* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical and Molecular Formulas PPT
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rigid rotor wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rotational–vibrational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Molecular graphics wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Ionic compound wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
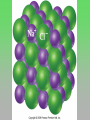
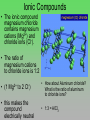
Chemical and Molecular Formulas Chemical and Molecular Formulas Q: How can two elements combine to form more than one chemical compound? A: Letters of the alphabet can be combined in many different ways to form words, the atoms of 2 or more elements can also be combined in different ways to form more than one type of compound • consider elements A&B: AB, A2B2, AB2 … • what does the subscript 2 represent in the chemical formula, H2O? Chemical Formulas • a chemical formula shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in the smallest representative unit of the substance • chemists have identified more than 10 million chemical compounds • some are molecular, such as proteins and hormones in your body, and others are ionic, such as the salts in body fluids Chemical Formulas • For monatomic elements, they are simply represented by their atomic symbols, He, Ne • If the molecules of an element have more than one atom, a number is used as a subscript • For example: the 7 diatomic molecules • H2 • F2 • O2 • N2 • Cl2 • Br2 • I2 Molecular Formulas Examples • A molecular formula shows the kinds and • H2O: subscripts indicate the # of atoms of each numbers of atoms element present in a molecule • 2 hydrogen of a compound • 1 oxygen (the subscript 1 is omitted) • subscripts always go after the atom it is • One molecule of ethane, representing C2H6 contains: • 2 carbons • 6 hydrogen Structure Although a molecular formula shows the composition of a molecule, it tells you nothing about the molecule’s structure. It doesn’t show you how the atoms are arranged Ionic Compounds Formula Units • Formula units are written for ionic compounds, they DO NOT represent a molecule • there are no separate molecular units, only a continuous array of ions • a formula unit is the lowest whole- number ratio of ions in a compound Ionic Compounds • The ionic compound magnesium chloride contains magnesium cations (Mg2+) and chloride ions (Cl-). • The ratio of magnesium cations to chloride ions is 1:2 • (1 Mg2+ to 2 Cl-) • this makes the compound electrically neutral • How about Aluminum chloride? What is the ratio of aluminum to chloride ions? • 1:3 = AlCl3 The Law of Definite Proportions states that in samples of any chemical compound, the masses of the elements are always in the same proportions (consistent with Dalton’s Atomic Theoryatoms combine in simple whole-number ratios) The Law of Multiple Proportions states that whenever two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small, whole-numbers Chemical and Molecular Formula Review Questions • Differentiate between a molecular formula and a formula unit. • a molecular formula shows the number of each kind of atom in a molecule of the compound. The formula unit shows the lowest whole-number ratio of ions in a compound Chemical and Molecular Formula Review Questions • Which law is illustrated by this statement: “When carbon and oxygen form the compounds carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, the different masses of carbon that combine with the same mass of oxygen are in the ratio of 2:1”? • law of multiple proportions Chemical and Molecular Formula Review Questions • - Which law is illustrated by this statement: “In every sample of carbon monoxide, the mass ratio of carbon to oxygen is 3:4”? • law of definite proportions Chemical and Molecular Formula Review Questions • If ionic compounds are composed of charged particles (ions), why isn’t every ionic compound either positively or negatively charged? • The net positive charge on the cations is exactly balanced by the net negative charge on the anions. Chemical and Molecular Formula Review Questions • Would you expect the following pairs of atoms to combine chemically to give an ionic or a molecular compound? • • • • • • Li and S O ans S Al and O F and Cl I and K H and N • • • • • • I M I M I M Chemical and Molecular Formula Review Questions Identify the number and kinds of atoms present in a molecule of each compound • • • • • ascorbic acid (vitamin C), C6H8O6 monosodium glutamate (MSG), C5H8O4Na sucrose (table sugar), C12H22O11 trinitrotoluene (TNT), C7H5N3O6 ammonium nitrate (fertilizer), NH4NO3