients. Henrich W L CJASN 2009;4:S106-S109 Reduction in systolic BP during hemodialysis in patients with and without HD-induced regional wall motion abnormalities (RWMAs). Burton J O et al. CJASN 2009;4:914-920 Change in EF at rest and during HD over 12 mo in patients with fixed reductions in segmental function of >60%. Burton J O et al. CJASN 2009;4:1925-1931 The association of hemodialysis-induced RWMAs with mortality and outcome. Burton J O et al. CJASN 2009;4:914-920 Unadjusted survival in patients with systolic and diastolic heart failure, by age, 2010–2011 Systolic Heart failure Diastolic Heart Failure USRDS 2013 Coronary artery disease in ESRD Approximately 20% of mortality in ESRD patient can be attributed to coronary artery disease. Many dialysis patients have more than one of the traditional risk factors , resulting in an even higher risk of adverse outcomes. Patients who have both DM and HTN have a 5-6 fold increased risk of having heart disease compared to those without history of either condition. Am J Kidney Dis.2005; 45(2):316 Biochemical, Functional, and Anatomic evaluation of Coronary Heart Disease in ESRD Stenvinkel P et al. JASN 2003;14:1927-1939 Stable Coronary Artery Disease Clinical manifestation: -Frequent hypotension or chest pain on hemodialysis. -Exercise induced chest discomfort. -Exertional dyspnea. -Sudden cardiac arrest. -Sudden cardiac death. -Arrhythmia. Screening - If there is a change in symptoms related to IHD or clinical status (e.g. Recurrent low BP , CHF unresponsive to dry weight changes, or inability to achieve dry weight because of hypotension), evaluation for CAD is recommended. -Dialysis patients with significant reduction in LV systolic function (EF<40%) should be evaluated for CAD. - Evaluation for heart disease should occur at initiation of dialysis and include a baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram. Both of these tests provide information pertinent to, but not restricted to, CAD evaluation. Annual ECGs are recommended after dialysis initiation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidlines Screening - If the patient has “complete” coronary revascularization (i.e., all ischemic coronary vascular beds are bypassed), the first re-evaluation for CAD should be performed 3 years after coronary artery bypass (CAB) surgery, then every 12 months thereafter. - If the patient has “incomplete” coronary revascularization after CAB surgery (i.e., not all ischemic coronary beds are re vascularized), then evaluation for CAD should be performed annually. K/DOQI clinical practice guidlines Screening - CAD evaluation should also include exercise or pharmacological stress echocardiographic or nuclear imaging tests. -“Automatic” CAD evaluation with stress imaging is currently not recommended for all dialysis patients . - Stress imaging is appropriate (at the discretion of the patient’s physician) in selected high-risk dialysis patients for risk stratification even in patients who are not renal transplant candidates. (C) -Patients who are candidates for coronary interventions and have stress teststhat are positive for ischemia should be referred for consideration of angiographic assessment. (C) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines Acute Coronary Syndrome The evaluation and diagnosis of the dialysis patients with an acute coronary syndrome is based upon the constellation of symptoms and signs, findings on electrocardiogram, and levels of cardiac biomarkers. Dialysis patients with an acute coronary syndrome may present with atypical symptoms and signs. Admission Variables for ESRD patient with ACS Dialysis (n=3049) Variable Non Dialysis (n=534935) Admission Diagnosis P.value < 0.0001 MI 657 (21.8) 229207 (43.8) R/O MI 713 (23.7) 122752 (23.5) Unstable Angina 291 (9.7) 59943 (11.9) other 1348 (44.8) 110836 (21.2) Systolic Blood Pressure Mean+/- SD 143.6 +/- 39.3 143.8+/-32.3 1.0000 Median 143 142 1.0000 Mean+/- SD 75.5+/-20.7 80.7+/- 18.5 < 0.0001 Median 74 80 < 0.0001 Pulse BPM : Mean +/- SD 94.7+/- 24.1 86.7+/-24.2 < 0.0001 Pulse BMD: Median 92 84 < 0.0001 Diastolic Blood Pressure Herzog et al Circulation September 25, 2007 Admission Variables for ESRD patient with ACS Variables Dialysis (n=3049) Chest Pain 1325 (44.4) 3553442 (68.3) < 0.0001 No CHF 1775 (58.4) 394914 (75.2) < 0.0001 Rales, JVP distention 764 (24.1) 83433 (15.9) < 0.0001 pulmonary oedema 461 (15.2) 40074 (7.6) < 0.0001 Cardiogenic Shock 39 6778 (1.3) < 0.0001 (1.3) Non dialysis (n=534935) P.value ECG: ST elevation 579 (19.1) 188099 (35.9) < 0.0001 ST depression 840 (27.7) 151492 (28.9) 1.0000 Non specific 1338 (44.1) 187650 (35.8) < 0.0001 Q wave 970 (5.6) 46744 (8.9) < 0.0001 LBBB 244 (8.1) 30134 (5.8) < 0.0001 RBBB 198 (6.5) 30485 (5.8) 1.0000 Normal 193 (6.4) 40196 (7.7) 0.3294 Other 760 (24.1) 92146 (17.6) < 0.0001 Herzog et al Circulation September 25, 2007 Admission Variables for ESRD patient with ACS Variables Dialysis (n=3049) Non dialysis (n=534935) P.values Myocardial Infarction type Antero/septal 508 (16.7) 126566 (23.7) < 0.0001 Inferior 555 (18.2) 163559 (30.6) < 0.0001 Posterior 65 (2.1) 23060 (4.3) < 0.0001 Lateral 293 (9.6) 66367 (12.4) < 0.0001 Rt. Ventricle involvement 13 (0.4) 3624 (0.7) 1.0000 Unspecified/other 1892 (62.1) 229312 ( 42.9) < 0.0001 Q wave 78 (22.1) 199602 ( 37.4) < 0.0001 Non Q wave 2371 ( 77.8) 334793 (62.6) < 0.0001 Herzog et al Circulation September 25, 2007 Rates of an AMI event in ESRD patients USRDS 2013 Estimated mortality of dialysis patients after acute myocardial infarction (MI). Herzog C A JASN 2003;14:2556-2572 Cause Specific Mortality of Dialysis patients after Coronary Revascularization Herzog C A et al. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008;23:2629-2633 Sudden Cardiac Death In ESRD Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) is the single most common cause of death in dialysis patients. It accounts for 20-30% of all deaths. Over all incidence of SCD in this population is greater than coronary events. The risk of SCD persist after coronary revascularization. Rate of Sudden Cardiac Death in Prevalent ESRD patient by Modality USRDS 2013 Distribution of deaths according to day of the week for hemodialysis patients Percentage of deaths 20 15 10 5 0 Sunday Monday Tuesday cardiac arrest Wedenesday all cardiac Thursday Friday Saturday control Bleyer et al, kidney International 1999.55:1553-1559 Probability of Sudden Cardiac Death in Incident ESRD patient by modality USRDS 2103 Risk Factors for Sudden Cardiac Death among ESRD Dialysis Patient Herzog et al. Seminars in Dialysis, 2008 Prevention of sudden death in dialysis patients. Reduction of ‐ Cardiac hypertrophy & fibrosis ‐ Fatal arrhythmia ‐ Heart rate variability Avoiding low K dialysate & rapid electrolyte shifts: Prevention of sudden death ACEI and ARBs To avoid ‐ Cardiac arrest and ‐ Life‐threatening ventricular tachycardia External & implantable defibrillator To avoid: ‐ QT dispersion ‐ Réentrant arrhythmias ‐ Premature VES Beta blockers Reduction of ‐ Cardiac hypertrophy & fibrosis ‐ Antifibrillary activity ‐ Ventricular arrhythmia ‐ Heart rate variability ‐ Increase in baroreflex sensitivity ‐ Reduced risk of acute MI Blood Purif 2010;30:135–145 Atrial Fibrillation End stage renal disease patients are more at risk for atrial fibrillation than the general population. AF is more prevalent in end-stage renal disease patients compared to age-matched individuals with normal renal function . Hemodialysis is associated with higher risk for AF compared to peritoneal dialysis. Left ventricular hypertrophy and electrolyte shift are strong predisposing factors for development of AF. Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation in Patient with ESRD Zimmerman D et al. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012;27:3816-3822 Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation in Patient with ESRD Zimmerman D et al. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012;27:3816-3822 Mortality in patients with ESRD with and without atrial fibrillation. Zimmerman D et al. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012;27:3816-3822 Anticoagulation Bleeding Thrombosis Stroke in patients with ESRD with and without atrial fibrillation. Zimmerman D et al. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012;27:3816-3822 Valvular Heart disease Valvular heart disease is common in patients on maintenance dialysis. Valvular and annular thickening and calcification of the heart valves with subsequent development of regurgitation and/or stenosis of the affected one. Aortic and mitral valve are commonly affected. Predisposing Factors: 1-Secondary hyperparathyrodisim 8-Infective endocarditis 2-HTN 9-Mitral valve prolapse 3-DM 10-High cardiac out put state 4-LVH 11-Anemia 5-Malnutrition/ inflammatory complex 12-Arteriovenous fistula 6-Uremia 7-Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 13-Hyperlipidemia Pericardial disease Patients with end-stage renal disease may develop pericarditis and pericardial effusions, and less commonly, chronic constrictive pericarditis. Two forms of pericarditis in renal failure have been described including uremic and dialysis-associated. Uremic pericarditis results from inflammation of the visceral and parietal membranes of the pericardial sac. At least two factors may contribute to dialysis associated pericarditis: inadequate dialysis and/or fluid overload . Alpert et al Am J Med Sci. 2003;325(4):228 Conclusion: End stage renal disease is a situation with a cardiovascular risk profile of almost unique severity. ESRD patient is at high cardiac risk precipitated by both traditional and non traditional risk factors. Different cardiac manifestations with various degree of severity and presentations are unique to ESRD patient on dialysis. Sudden cardiac death is the single most common cause of death in ESRD patient.