* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Columbus State Community College
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
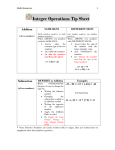
Columbus State Community College Chapter 1 Section 4 Subtracting Integers Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #1 Subtracting Integers 1. Find the opposite of a signed number. 2. Subtract integers. 3. Combine adding and subtracting of integers. Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #2 Finding the Opposites of Signed Numbers EXAMPLE 1 Finding the Opposites of Signed Numbers Find the opposite (additive inverse) of each number. Show that the sum of the number and its opposite is 0. (a) 9 The opposite of 9 is –9 and 9 + –9 = 0 (b) –14 The opposite of –14 is 14 and –14 (c) 0 The opposite of 0 is 0 and 0 + 0 = 0 + 14 = 0 Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #3 Subtracting Two Integers Subtracting Two Integers To subtract two numbers, add the first number to the opposite of the second number. Remember to change two things: Step 1 Make a pencil stroke to change the subtraction symbol to an addition symbol. Step 2 Make a second pencil stroke to change the second number to its opposite. If the second number is positive, change it to negative. If the second number is negative, change it to positive. Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #4 CAUTION CAUTION When changing a subtraction problem to an addition problem, do not make any change in the first number. The pattern is 1st number – 2nd number = 1st number + opposite of 2nd number. Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #5 Subtracting Two Integers EXAMPLE 2 Subtracting Two Integers Make two pencil strokes to change each subtraction problem into an addition problem. Then find the sum. (a) 9 – 15 9 +– – 15 = –6 Changeto15addition. to –15 Change subtraction Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #6 Subtracting Two Integers EXAMPLE 2 Subtracting Two Integers Make two pencil strokes to change each subtraction problem into an addition problem. Then find the sum. (b) –17 – –8 –17 +– –+8 = –9 Changeto–8addition. to +8 Change subtraction Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #7 Subtracting Two Integers EXAMPLE 2 Subtracting Two Integers Make two pencil strokes to change each subtraction problem into an addition problem. Then find the sum. (c) 4 – –12 4 – –12 Change subtraction to addition. 4 + –12 Change –12 to 12. 4 + +12 16 Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #8 Subtracting Two Integers EXAMPLE 2 Subtracting Two Integers Make two pencil strokes to change each subtraction problem into an addition problem. Then find the sum. (d) –3 – 6 –3 – 6 Change subtraction to addition. –3 + 6 Change 6 to –6. –3 + –6 –9 Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #9 Combining Addition and Subtraction EXAMPLE 3 Combining Addition and Subtraction Simplify by completing all the operations. –5 – –10 + –7 – 2 –10 to ChangeChange subtraction to10. addition. Change 2 to –2. –5 – –10 + –7 – 2 –5 + +–10 + –7 + –2 5 + –7 + –2 –2 + –2 –4 Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #10 Calculator Tip – TI-30X IIS Calculator Tip You can use the negative sign key on your TI-30X IIS calculator to enter negative numbers. Example 3: (–) 5 – (–) 10 –5 (–) – –10 + –7 – 2 + (–) 7 – 2 = –4 (–) Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #11 Subtracting Integers Chapter 1 Section 4 – End Written by John T. Wallace Ch 1 Sec 4: Slide #13