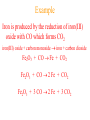* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 5
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Rigid rotor wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Magnetorotational instability wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
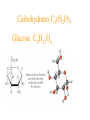
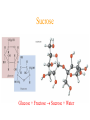
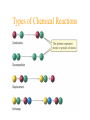
Simplest (Empirical) Formula • Simplest integer ratio of the atoms in a compound • Assume 100 g of compound, %element is then g element in sample • g element x 1 mol element = mol element g element CHCl3 10.061 g C x 1 mol C = 0.83765 mol C 12.011 g C Determine simplest integer mole ratio EXAMPLE: Phosphorus burns in air to produce a white compound that is 43.7% P and 56.3% O by mass. What is the empirical formula of the compound? Assume 100 g of compound mass 43.7g P 56.3g O Relative Number of Atoms (mass/atomic mass) Divide by Smaller = 1.41 56.3/15.9994 = 3.52 43.7/30.97 1.41/1.41 = 1.00 3.52/1.41 = 2.50 Empirical Formula P2O5 Multiply by Integer 2 1.00 2 2 2.50 5 .25, .33, .5, .67, .75 ¼, ⅓, ½, ⅔, ¾ 1:1.25 = 4:5 Molecular Formula • The exact proportions of the elements that are contained in a molecule • An integer multiple (X) of the empirical formula MF = X EF Molecular Formula from Simplest Formula empirical formula mass FM sum of the atomic weights represented by the empirical formula molar mass = MM = X FM Molecular Formula from Simplest Formula first, knowing MM and FM X = MM/FM then MF = X EF EXAMPLE: Our phosphorus compound has a molar mass of ~285. What is the molecular formula? FM = 2 x 30.97 + 5 x 16.00 = 141.94 MM 285 X= = =2 FM 141.94 thus MF = 2 EF P4O10 The empirical formula of a substance is found to be CH3O and its molecular weight is found to be roughly 61 g/mol. What is the true molecular weight of the substance? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 130 30.5 g/mol 31.0 g/mol 61.0 g/mol 62.0 g/mol 124.0 g/mol 10 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% g/ m ol 12 4. 0 g/ m ol 62 .0 g/ m ol 61 .0 g/ m ol .0 31 0 30 .5 g/ m ol 0 Biological Periodic Table Carbohydrates Cx(H2O)y Glucose C6H12O6 Sucrose Glucose + Fructose Sucrose + Water Tristearin - Glycerol - Stearic Acid 3H2O+ +3 Chapter 4 Quantities of Reactants and Products Balanced Chemical Equation • Representation of a chemical reaction which uses stoichiometric coefficients (prefix numbers) to represent the relative amounts of reactants and products • 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 H2O (l) • Molecule to Molecule or Mole to Mole EXAMPLE How much H2O, in moles results from burning an excess of H2 in 3.3 moles of O2? 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O #mol H2O = (3.3 mol O2) (2 mol H2O) (1 mol O2) Mole ratio from balanced chemical equation = 6.6 mol H2O Reaction of H2 and Cl2 H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g) one to one gives two or four to four gives eight Types of Reactions • • • • synthesis or combination reactions decomposition reactions displacement reactions exchange reactions Types of Chemical Reactions Synthesis or Combination Reactions Formation of a compound from simpler compounds or elements. Combination Reaction Decomposition Reactions Separation into constituents by chemical reaction. Dynamite Electrolysis Displacement Reactions Reaction of a compound with a more reactive element to produce a new compound and release a less reactive element Displacement Reactions Exchange Reactions Reaction where ion partners are exchanged Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CrO4 (aq) PbCrO4 (s) + 2 KNO3 (aq) When Zn(s) is placed in aqueous HCl, hydrogen gas is evolved and zinc chloride solution is obtained. Predict the reaction type. 1. 2. 3. 4. Combination Combustion Decomposition Displacement (single displacement) Exchange (double displacement) 5. 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0 ch a ng e (d o ub l e di ... ... n t( si ng le si tio em en Ex D is p la c D ec o m po bu s om C bi n C om 0 at io 10 tio n n 130 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations • Determine the type of reaction and formulae of the products • Write an unbalanced equation with the correct reactants and products • Balance the equation by the use of prefixes (coefficients) to balance the number of each type of atom on the reactant and product sides of the equation. Example Iron is produced by the reduction of iron(III) oxide with CO which forms CO2 iron(III) oxide + carbon monoxide iron + carbon dioxide Fe2O3 + CO Fe + CO2 Fe2O3 + CO 2 Fe + CO2 Fe2O3 + 3 CO 2 Fe + 3 CO2 When aluminum reacts with sulfuric acid to yield aluminum sulfate and hydrogen what is the SUM of the coefficients in the balanced equation? 130 10 0% 0% 0% 9 0 0% 7 0% 8 0 6 4 6 7 8 9 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.