* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Underwriting Puzzler Answer (2/15/14, Vol. 5, #1)
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
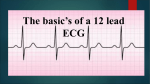
ECG Underwriting Puzzler Presented by: Bill Rooney, M.D. Obtaining Best Results from this presentation • For best results—please do the following: Select “Slide Show” from the menu option on top • Select “From the beginning” • • Slowly click through the presentation Have fun!---Good luck 2 ECG Puzzler Here is an ECG on a 31 y/o male who is applying for life insurance. Application mentions having a “Mustard Procedure” as a child. How would you interpret this ECG? 3 ECG Puzzler After inspecting for technical issues let’s examine the ECG using our usual routine: 1) Rhythm 2) Axis 3) Intervals 4) Q waves 5) Hypertrophy 6) ST/T waves Technically, any issues? No. The copy could be of better quality but…. Normal rhythm? Yes, normal sinus rhythm Normal Axis? No! Right Axis Deviation (RAD) present. ~ +145o Normal Intervals? No. QRS complex ~0.10 sec. ICRBBB Significant Q waves? No. Hypertrophy? Yes, Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) present ST/T wave abnormalities? Yes, RVH strain pattern with ST depression/T wave inversion in the right precordial leads (V1-3) 4 ECG Puzzler RVH should be suspected when there is: R in V1 >6 mm R in V1 and S in V5 or V6 >10.5 mm Right Axis Deviation (RAD) R/S ratio in V1 >1 Right atrial hypertrophy Incomplete RBBB present So, what is the Mustard procedure? How does it compare to other surgical procedures? The Mustard Procedure is one of the surgical procedures performed shortly after birth when the congenital heart defect known as transposition of the great arteries occurs. Let’s go to the next slide and review that condition. 5 D-Transposition of the Great Arteries Transposition of the great arteries is a congenital heart defect. • The aorta arises from the right ventricle. • The pulmonary artery arises from the left ventricle. Surgery is required for survival There are two commonly performed operations for this condition (Sometimes there are other associated heart defects requiring other procedures but we won’t get into that today) • Arterial switch procedure • Atrial switch procedures (Mustard and Senning procedure) 66 Atrial switch procedure Before After The Mustard procedure is what this individual had performed. In this procedure an intra-Atrial tunnel is surgically formed. The result of this procedure is that the right ventricle pumps blood to the systemic circulation instead of the typical pumping of blood to the lungs. This can eventually cause significant right ventricular hypertrophy. http://www.yorksandhumberhearts.nhs.uk/templates/page.aspx?id=415 Long term risk of this procedure include: • Right ventricular failure • Arrhythmias • Tunnel (baffle) related complications such as obstruction at the right atrialsuperior vena cava junction 7 Arterial switch procedure The arterial switch procedure is what is more commonly used now. The aorta and the pulmonary artery are transected and then translocated to the opposite root. This creates ventriculo-arterial concordance (aorta-left ventricle; pulmonary artery-right ventricle) Suture lines This procedure requires dissection and then reimplantation of the coronary arteries. The procedure is usually done within the first 2 weeks of life. 8 Long term complications of the arterial switch procedure include: • Pulmonary artery stenosis • Coronary artery insufficiency • Neo-aortic root dilation • Neo-aortic regurgitation However, this procedure can change a uniformly fatal disorder without some kind of repair to a long term fairly favorable outcome! Back to this specific ECG. The ECG showing RVH is a clue that there appears to be significant mortality concerns in this individual. Interesting ECG indeed!! That concludes this issue’s ECG Underwriting Puzzler!! Contact me if you have any questions!! 9