* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parallel Circuit Characteristics
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
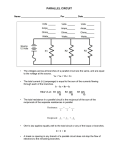
Parallel Circuits – Chapter 5 • A parallel circuit provides more than one current path between any two points. • Each current path in a parallel circuit is referred to as a branch. Two Branches Three Branches How many branches? Parallel Circuit Characteristics Voltage and Current Values Voltage is the same across all components (a) No parallel branches (b) V1 = V2 = VS Parallel Circuit Characteristics Current Characteristics Source current is the sum of all branch currents I T I1 I 2 ... I n where In = the current through the nth branch in the circuit The total current in the circuit is IT = I1 + I2 + I3 IT = 5mA + 10mA + 20mA = 35mA Parallel Circuit Characteristics Voltage and Current Values Current through each branch is determined by the source voltage and the resistance of the branch. I branch VS Rbranch TEAM ACTIVITY Use Ohm’s law to calculate the resistance in each branch. TEAM ACTIVITY 10 R1 2000 0.005 10 R2 1000 0.010 10 R3 500 0.020 TEAM ACTIVITY Use Ohm’s law to calculate the total resistance. TEAM ACTIVITY 10 RT 285.71 0.035 TEAM ACTIVITY 10 R1 2000 0.005 10 R2 1000 0.010 10 R3 500 0.020 10 RT 285.71 0.035 1 1 1 Calculate R1 R2 R3 1 RT Summary 1 1 1 1 R1 R2 R3 RT I1 I 2 I 3 IT V1 V2 V3 VS 1 RT 1 1 1 R1 R2 R3 Common Mistake 1 1 1 1 R1 R2 R3 RT R1 R2 R3 RT Series Circuit TEAM ACTIVITY P1 P2 P3 PT TEAM ACTIVITY P1 0.05W P2 0.1W PT 0.35W P3 0.2W PT P1 P2 P3 Special Case – Equal Resistances • When any number of equal resistances are connected in parallel, the total resistance is equal to the value of one resistor divided by the number of branches Shorthand notation for parallel Special Case – Equal Resistances Shorthand notation for parallel 1 1 1 1 3 RT R R R R R 5.1k RT 1.7k 3 3 Adding Additional Branches • The addition of a parallel branch decreases the resistance of the circuit • single branch in (a) draws 5mA from the source • additional branch in (b) increases the current drawn from the source to 10mA TEAM ACTIVITY Determine the branch currents and the total current for each circuit. Check with MultiSim. Vs 8V R1 1kOhm R2 200 Ohm Vs 12 V R1 1.5kOhm R2 3kOhm