* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Measurement, Sci. Notation and SF
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Musical notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
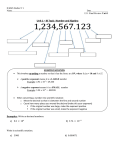
Objective of the day: To understand how to measure using a graduated cylinder, triple beam balance and a ruler Daily Question # 1 What is the volume measurement in the following diagram? Back to the Basics Science Lab Equipment Graduated Cylinder • Measure about 26.1 mL Scale • Weigh the object Ruler • Measure the length of the object SI Units • International System of Units (SI) Metric Prefixes BIGGER SMALLER 1000 BIG k kilo 100 h hecto 10 dk deca 1 BASE (m, g, L) .1 d deci .01 c centi .001 m milli SMALL How do you convert between metric units? 1. Determine whether you are going up the ladder or down the ladder. •If you go up, move the decimal to the left. •If you go down, move the decimal to the right. 2. Use the ladder to determine how many places to move the decimal. •The number of steps on the ladder is equal to the number of decimal places. 3. Write the correct units with your answer. • Practice Problems 1. 0.7834 mg = ____________ g 2. 100 cm = ______________ m 15. 345,000 ng = ____________ g 19. 2.5 mm = _______________ μm Dimensional Analysis Convert 892cm to meters…… ①Find the conversion factor 1) What unit is bigger? (This will have the value of 1) 2) What unit is smaller (This will have the big number) 3) What is the difference between them (Count how many you pass on the chart, each one is 101 more) ②Make the units cancel to get the units you want Conversions ① 3.46 cg = _____ mg ② 1.00 km = _____ cm ③ 1470 mg = ______ μg ④ 15.5 ng = _____ dg ⑤ 100 cm = ______ pm Conversions ① 8.9g/cm = _______ kg/m ② 4.23m/L = _______ cm/mL ③ 19.6cm/L = ______ m/mL ④ 2.5g/m = ______ g/cm Scientific Notation • Method of writing very small or very large numbers – A positive exponent means the decimal moved to the left. A negative exponent means the decimal moved to the right Scientific Notation • 602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 = ? – Step 1: Make the Coefficient less than 10 and more than 1. – Step 2: Find out how many places over the decimal has to move to give you the number in step 1. Scientific Notation ① 5,300,000 = ? ② 4,302,000,000 = ? ③ -24,500 = ? ④ .000034 = ? ⑤ -.0000007 = ? Scientific Notation ① 5.3 x 104 = ? ② 7.02 x 108 = ? ③ -3.21 x 103 = ? ④ 7.093 x 10-4 = ? ⑤ -5 x 10-3 Scientific Notation • Addition and Subtraction: 1) Make the exponents the same number 2) Add/Subtract the coefficient 5.3x102 + 2.6x103 = 5.3x102 + 26.x102 = 31.3x102= 3.13x103 Scientific Notation • Multiplication and Division 1) Add or Subtract exponents 2) Multiply or Divide coefficients Multiply 5.2x102 x 4.8x104 = (5.2 x 4.8) x10(2 + 4) 3)= 24.96x106 2.496x107 Divide 5.0x104 ÷ 2.5x103= (5.0 ÷ 2.5) x10(42.0x101 Scientific Notation ① 5.6x104 + 4.3x102 = ? ② 4.0x106 – 8.3x105 = ? ③ 2.3x105 x 4.3x106 = ? ④ 8.2x1012 ÷ 4.1x107 = ? Derive a relationship between the following 17 = 2 300 = 1 345 = 3 1000 = 1 1001 = 4 100.0 = 4 Accuracy vs. Precision • Accuracy: How close to the real value • Precision: How close a series of measurements are to each other Significant Figures – Rounding Numbers: -Round up if the digit to the right is between 5-9 59.48 59.5 -Drop the number to the right if it’s between 0-4 3.84 3.8 Significant Figures Tell You What Number To Round To! Significant Figures • All Non-zero numbers (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) are significant • Zeros – 1) Front of number are NEVER significant 0.0071, 0.42, .000099 all have 2 sig. figs 2) Middle of number are ALWAYS significant 7003, 40.79, 1.503 all have 4 sig. figs 3) End are SOMETIMES significant At end AFTER decimal, ALWAYS significant 36.00, 1.010, 9.000 all have 4 sig figs At end BEFORE decimal, NEVER significant 300, 7000, 20000 all have 1 sig fig Significant Figures ① 5.30 = ? ② 76009.0 = ? ③ 1900 = ? ④ .0000000891 = ? Significant Figures • Addition and Subtraction – Match the number with the least number of decimals • Ex: 13.21 + 4.1 = 17.3 13.21 + 4.100 = 17.31 13.21 + 4 = 17 • Multiplication and Division – Match value with fewest number of sig figs • Ex: 2.00 x 11 =22 2.00 x 11.0 = 22.0 2 x 11 = 20