* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Graduated Cylinder
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Musical notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
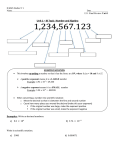
SI Units • International System of Units (SI) Metric Preferences Graduated Cylinder • Measure 26.1mL Scale • Weigh the object Ruler • Measure the length of the object Bubble Lab • Does sugar or salt affect the ability to blow bubbles? What are the steps of the scientific method? • Problem • The problem is the question we want to answer • Must be specific and testable • Observations • Objective (using facts), not subjective (using opinions) • Quantitative (counting or measuring) and qualitative • Hypothesis • A hypothesis is an educated prediction based on observations. • MUST BE TESTABLE. • Experiment • An experiment tests the hypothesis • Controlled variables—factors that are kept constant • Ex. • Manipulated variable—factor that changes (only have one of these at a time) • Ex. • Independent variable—factor that causes a change • Ex. • Dependent variable—factor that changes (the thing you’re measuring). • Ex. • Data analysis • Data analysis is making judgments or evaluations about the results of an experiment • Use graphs, tables, and statistics •Conclusion • A conclusion explains the results of the experiment • Tell whether or not the hypothesis was supported • Explain sources of error • Retest (OR revise hypothesis) • Experiment is redone many times • Theory • A theory is a conclusion that is accepted by many scientists that EXPLAINS something. •Law • A law describes behavior of natural events PROBLEM OBSERVATIONS HYPOTHESIS EXPERIMENT ANALYZE DATA DRAW CONCLUSIONS RETEST THEORY DISCARD Accuracy vs. Precision • Accuracy: How close to the real value • Precision: How close a series of measurements are to each other Scientific Notation • Method of writing very small or very large numbers – A positive exponent means the decimal moved to the left. – A negative exponent means the decimal moved to the right Scientific Notation • 602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 = ? – Step 1: Make the Coefficient less than 10 and more than 1. – Step 2: Find out how many places over the decimal has to move to give you the number in step 1. Scientific Notation ① 5,300,000 = ? ② 4,302,000,000 = ? ③ -24,500 = ? ④ .000034 = ? ⑤ -.0000007 = ? Scientific Notation ① 5.3 x 104 = ? ② 7.02 x 108 = ? ③ -3.21 x 103 = ? ④ 7.093 x 10-4 = ? ⑤ -5 x 10-3 Scientific Notation • Addition and Subtraction: 1) Make the exponents the same number 2) Add/Subtract the coefficient 5.3x102 + 2.6x103 = 5.3x102 + 26.x102 = 31.3x102= 3.13x103 Scientific Notation • Multiplication and Division 1) Add or Subtract exponents 2) Multiply or Divide coefficients Multiply 5.2x102 x 4.8x104 = (5.2 x 4.8) x10(2 + 4) 3)= 24.96x106 2.496x107 Divide 5.0x104 ÷ 2.5x103= (5.0 ÷ 2.5) x10(42.0x101 Scientific Notation ① 5.6x104 + 4.3x102 = ? ② 4.0x106 – 8.3x105 = ? ③ 2.3x105 x 4.3x106 = ? ④ 8.2x1012 ÷ 4.1x107 = ? Significant Figures – Rounding Numbers: -Round up if the digit to the right is between 5-9 59.48 59.5 -Don’t change the number if the digit is between 0-4 3.84 3.8 Significant Figures Tell You What Number To Round To! Significant Figures • All Non-zero numbers (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) are significant • Zeros – 1) Front of number are NEVER significant 0.0071, 0.42, .000099 all have 2 sig. figs 2) Middle of number are ALWAYS significant 7003, 40.79, 1.503 all have 4 sig. figs 3) End are SOMETIMES significant At end AFTER decimal, ALWAYS significant 36.00, 1.010, 9.000 all have 4 sig figs At end BEFORE decimal, NEVER significant 300, 7000, 20000 all have 1 sig fig Significant Figures ① 5.30 = ? ② 76009.0 = ? ③ 1900 = ? ④ .0000000891 = ? Significant Figures • Addition and Subtraction – Match the number with the least number of decimals • Ex: 13.21 + 4.1 = 17.3 13.21 + 4.100 = 17.31 13.21 + 4 = 17 • Multiplication and Division – Match value with fewest number of sig figs • Ex: 2.00 x 11 =22 2.00 x 11.0 = 22.0 2 x 11 = 20 BIG 1000 k kilo 100 h hecto 10 dk deca 1 BASE (m, g, L) .1 d deci .01 c centi .001 m milli SMALL How do you convert between metric units? 1. Determine whether you are going up the ladder or down the ladder. • If you go up, move the decimal to the left. • If you go down, move the decimal to the right. 2. Use the ladder to determine how many places to move the decimal. • The number of steps on the ladder is equal to the number of decimal places. 3. Write the correct units with your answer. Conversions • How many quarters make up $2? • How many dimes make up $3? • How many inches make up 2ft? Conversions Convert 892cm to meters…… ①Make the units cancel to get the units you want ②Find the conversion factor 1) Which is bigger? (This will have the value of 1) 2) Which one is smaller (This will have the big number) 3) What is the difference between them (Count how many steps you take, each one is 101 more) Conversions ① 23mL = _____ L ② 45km = _____ cm ③ 78.1cm = ______ mm ④ 750dg = _____ mg ⑤ .073m = ______ mm Conversions ① 8.9g/cm3 = _______ kg/m3 ② 4.23m/L = _______ cm/mL ③ 19.6cm/L = ______ m/mL ④ 2.5g/m3 = ______ g/cm3