* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mat_306-05_files/Lesson #13- Intervals and Inequalities
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Musical notation wikipedia , lookup
World 3-3
Intervals and Inequalities
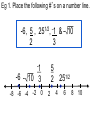
Eg 1. Place the following #’s on a number line.
-6, 5 , 251/2, -1 & - 10
2
3
-1
5
2
-6 - 10 3
-8 -6 -4
-2
0
2
1/2
25
4
6
8
10
Sometimes it is useful to talk about a
RANGE of numbers.
There are 3 ways to accomplish this.
1) Number Line
-8 -6 -4
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
Identifies the interval of numbers
The end number IS in the set
The end number IS NOT in the set
2) Bracket Notation
[ -2, 8 [
Lowest #
Highest #
[ 7 ]
-5,
] 9 [
5,
HUGGING brackets
mean the end number
it is CONTAINED in
the set.
BACK FACING brackets
means the end number is
NOT CONTAINED in the
set.
Eg. 2 Inequalities Language
The mouth always OPENS
to the larger number.
Less than 5
Greater than 10
At Most 22
At Least 15
x <5
_________
x >10
_________
x £22
_________
x ³15
_________
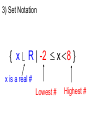
3) Set Notation
{ x Î R | -2 £ x < 8 }
x is a real #
Lowest #
Highest #
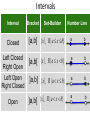
Intervals
Interval
Bracket
Set-Builder
Number Line
Closed
[a,b] {x Î R | a £ x £ b}
a
b
Left Closed
Right Open
[a,b[ {x Î R | a £ x < b}
a
b
Left Open
Right Closed
]a,b] {x Î R | a < x £ b}
a
b
Open
]a,b[ {x Î R | a < x < b}
a
b
World 3-3






![{ } ] (](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008467374_1-19a4b88811576ce8695653a04b45aba9-150x150.png)










