* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
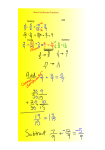
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions 7th Grade Math August, 2012 Lesson Overview: This lesson will serve as a REVIEW of multiplying and dividing fractions. If you struggle with this concept, please pay close attention and let’s master this stuff!!! MULTIPLYING FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS! Discovery Education Videos A Quick Review: KEY POINT when multiplying or dividing fractions: ☼☼ Change a mixed number into an improper fraction, Still simplify your answer. More on Multiplying Fractions: The word “of” in a problem usually means multiply! Here is an example: There are 8 cars in Michael’s toy collection. 1/2 of the cars are red. How many red cars does Michael have? This problem is asking “What is 1/2 of 8?” A way to answer it is to put a multiplication sign in place of “of.” You then get 1/2 x 8 or 8 x ½ (remember that multiplication is commutative). Multiplication Continued: What operation will I use for 2/3 of 15? It means 2/3 x 15 It could mean anything. It is helpful if you think of a situation such as: Mike ate 2/3 of 15 cookies. Susie took 2/3 of her 15 marbles to school. The dog ran 2/3 of its 15 laps around the yard. Multiplying Fractions: Multiplying fractions is easier than adding or subtraction because you don’t need to find common denominators. YAY!!!!!! Just multiply straight across. Multiply numerators together. Then, multiply denominators together. A Few Examples: Example #1: 2/3 X 4/5 Example #2: 9/2 X 3/7 Answer: 27/14=1 13/27 Example #3: 2 1/6 X 3/2 Answer: 8/15 Answer: 39/12=3 3/12=3 ¼ Example #4: 5 X 2/7 Answer: 10/7=1 3/7 Examples: Example #5: ¾ • 7/8 Example #6: 5 1/3 • 9 ½ Example #7: 6(1 2/5) Make Life Easier!! Cross Reduce When multiplying, you can simplify your factors by “cross reducing”. Examples: 6/35 • 5/24 2/15 • 3/18 1/8 (4/5) Practice Problems – Glencoe Textbook Page 255 - #1-6 Partners Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers Discovery Education Videos 2 minute – 4 minute mark What in the World is a “Reciprocal”? When two fractions are multiplied together and their product is 1. 2 3 3 2 1 AKA “inverting” or “flipping” a number Examples: The reciprocal of ½ is _______. The reciprocal of 1 ¾ is _______. The reciprocal of 8 is ________. Rules for Dividing Fractions Keep the first fraction the same STEP 2: Change the "÷" sign to "x" STEP 3: Invert the second fraction STEP 1: (Use its reciprocal) STEP 4: Multiply. STEP 5: Simplify, if needed. Example: ¼ ÷ ½ changes to 1 2 4 1 Algorithm: Dividing Fractions Remember these three words: KEEP, CHANGE, RECIPROCAL First fraction remains the same (KEEP) Division symbol is changed to multiplication (CHANGE) Last fraction is changed to its reciprocal (RECIPROCAL) Then, Multiply and simplify your answer (Don’t forget to cross reduce if possible) Some Examples: 5 Example #1: 3 4 6 8 2 Example #2: 3 4 Example #3: 5 1 3 1 2 Example #4: 6 4 2 3 Don’t forget to cross reduce if possible ONLY when multiplying! Examples: Example #5: 3 1 4 2 Example #6: 5 1 8 2 Example #7: 1 2 4 2 3 Don’t forget to cross reduce if possible ONLY when multiplying! Practice Problems – “Practice Section” of your notebook Glencoe Textbook Page 267 - #1-8 Partners “Card and Domino Multiplication” Each partner draws one (1) card and one (1) domino Card = whole number Domino = fraction Multiply your two numbers together (individually) Then, compare your answers. Sources: http://www.helpwithfractions.com/dividing-fractions.html accessed 11/25/03 http://mathforum.org/library/drmath/view/58170.html accessed 11/25/03 http://school.discovery.com/homeworkhelp/webmath/fractions.html accessed 11/25/03 Van De Walle, J.A. (2001). Elementary and middle school mathematics. New York: Longman.