* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resistance
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
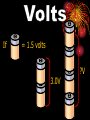
• Def : the energy or pushing force available to move electrons through a circuit • Unit: volt (V) • Symbol: V • Measured using an instrument called a voltmeter V If = 1.5 volts 3.0V ?V Def: difference between the charges at the beginning of a circuit and at the end Charges flow because of ‘potential difference’. 3.0 V 3.0 V 0.0 V •By the time a charge travels through a circuit it will essentially have lost its voltage or “push” • Def: how much the voltage decreases as it passes through each resistor on the way back to the negative end of the battery • The more light bulbs you have in a series circuit, the dimmer they are because they have to share voltage • Resistance is the tendency for materials to oppose the flow of electricity Symbol: (R) Unit: ohm (Ω) Measured by an ohmmeter Ω High resistance = insulators. Low resistance = conductors. Anything using electricity is a resistor!! Your Turn… •Find the voltage drop across the missing 40 bulbs 5 • In a parallel circuit, the voltage drop across EACH resistor is equal to the total voltage • Light bulbs wired in parallel have the same brightness! • Def : the rate of “FLOW” of electrons through a wire • Unit: Amperes (amp) • Symbol: I • It is measured using an ammeter A • Current in a series circuit is the same for each resistor (light bulb). Current is divided up between each path; Each path gets the necessary number of amps. TYPES of CURRENT Direct Current (DC) Alternating Current (AC) flows in one direction reverses back and forth Ex. - Batteries Ex. – Household current to Electrical Current Which of the following do you think would be most resistant to electrical Plastic current? OR Insulator Conductor Resistance is affected by… • Length • The longer the wire, the greater the resistance • Diameter • The smaller the diameter, greater the resistance • Material • Poor conductors have high resistance • Temperature • The hotter the wire, the greater the resistance Match the word on the left to the phrase on the right. Resistance How Fast? Current How much? Ohms or R AMPS (I) Voltage Volts (V) How much is it slowed down?